Abdominal wall(1) - Operative surgery - gblnetto
... Each rectus abdominis muscle is enclosed in a fibrous sheath formed by the aponeurotic tendons of the three lateral muscles. The external oblique contributes to the anterior layer the sheath over its whole extent. Below the costal margin the internal obliÂque aponeurosis splits around the muscle co ...
... Each rectus abdominis muscle is enclosed in a fibrous sheath formed by the aponeurotic tendons of the three lateral muscles. The external oblique contributes to the anterior layer the sheath over its whole extent. Below the costal margin the internal obliÂque aponeurosis splits around the muscle co ...
The Path to Massive Traps - St. Raymond High School for Boys
... The One Neglected Exercise You Need Get Trapped Even if you are not where you want to be yet, by pounding iron in the gym, your sweat and effort will eventually pay off with a thick chest, arms that will give your shirt stretch marks, and carved mass across your middle back. When it comes to the bac ...
... The One Neglected Exercise You Need Get Trapped Even if you are not where you want to be yet, by pounding iron in the gym, your sweat and effort will eventually pay off with a thick chest, arms that will give your shirt stretch marks, and carved mass across your middle back. When it comes to the bac ...
PDF - SAS Publishers
... quadratus muscle and from the adjacent interosseous membrane [4]. In addition the flexor digitorum profundus or flexor pollicis longus, muscles may have additional head which arises from the medial border of the coronoid process of the ulna or from the medial epicondyle of the humerus, such accessor ...
... quadratus muscle and from the adjacent interosseous membrane [4]. In addition the flexor digitorum profundus or flexor pollicis longus, muscles may have additional head which arises from the medial border of the coronoid process of the ulna or from the medial epicondyle of the humerus, such accessor ...
What is mental life
... Two of the bundles of the ciliary muscles attach to the sclera and stretch the ciliary body when the contract In this way, the ciliary muscle regulates the tension of the zonule fibers The reduced tension results in thickening of the lens, which focuses the lens on close objects This process i ...
... Two of the bundles of the ciliary muscles attach to the sclera and stretch the ciliary body when the contract In this way, the ciliary muscle regulates the tension of the zonule fibers The reduced tension results in thickening of the lens, which focuses the lens on close objects This process i ...
Pdf - McMed International
... damage, controlling the inflammatory cascade, limiting pain in order to promote early mobilization. Later, proper repair and regeneration of both muscle tissue, and its connective tissue components become the focus of treatment, as excessive fibrosis scar-tissue formation is one of the major factors ...
... damage, controlling the inflammatory cascade, limiting pain in order to promote early mobilization. Later, proper repair and regeneration of both muscle tissue, and its connective tissue components become the focus of treatment, as excessive fibrosis scar-tissue formation is one of the major factors ...
Practical 2 Worksheet-‐KEY
... c. What muscle is found just lateral to the cubital fossa? Brachioradialis d. What muscle is found just medial to the cubital fossa? Pronator teres 52. Is the palm of the hand found on the anter ...
... c. What muscle is found just lateral to the cubital fossa? Brachioradialis d. What muscle is found just medial to the cubital fossa? Pronator teres 52. Is the palm of the hand found on the anter ...
COMMENTARY The diversity of hydrostatic skeletons
... fibers are typically arranged as a ‘crossed-fiber helical connective tissue array’ in which sheets of connective tissue fibers (often collagenous) wrap the body or structure in right- and left-handed helices. Even though the connective tissue fibers are typically stiff in tension and are thus relati ...
... fibers are typically arranged as a ‘crossed-fiber helical connective tissue array’ in which sheets of connective tissue fibers (often collagenous) wrap the body or structure in right- and left-handed helices. Even though the connective tissue fibers are typically stiff in tension and are thus relati ...
structure of the thoracic wall
... relation ship to the nerve of the brachial plexus and main vessels to the arm ,namely the subclavian vessels .this rib is flattened from above down ward . it has tubercle on the inner border , known as the scalene tubercle , for the insertion of the scalenus anterior muscle . anterior to the tubercl ...
