Stoichiometry worksheet KEY
... 8) Hydrogen and chlorine react to form hydrogen chloride. H2 + Cl2 → 2 HCl a) If you have 3.56 g of hydrogen, and 8.94 g chlorine, how much hydrogen chloride can you make? (Hint: One of them will be used completely, the other will have leftovers, find which is which, then do the stoichiometry.) 9.1 ...
... 8) Hydrogen and chlorine react to form hydrogen chloride. H2 + Cl2 → 2 HCl a) If you have 3.56 g of hydrogen, and 8.94 g chlorine, how much hydrogen chloride can you make? (Hint: One of them will be used completely, the other will have leftovers, find which is which, then do the stoichiometry.) 9.1 ...
Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Notice that in Interactive Figure 4.2.1 the water molecules orient themselves so that the oxygen atoms are near the Na+ cations and the hydrogen atoms are near the Cl− anions. This is due to the polar nature of water, a result of uneven electron distribution in water molecules. ( Flashforward to Se ...
... Notice that in Interactive Figure 4.2.1 the water molecules orient themselves so that the oxygen atoms are near the Na+ cations and the hydrogen atoms are near the Cl− anions. This is due to the polar nature of water, a result of uneven electron distribution in water molecules. ( Flashforward to Se ...
1.6 Energy changes in chemical reactions
... Chemists deal with matter on a macroscopic scale in the laboratory, but explain its behaviour in terms of atoms and molecules. This requires a wide range of distances (see Figure 1.4). You will need to become familiar with the multiplication prefixes in Table 1.3 used to describe lengths on atomic a ...
... Chemists deal with matter on a macroscopic scale in the laboratory, but explain its behaviour in terms of atoms and molecules. This requires a wide range of distances (see Figure 1.4). You will need to become familiar with the multiplication prefixes in Table 1.3 used to describe lengths on atomic a ...
Section 4.9 Oxidation–Reduction Reactions
... • Say you are asked how much CO2 is produced from the combustion of 15.0 moles of octane? • 2 C8H18 (l) + 25 O2 (g) → 16 CO2 (g) + 18 H2O (g) 16 mol CO 2 15.0 mol C 8H18 x 1.20 x 10 2 mol CO 2 2 mol C 8H18 ...
... • Say you are asked how much CO2 is produced from the combustion of 15.0 moles of octane? • 2 C8H18 (l) + 25 O2 (g) → 16 CO2 (g) + 18 H2O (g) 16 mol CO 2 15.0 mol C 8H18 x 1.20 x 10 2 mol CO 2 2 mol C 8H18 ...
thermodynamics
... Chemical energy stored by molecules can be released as heat during chemical reactions when a fuel like methane, cooking gas or coal burns in air. The chemical energy may also be used to do mechanical work when a fuel burns in an engine or to provide electrical energy through a galvanic cell like dry ...
... Chemical energy stored by molecules can be released as heat during chemical reactions when a fuel like methane, cooking gas or coal burns in air. The chemical energy may also be used to do mechanical work when a fuel burns in an engine or to provide electrical energy through a galvanic cell like dry ...
g - Haiku
... constant pressure, the enthalpy change equals the quantity of heat absorbed or released, ΔH = qP. Plan We must predict whether heat is absorbed or released by the system in each process. Processes in which heat is absorbed are endothermic and have a positive sign for ΔH; those in which heat is relea ...
... constant pressure, the enthalpy change equals the quantity of heat absorbed or released, ΔH = qP. Plan We must predict whether heat is absorbed or released by the system in each process. Processes in which heat is absorbed are endothermic and have a positive sign for ΔH; those in which heat is relea ...
Unit F325 - Equilibria, energetics and elements - High band
... candidate. The final answer should have been given to 3 significant figures as all values in the question are to this precision. The answer of 0.8 against the actual calculated value of 0.848 introduces a 6% rounding error. This is a basic error and loss of marks such as this could prove costly for ...
... candidate. The final answer should have been given to 3 significant figures as all values in the question are to this precision. The answer of 0.8 against the actual calculated value of 0.848 introduces a 6% rounding error. This is a basic error and loss of marks such as this could prove costly for ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry 4.1
... The most common precipitation reactions occurring in aqueous solution involve the formation of an insoluble ionic compound when two solutions containing soluble compounds are mixed. Consider what happens when an aqueous solution of NaCl is added to an aqueous solution of AgNO3. The first solution co ...
... The most common precipitation reactions occurring in aqueous solution involve the formation of an insoluble ionic compound when two solutions containing soluble compounds are mixed. Consider what happens when an aqueous solution of NaCl is added to an aqueous solution of AgNO3. The first solution co ...
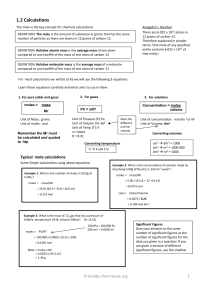
1.2 Calculations
... It does not affect the titration reading as water does not react with the reagents or change the number of moles of acid added. ...
