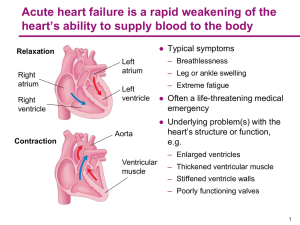
Heart Intro
... II. Pericardial Cavity – space between parietal and visceral layers to reduce friction. ...
... II. Pericardial Cavity – space between parietal and visceral layers to reduce friction. ...
Chapter 19 – Circulation
... diagram. Include aorta, pulmonary veins, pulmonary arteries, right atrium, left atrium and right ventricle. All parts of body Vena cava ...
... diagram. Include aorta, pulmonary veins, pulmonary arteries, right atrium, left atrium and right ventricle. All parts of body Vena cava ...
(ASD) Repair - Children`s Heart Clinic
... patch of the patient’s own pericardium (sac surrounding the heart). Patent foramen ovale (PFO): Most close spontaneously or don’t require a surgical intervention. Primum ASD: Surgery: A median sternotomy (incision through the middle of the chest) is done. The child is placed onto cardiopulmonary b ...
... patch of the patient’s own pericardium (sac surrounding the heart). Patent foramen ovale (PFO): Most close spontaneously or don’t require a surgical intervention. Primum ASD: Surgery: A median sternotomy (incision through the middle of the chest) is done. The child is placed onto cardiopulmonary b ...
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS)
... significant minority is only diagnosed in adult life. Initially right ventricular compliance is substantially greater than the left ventricle and this is associated with the development of a left-to-right shunt. Pulmonary blood flow is increased and pulmonary hypertension develops with increasing ag ...
... significant minority is only diagnosed in adult life. Initially right ventricular compliance is substantially greater than the left ventricle and this is associated with the development of a left-to-right shunt. Pulmonary blood flow is increased and pulmonary hypertension develops with increasing ag ...
Congenital Heart Defects
... They are problems with the heart that are present at birth. They affect the flow of blood through the heart. Defects can range from no symptoms to life threatening ...
... They are problems with the heart that are present at birth. They affect the flow of blood through the heart. Defects can range from no symptoms to life threatening ...
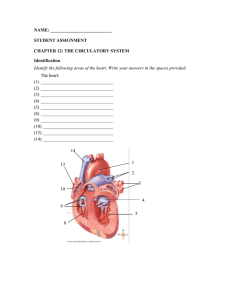
NAME
... C. sinoatrial node D. bundle of His 30. What is the outside covering that surrounds and protects the heart called? A. endocardium B. myocardium C. pericardium D. ectocardium 31. What are the thin-walled upper heart cavities that receive blood from veins called? A. chordae tendineae B. atria C. peric ...
... C. sinoatrial node D. bundle of His 30. What is the outside covering that surrounds and protects the heart called? A. endocardium B. myocardium C. pericardium D. ectocardium 31. What are the thin-walled upper heart cavities that receive blood from veins called? A. chordae tendineae B. atria C. peric ...
Intracardiac Shunts - National Jewish Health
... Treatment of intracardiac shunts depends on the kind of defect and presence (or absence) of other medical problems. ASD’s almost always requires treatment due to the risk of developing heart failure and high blood pressure in the lungs (pulmonary hypertension). Although ASD’s can be treated surgical ...
... Treatment of intracardiac shunts depends on the kind of defect and presence (or absence) of other medical problems. ASD’s almost always requires treatment due to the risk of developing heart failure and high blood pressure in the lungs (pulmonary hypertension). Although ASD’s can be treated surgical ...
Atrial Septal Defect and the CardioSEAL™ Device
... If an ASD is not detected in early childhood, the flow of blood from the left atrium to the right atrium causes the right ventricle and the lungs to work harder. Thus resulting in an enlargement of the right ventricle, and an increase in the pressure of the main arteries of the lungs. Sometimes an A ...
... If an ASD is not detected in early childhood, the flow of blood from the left atrium to the right atrium causes the right ventricle and the lungs to work harder. Thus resulting in an enlargement of the right ventricle, and an increase in the pressure of the main arteries of the lungs. Sometimes an A ...
Document
... Secundum: most common (most of these close on their own). Primum: least common (usually occurs with other abnormalities in the heart). Sinus Venosus: occurs in the upper part of the heart (rare). ...