... relation ship to the nerve of the brachial plexus and main vessels to the arm ,namely the subclavian vessels .this rib is flattened from above down ward . it has tubercle on the inner border , known as the scalene tubercle , for the insertion of the scalenus anterior muscle . anterior to the tubercl ...
Neck(1)
... following fat spaces of the neck: 1. Sheath for submandibular gland, which contains vessels, nerves, submandibular gland, lymphatic modes and fat. 2. Sheath for sternocleidomastoid muscle. Fat is located between posterior surface of the muscle and its sheath. 3. Between the second fascia and the thi ...
... following fat spaces of the neck: 1. Sheath for submandibular gland, which contains vessels, nerves, submandibular gland, lymphatic modes and fat. 2. Sheath for sternocleidomastoid muscle. Fat is located between posterior surface of the muscle and its sheath. 3. Between the second fascia and the thi ...
Flexor Digitorum Longus Muscle — an Unusual
... usage of the fifth toe in humans is minimal. According to Darwin’s disuse theory, therefore, FDB tendon to the fifth toe may be undergoing phylogenetic variation. This is supported by Reeser et al. (5) in their electromyographic study of human foot which showed that FDB is not preferentially recruit ...
... usage of the fifth toe in humans is minimal. According to Darwin’s disuse theory, therefore, FDB tendon to the fifth toe may be undergoing phylogenetic variation. This is supported by Reeser et al. (5) in their electromyographic study of human foot which showed that FDB is not preferentially recruit ...
Manuscript (Kawakami)
... The characteristics and properties of the MMG in biceps, quadriceps, and lower-back muscles have been reported in several studies (Kimura et al., 2004; Ryan et al., 2008a; Yoshitake et al., 2001). However, there are only few studies (Ioi et al., 2008) using MMG on the masseter muscle, and to date, n ...
... The characteristics and properties of the MMG in biceps, quadriceps, and lower-back muscles have been reported in several studies (Kimura et al., 2004; Ryan et al., 2008a; Yoshitake et al., 2001). However, there are only few studies (Ioi et al., 2008) using MMG on the masseter muscle, and to date, n ...
PECTORALIS MAJOR FLAP
... of myocutaneous perforators. For additional length, the skin paddle may be extended as a random-pattern flap beyond the inferior edge of the muscle. Excessive thickness of the fatty tissue is associated with a higher risk of skin necrosis. Figure 2 The first incision is made from the lateral edge of ...
... of myocutaneous perforators. For additional length, the skin paddle may be extended as a random-pattern flap beyond the inferior edge of the muscle. Excessive thickness of the fatty tissue is associated with a higher risk of skin necrosis. Figure 2 The first incision is made from the lateral edge of ...
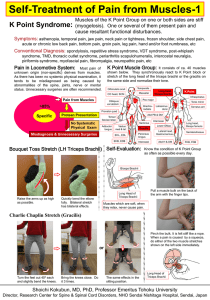
Stretch
... shown below. They synchronously react to K Point block or stretch of the long head of the triceps brachii or the gracilis on the same side and normalize their tone. ...
... shown below. They synchronously react to K Point block or stretch of the long head of the triceps brachii or the gracilis on the same side and normalize their tone. ...
Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate
... The prevertebral fascia covers the prevertebral muscles and scalene muscles, and continues on the floor of the posterior triangle of the neck. It extends superiorly to the base of the skull and inferiorly into the upper posterior part of the thorax, there becoming endothoracic fascia. As the subcla ...
... The prevertebral fascia covers the prevertebral muscles and scalene muscles, and continues on the floor of the posterior triangle of the neck. It extends superiorly to the base of the skull and inferiorly into the upper posterior part of the thorax, there becoming endothoracic fascia. As the subcla ...
Temoral region and muscle of mastication Dr. Hany Sonpol
... Branches of the 3rd part: 1) Posterior superior alveolar artery: Arise before the artery enters the pterygomaxillary fissure Descends on the back of maxilla to supply the following: Molar and premolar teeth of the upper jaw and related gum 2) Infraorbital artery: Enters the orbit by passing ...