... It does not affect the titration reading as water does not react with the reagents or change the number of moles of acid added. ...
Chemical Equilibrium - Department of Chemistry
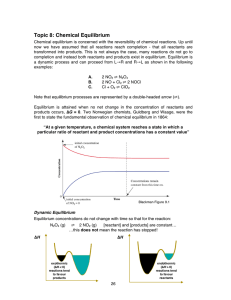
... • For a given set of reaction conditions, the equilibrium amounts of reactants and products in a reversible reaction are independent of whether the reaction is homogeneous, heterogeneous or otherwise catalysed. • A catalyst does not change the position of equilibrium. • The catalyst only acts to dec ...
... • For a given set of reaction conditions, the equilibrium amounts of reactants and products in a reversible reaction are independent of whether the reaction is homogeneous, heterogeneous or otherwise catalysed. • A catalyst does not change the position of equilibrium. • The catalyst only acts to dec ...
Physical Chemistry Problems. ©Mike Lyons 2009
... Answer either : part (a) and part (b) or part (c) and part (d). a. What is the internal energy U and the enthalpy H of a system? Write down an expression for the First Law of Thermodynamics which relates the change in internal energy of a system to the work done on the system and the heat absorbed b ...
... Answer either : part (a) and part (b) or part (c) and part (d). a. What is the internal energy U and the enthalpy H of a system? Write down an expression for the First Law of Thermodynamics which relates the change in internal energy of a system to the work done on the system and the heat absorbed b ...
AP Chemistry Lab Manual
... sig figs and always include proper units. Underline, use capital letters or use any device you choose to help organize this section well. Space things out – don’t try to cram everything on one page. A data table must have a label and a title. e.g. – Table 1: Density Values for Sugar Solutions. 7. Ca ...
... sig figs and always include proper units. Underline, use capital letters or use any device you choose to help organize this section well. Space things out – don’t try to cram everything on one page. A data table must have a label and a title. e.g. – Table 1: Density Values for Sugar Solutions. 7. Ca ...
File
... sig figs and always include proper units. Underline, use capital letters or use any device you choose to help organize this section well. Space things out – don’t try to cram everything on one page. A data table must have a label and a title. e.g. – Table 1: Density Values for Sugar Solutions. 7. Ca ...
... sig figs and always include proper units. Underline, use capital letters or use any device you choose to help organize this section well. Space things out – don’t try to cram everything on one page. A data table must have a label and a title. e.g. – Table 1: Density Values for Sugar Solutions. 7. Ca ...
1. True
... 19.1. Which of the following statements is FALSE? 1. The total amount of energy and matter in the Universe is constant. 2. Breaking chemical bonds is an endothermic process. 3. It is more efficient to use a primary energy source than a secondary energy source. 4. Entropy must be conserved in all che ...
... 19.1. Which of the following statements is FALSE? 1. The total amount of energy and matter in the Universe is constant. 2. Breaking chemical bonds is an endothermic process. 3. It is more efficient to use a primary energy source than a secondary energy source. 4. Entropy must be conserved in all che ...
- Catalyst
... Polar covalent compounds are very soluble in water. They often have OH groups that can form “hydrogen bonds” with water. Examples are table sugar (C12H22O11), ethanol (C2H5OH), ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) in antifreeze, and methanol (CH3OH). These also are written with “(aq)” (i.e., aqueous) when disso ...
... Polar covalent compounds are very soluble in water. They often have OH groups that can form “hydrogen bonds” with water. Examples are table sugar (C12H22O11), ethanol (C2H5OH), ethylene glycol (C2H6O2) in antifreeze, and methanol (CH3OH). These also are written with “(aq)” (i.e., aqueous) when disso ...
CHAPTER 16
... molecules. The quantity of energy released as heat in this or any other reaction depends on the amounts of reactants and products. The quantity of energy as heat released during the formation of water from H2 and O2 is proportional to the quantity of water formed. Producing twice as much water vapor ...
... molecules. The quantity of energy released as heat in this or any other reaction depends on the amounts of reactants and products. The quantity of energy as heat released during the formation of water from H2 and O2 is proportional to the quantity of water formed. Producing twice as much water vapor ...
Week 1 NEPHAR 201- Analytical Chemistry II_Introduction_5
... 5.0 mL of the original concentrated H2SO4 solution are withdrawn into a pipette and transferred into a 250-mL volumetric flask. A small amount of DI water is added and the solution is swirled. The solution is made up to the mark with DI water using a wash bottle. Describe how 100 mL, 0.5 M nitric ac ...
... 5.0 mL of the original concentrated H2SO4 solution are withdrawn into a pipette and transferred into a 250-mL volumetric flask. A small amount of DI water is added and the solution is swirled. The solution is made up to the mark with DI water using a wash bottle. Describe how 100 mL, 0.5 M nitric ac ...