... Secundum: most common (most of these close on their own). Primum: least common (usually occurs with other abnormalities in the heart). Sinus Venosus: occurs in the upper part of the heart (rare). ...
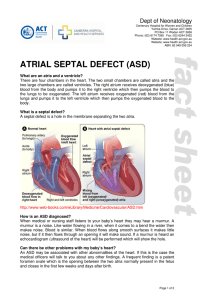
ASD-Atrial Septal Defect
... The normal heart has four chambers. The two top chambers receive blood from the body and lungs. These chambers are called the atria. The two bottom chambers pump blood to the body and lungs. These are called the ventricles. These chambers are separated by walls known as the atrial septum and ventric ...
... The normal heart has four chambers. The two top chambers receive blood from the body and lungs. These chambers are called the atria. The two bottom chambers pump blood to the body and lungs. These are called the ventricles. These chambers are separated by walls known as the atrial septum and ventric ...
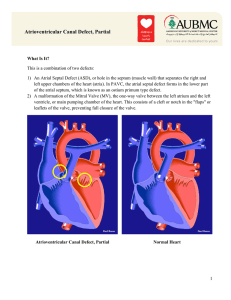
Atrioventricular Canal Defect, Partial
... The atrial septal defect allows the mixing of oxygen-rich blood from the left atrium with oxygen-poor blood in the right atrium. This is known as a left to right shunt. The mixed blood in the right atrium is pumped to the lungs via the right ventricle, reducing the efficiency of the circulatory syst ...
... The atrial septal defect allows the mixing of oxygen-rich blood from the left atrium with oxygen-poor blood in the right atrium. This is known as a left to right shunt. The mixed blood in the right atrium is pumped to the lungs via the right ventricle, reducing the efficiency of the circulatory syst ...
How do you manage this patient?
... • Endocarditis prophylaxis and aspirin are recommended for 6 months following device closure ...
... • Endocarditis prophylaxis and aspirin are recommended for 6 months following device closure ...
Cardiac Anatomy
... 16 Blood returns to the heart from the lungs via the pulmonary _______ 17 How many pulmonary veins are there? 18 Receives blood from the right atrium 19 This valve connects the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery ...
... 16 Blood returns to the heart from the lungs via the pulmonary _______ 17 How many pulmonary veins are there? 18 Receives blood from the right atrium 19 This valve connects the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery ...
Secundum Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)
... contractions (PVCs) and fixed splitting of his second heart sound (S2) on physical exam underwent a transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) to assess for underlying structural heart disease. His TTE was notable for mild right atrial (RA) enlargement, moderate right ventricular (RV) dilatation, and the pr ...
... contractions (PVCs) and fixed splitting of his second heart sound (S2) on physical exam underwent a transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE) to assess for underlying structural heart disease. His TTE was notable for mild right atrial (RA) enlargement, moderate right ventricular (RV) dilatation, and the pr ...
ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT
... • Echocardiography demonstrates evidence of RA and RV volume overload. The atrial defect is usually observed, though sinus venosus defects may be elusive. • Many patients with a PFO also have a redundant atrial septum (atrial septal aneurysm) that promotes right-to-left shunting. Echocardiography wi ...
... • Echocardiography demonstrates evidence of RA and RV volume overload. The atrial defect is usually observed, though sinus venosus defects may be elusive. • Many patients with a PFO also have a redundant atrial septum (atrial septal aneurysm) that promotes right-to-left shunting. Echocardiography wi ...
CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE - South Jersey Heart Group
... DIVIDED INTO TWO • SPACE BETWEEN THE TWO SEPTUM IS OSTIUM PRIMUM, OR FIRST HOLE. • FENESTRATIONS APPEAR IN CENTER LEADING TO SECOND HOLE- OSTIUM SECUNDUM. ...
... DIVIDED INTO TWO • SPACE BETWEEN THE TWO SEPTUM IS OSTIUM PRIMUM, OR FIRST HOLE. • FENESTRATIONS APPEAR IN CENTER LEADING TO SECOND HOLE- OSTIUM SECUNDUM. ...
ATRIAL SEPTAL DEFECT
... (blue) blood returns to the right atrium from the body, travels to the right ventricle, then is pumped into the lungs where it receives oxygen. Oxygenrich (red) blood returns to the left atrium from the lungs, passes into the left ventricle, and then is pumped out to the body through the aorta. ...