... Branches of the 3rd part: 1) Posterior superior alveolar artery: Arise before the artery enters the pterygomaxillary fissure Descends on the back of maxilla to supply the following: Molar and premolar teeth of the upper jaw and related gum 2) Infraorbital artery: Enters the orbit by passing ...
DEEP MUSCLES - INTRODUCTION
... done by cutting them at right angles to the direction of the fibers at the central belly area. They are then folded back, or reflected, to their origins and insertions. They can thus easily be "reconstructed" at any time in order to examine the relationship of the deeper muscles to those of the supe ...
... done by cutting them at right angles to the direction of the fibers at the central belly area. They are then folded back, or reflected, to their origins and insertions. They can thus easily be "reconstructed" at any time in order to examine the relationship of the deeper muscles to those of the supe ...
Circular Muscles
... If you open the mouth and look at the tonsils on the side of the throat wall, you will see that there is a vertical fold of tissue in front of and behind each tonsil. These are called the anterior and posterior faucial pillars, or the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal folds, respectively. Beneath t ...
... If you open the mouth and look at the tonsils on the side of the throat wall, you will see that there is a vertical fold of tissue in front of and behind each tonsil. These are called the anterior and posterior faucial pillars, or the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal folds, respectively. Beneath t ...
The clavicular part of the pectoralis major: a true entity of the upper
... of both the sclerotomes and the myotomes are extended into the body wall. The upper limb is more advanced in development than the lower. At the level of the first intercostal space four premuscular anlagen are recognizable as partitions of the premuscolar lateral mass. The first of these develops ve ...
... of both the sclerotomes and the myotomes are extended into the body wall. The upper limb is more advanced in development than the lower. At the level of the first intercostal space four premuscular anlagen are recognizable as partitions of the premuscolar lateral mass. The first of these develops ve ...
Unilateral absence of ascending and transverse trapezius fibers
... patient with Poland Syndrome, a disorder characterized by unilateral pectoralis muscle deficiency with or without other ipsilateral abnormalities. Specifically, this patient had pectoralis muscle deficiency and a unilateral aplastic trapezius muscle. The cause of Poland Syndrome is unknown, but it h ...
... patient with Poland Syndrome, a disorder characterized by unilateral pectoralis muscle deficiency with or without other ipsilateral abnormalities. Specifically, this patient had pectoralis muscle deficiency and a unilateral aplastic trapezius muscle. The cause of Poland Syndrome is unknown, but it h ...
It is All About the Foot - Pedorthic Footcare Association
... to the…Connective Tissue Thus far, we have covered the bones and articulations of the foot, along with bipedal motion in this series. These are the foundations of what makeups the foot, but this is not enough. We need to ask now, what makes it come all together? It is time to connect all the previou ...
... to the…Connective Tissue Thus far, we have covered the bones and articulations of the foot, along with bipedal motion in this series. These are the foundations of what makeups the foot, but this is not enough. We need to ask now, what makes it come all together? It is time to connect all the previou ...
Skeletal muscle

Skeletal muscle is a form of striated muscle tissue which is under the voluntary control of the somatic nervous system. It is one of three major muscle types, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. Most skeletal muscles are attached to bones by bundles of collagen fibers known as tendons.Skeletal muscle is made up of individual muscle cells or myocytes, known as muscle fibers. They are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts (a type of embryonic progenitor cell that gives rise to a muscle cell) in a process known as myogenesis. Muscle fibres are cylindrical, and multinucleated.Muscle fibers are in turn composed of myofibrils. The myofibrils are composed of actin and myosin filaments, repeated in units called sarcomeres, the basic functional units of the muscle fiber. The sarcomere is responsible for the striated appearance of skeletal muscle, and forms the basic machinery necessary for muscle contraction. The term muscle refers to multiple bundles of muscle fibers called fascicles. All muscles also contain connective tissue arranged in layers of fasciae. Each muscle is enclosed in a layer of fascia; each fascicle is enclosed by a layer of fascia and each individual muscle fiber is also enclosed in a layer of fascia.