Topic 8: Chemical Equilibrium
... Relation between Kp and Kc In reactions involving gaseous reactants and/or products, equilibrium constants Kp or Kc can be written based on either partial pressures or molar concentrations for each component. These equilibrium constants are related since partial pressures and molar concentrations ar ...
... Relation between Kp and Kc In reactions involving gaseous reactants and/or products, equilibrium constants Kp or Kc can be written based on either partial pressures or molar concentrations for each component. These equilibrium constants are related since partial pressures and molar concentrations ar ...
5 SURFACE CHEMISTRY CATEGORY
... freezing point by 7.5°C? The freezing point depression constant, Kf , for water is 1.86 K kg mol–1. Assume van’t Hoff factor for NaCl is 1.87. 8. 18 g of glucose, C6H12O6 (Molar Mass = 180 g mol–1) is dissolved in 1 kg of water in a sauce pan. At what temperature will this solution boil? 9.Determine ...
... freezing point by 7.5°C? The freezing point depression constant, Kf , for water is 1.86 K kg mol–1. Assume van’t Hoff factor for NaCl is 1.87. 8. 18 g of glucose, C6H12O6 (Molar Mass = 180 g mol–1) is dissolved in 1 kg of water in a sauce pan. At what temperature will this solution boil? 9.Determine ...
CH 8 blackboard
... chemical reaction occurs depends on the amounts of reactants that actually react. ...
... chemical reaction occurs depends on the amounts of reactants that actually react. ...
Mock Examination (2016/2017) CHEMISTRY PAPER 1 SECTION B
... Name the ionic compound present in aqueous layer after Step 2. Sodium carbonate, sodium ethanoate ...
... Name the ionic compound present in aqueous layer after Step 2. Sodium carbonate, sodium ethanoate ...
Stoichiometry
... Mole Ratio – the ratio of moles of one substance to moles of another substance in a balanced chemical equation The coefficients in a balanced equation give the relative numbers of molecules, as well as, the relative number of moles. ...
... Mole Ratio – the ratio of moles of one substance to moles of another substance in a balanced chemical equation The coefficients in a balanced equation give the relative numbers of molecules, as well as, the relative number of moles. ...
Chapter 4: Aqueous Solutions (Chs 4 and 5 in Jespersen, Ch4 in
... Chemical equilibrium - chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates ...
... Chemical equilibrium - chemical equilibrium is the state in which both reactants and products are present in concentrations which have no further tendency to change with time. Usually, this state results when the forward reaction proceeds at the same rate as the reverse reaction. The reaction rates ...
ch17
... PROBLEM: Fuel engineers use the extent of the change from CO and H2O to CO2 and H2 to regulate the proportions of synthetic fuel mixtures. If 0.250 mol of CO and 0.250 mol of H2O are placed in a 125-mL flask at 900 K, what is the composition of the equilibrium mixture? At this temperature, Kc is 1.5 ...
... PROBLEM: Fuel engineers use the extent of the change from CO and H2O to CO2 and H2 to regulate the proportions of synthetic fuel mixtures. If 0.250 mol of CO and 0.250 mol of H2O are placed in a 125-mL flask at 900 K, what is the composition of the equilibrium mixture? At this temperature, Kc is 1.5 ...
Thermodynamics ppt
... 32. A system composed of a ideal gas expands spontaneously in one step from an initial volume of 1.00 L to a final volume of 2.00 L at a constant temperature of 200 K. During the process the gas does 200 J of work. What conclusion can be reached about the value of the entropy change, ΔS, for this pr ...
... 32. A system composed of a ideal gas expands spontaneously in one step from an initial volume of 1.00 L to a final volume of 2.00 L at a constant temperature of 200 K. During the process the gas does 200 J of work. What conclusion can be reached about the value of the entropy change, ΔS, for this pr ...
Thermometric titration

A thermometric titration is one of a number of instrumental titration techniques where endpoints can be located accurately and precisely without a subjective interpretation on the part of the analyst as to their location. Enthalpy change is arguably the most fundamental and universal property of chemical reactions, so the observation of temperature change is a natural choice in monitoring their progress. It is not a new technique, with possibly the first recognizable thermometric titration method reported early in the 20th century (Bell and Cowell, 1913). In spite of its attractive features, and in spite of the considerable research that has been conducted in the field and a large body of applications that have been developed; it has been until now an under-utilized technique in the critical area of industrial process and quality control. Automated potentiometric titration systems have pre-dominated in this area since the 1970s. With the advent of cheap computers able to handle the powerful thermometric titration software, development has now reached the stage where easy to use automated thermometric titration systems can in many cases offer a superior alternative to potentiometric titrimetry.The applications of thermometric titrimetry discussed on this page are by no means exhaustive. The reader is referred to the bibliography for further reading on the subject.