... (blue) blood returns to the right atrium from the body, travels to the right ventricle, then is pumped into the lungs where it receives oxygen. Oxygenrich (red) blood returns to the left atrium from the lungs, passes into the left ventricle, and then is pumped out to the body through the aorta. ...
ASD AND PS - Mike Poullis
... • Sinus venosus type-associated with anomalous return of right upper pulmonary vein • Ostium primum ASD • Raghib type-absent coronary sinus with Left SVC connection to left atrium. • Multiple coalescent defects-essentially forming common atrium ...
... • Sinus venosus type-associated with anomalous return of right upper pulmonary vein • Ostium primum ASD • Raghib type-absent coronary sinus with Left SVC connection to left atrium. • Multiple coalescent defects-essentially forming common atrium ...
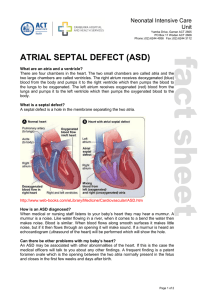
atrial septal defect (asd)
... makes noise. Blood is similar. When blood flows along smooth surfaces it makes little noise, but if it then flows through an opening it will make sound. If a murmur is heard an echocardiogram (ultrasound of the heart) will be performed which will show the hole. Can there be other problems with my ba ...
... makes noise. Blood is similar. When blood flows along smooth surfaces it makes little noise, but if it then flows through an opening it will make sound. If a murmur is heard an echocardiogram (ultrasound of the heart) will be performed which will show the hole. Can there be other problems with my ba ...
atrial septal defect (asd)
... makes noise. Blood is similar. When blood flows along smooth surfaces it makes little noise, but if it then flows through an opening it will make sound. If a murmur is heard an echocardiogram (ultrasound of the heart) will be performed which will show the hole. Can there be other problems with my ba ...
... makes noise. Blood is similar. When blood flows along smooth surfaces it makes little noise, but if it then flows through an opening it will make sound. If a murmur is heard an echocardiogram (ultrasound of the heart) will be performed which will show the hole. Can there be other problems with my ba ...
Patent Foramen Ovale or Atrial Septal Defect
... This is a small hole between the top two chambers of the heart (the atria). This condition occurs in approximately 15% of all people. Usually undetected, if the hole is large enough, it can lead to blood with oxygen mixing with blood that has not yet received oxygen from the lungs. Can also cause pr ...
... This is a small hole between the top two chambers of the heart (the atria). This condition occurs in approximately 15% of all people. Usually undetected, if the hole is large enough, it can lead to blood with oxygen mixing with blood that has not yet received oxygen from the lungs. Can also cause pr ...
Atrial septal defect

Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect in which blood flows between the atria (upper chambers) of the heart. Normally, the atria are separated by a dividing wall, the interatrial septum. If this septum is defective or absent, then oxygen-rich blood can flow directly from the left side of the heart to mix with the oxygen-poor blood in the right side of the heart, or vice versa. This can lead to lower-than-normal oxygen levels in the arterial blood that supplies the brain, organs, and tissues. However, an ASD may not produce noticeable signs or symptoms, especially if the defect is small.A ""shunt"" is the presence of a net flow of blood through the defect, either from left to right or right to left. The amount of shunting present, if any, determines the hemodynamic significance of the ASD. A ""right-to-left-shunt"" typically poses the more dangerous scenario.During development of the fetus, the interatrial septum develops to separate the left and right atria. However, a hole in the septum called the foramen ovale, allows blood from the right atrium to enter the left atrium during fetal development. This opening allows blood to bypass the nonfunctional fetal lungs while the fetus obtains its oxygen from the placenta. A layer of tissue called the septum primum acts as a valve over the foramen ovale during fetal development. After birth, the pressure in the right side of the heart drops as the lungs open and begin working, causing the foramen ovale to close entirely. In approximately 25% of adults, the foramen ovale does not entirely seal. In these cases, any elevation of the pressure in the pulmonary circulatory system (due to pulmonary hypertension, temporarily while coughing, etc.) can cause the foramen ovale to remain open. This is known as a patent foramen ovale (PFO), which is a type of atrial septal defect.