Some Basics 5.1.3 Basic Wave Optics
... A first important conclusion can be arrived at. If we look at an ensemble of waves with the same wavelength, or better: with the same wave vector k = 2π/λ since it contains in addition to the wavelength also the direction of propagation (that's why it's a vector), we note that: An ensemble of suffic ...
... A first important conclusion can be arrived at. If we look at an ensemble of waves with the same wavelength, or better: with the same wave vector k = 2π/λ since it contains in addition to the wavelength also the direction of propagation (that's why it's a vector), we note that: An ensemble of suffic ...
Q - IndiaStudyChannel
... If we know the shape of front at t = 0 then from Huygens principle allows us to determine the shape of wave front at any time t. Let us consider a diverging wave originating from point 0. f1 f2 represent a portion of the spherical wave front at t = 0 Now according to Huygens principle, each point of ...
... If we know the shape of front at t = 0 then from Huygens principle allows us to determine the shape of wave front at any time t. Let us consider a diverging wave originating from point 0. f1 f2 represent a portion of the spherical wave front at t = 0 Now according to Huygens principle, each point of ...
Question paper
... Light has a dual wave-particle nature. State and outline a piece of evidence for the wave nature of light and a piece of evidence for its particle nature. For each piece of evidence, outline a characteristic feature that has been observed or measured and give a short explanation of its relevance to ...
... Light has a dual wave-particle nature. State and outline a piece of evidence for the wave nature of light and a piece of evidence for its particle nature. For each piece of evidence, outline a characteristic feature that has been observed or measured and give a short explanation of its relevance to ...
photoelectric effect
... When metal surfaces are exposed to electromagnetic radiation with sufficient energy they absorb the photons of energy and emit electrons. This process is called the photoelectric effect. ...
... When metal surfaces are exposed to electromagnetic radiation with sufficient energy they absorb the photons of energy and emit electrons. This process is called the photoelectric effect. ...
BPUT QUESTION BANK FOR 4th SEM STUDENTS OF CS1, CS2
... 3) What is meant by compound semiconductor? 4) What is the difference between a semiconductor and a good conductor? 5) What is Meissner effect? 6) How according to Kronig-Penny model, does the width of forbidden energy gap in solid changes as the energy increases? 7) In a fermionic system in the gro ...
... 3) What is meant by compound semiconductor? 4) What is the difference between a semiconductor and a good conductor? 5) What is Meissner effect? 6) How according to Kronig-Penny model, does the width of forbidden energy gap in solid changes as the energy increases? 7) In a fermionic system in the gro ...
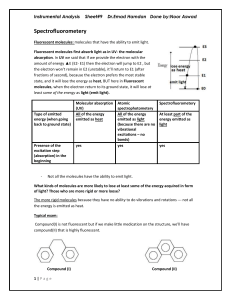
L09 Instru Spectrofluorometery
... Then to measure the intensity of the monochromatic emitted light, we’ll use a photocell *detector*(the photocell in UV designed to measure I° and It and take the ratio but here in spectrofluorometer it will measure the intensity of the monochromatic emitted light). Note the design of the spectrofluo ...
... Then to measure the intensity of the monochromatic emitted light, we’ll use a photocell *detector*(the photocell in UV designed to measure I° and It and take the ratio but here in spectrofluorometer it will measure the intensity of the monochromatic emitted light). Note the design of the spectrofluo ...
Properties of Waves
... When a sound wave reflects off a hard surface and we hear it again – this is an echo. The distance between a sound and an object can be found by using the wave equation – but remember, it will be double the distance between the sound and the hard surface s = 2d/t Where s is the speed of sound in air ...
... When a sound wave reflects off a hard surface and we hear it again – this is an echo. The distance between a sound and an object can be found by using the wave equation – but remember, it will be double the distance between the sound and the hard surface s = 2d/t Where s is the speed of sound in air ...
Thomas Young (scientist)
.jpg?width=300)
Thomas Young (13 June 1773 – 10 May 1829) was an English polymath and physician. Young made notable scientific contributions to the fields of vision, light, solid mechanics, energy, physiology, language, musical harmony, and Egyptology. He ""made a number of original and insightful innovations""in the decipherment of Egyptian hieroglyphs (specifically the Rosetta Stone) before Jean-François Champollion eventually expanded on his work. He was mentioned by, among others, William Herschel, Hermann von Helmholtz, James Clerk Maxwell, and Albert Einstein. Young has been described as ""The Last Man Who Knew Everything"".