Dimensions of schizophrenic positive symptoms: an exploratory
... the results of factor analysis may differ even among the same subjects, if a different set of symptoms is being assessed. Statistical requirement is to reduce the number of symptomatic items into one that will enable the results of factor analysis to be stable. However, this makes it difficult to ex ...
... the results of factor analysis may differ even among the same subjects, if a different set of symptoms is being assessed. Statistical requirement is to reduce the number of symptomatic items into one that will enable the results of factor analysis to be stable. However, this makes it difficult to ex ...
Advanced Placement Psychology Mrs. Kerri Hennen Study Guide
... B) A behavior cannot be defined as abnormal unless it is considered harmful to society. C) Abnormal behavior can be defined as any behavior that is atypical. D) Definitions of abnormal behavior are based on physiological factors. 2. The criteria for classifying behavior as psychologically disordered ...
... B) A behavior cannot be defined as abnormal unless it is considered harmful to society. C) Abnormal behavior can be defined as any behavior that is atypical. D) Definitions of abnormal behavior are based on physiological factors. 2. The criteria for classifying behavior as psychologically disordered ...
psychologicaldisroders - Ms. Bishop`s Classroom
... Somatoform Disorders Somatoform disorders are characterized by ...
... Somatoform Disorders Somatoform disorders are characterized by ...
SpEd-OHD-ADHD-MEDICAL-DOCUMENTATION-blank
... Often interrupts others (e.g., butts into conversations or games; may start using other people’s things without asking or receiving permission; for adolescents and adults, may intrude into or take over what others are doing ...
... Often interrupts others (e.g., butts into conversations or games; may start using other people’s things without asking or receiving permission; for adolescents and adults, may intrude into or take over what others are doing ...
Chapter 15: Psychological Disorders
... • Dissociative disorders – Psychological dysfunctions characterized by the separation of critical personality facets that are normally integrated, allowing stress avoidance through escape • Dissociative identity disorder (multiple personality) – Individual displays characteristics of two or more dis ...
... • Dissociative disorders – Psychological dysfunctions characterized by the separation of critical personality facets that are normally integrated, allowing stress avoidance through escape • Dissociative identity disorder (multiple personality) – Individual displays characteristics of two or more dis ...
Evidence that three dimensions of psychosis have a
... measures of schizotypy are strongly associated with neuroticism and depression in crosssectional, longitudinal and family studies (Chapman et al. 1980, 1994 ; Schulz et al. 1986 ; Allen et al. 1987 ; Lenzenweger & Loranger, 1989 ; Tien et al. 1992 ; Torgersen et al. 1993 ; Corruble et al. 1996 ; Kan ...
... measures of schizotypy are strongly associated with neuroticism and depression in crosssectional, longitudinal and family studies (Chapman et al. 1980, 1994 ; Schulz et al. 1986 ; Allen et al. 1987 ; Lenzenweger & Loranger, 1989 ; Tien et al. 1992 ; Torgersen et al. 1993 ; Corruble et al. 1996 ; Kan ...
Association Between Symptom Dimensions and Categorical
... overlap between dimensions is vague across diagnoses. Although the above studies support the presence of multiple symptom dimensions across psychotic disorders, at present 3 critical questions pertinent to the validity of the dimensional approach remain unresolved. First, there is no consensus regar ...
... overlap between dimensions is vague across diagnoses. Although the above studies support the presence of multiple symptom dimensions across psychotic disorders, at present 3 critical questions pertinent to the validity of the dimensional approach remain unresolved. First, there is no consensus regar ...
Unit 12 Study Guide
... D) dramatic, attention-getting behaviors. E) delusions and hallucinations. 38. Within the last year, Mr. Shangkun has been fired by three different employers because they each discovered that he was stealing money or materials from their companies. Although he feels no remorse for his misdeeds, his ...
... D) dramatic, attention-getting behaviors. E) delusions and hallucinations. 38. Within the last year, Mr. Shangkun has been fired by three different employers because they each discovered that he was stealing money or materials from their companies. Although he feels no remorse for his misdeeds, his ...
Lucy Johnstone Alternative to Psychiatric Diagnosis Powerpoint
... do so too. This book is about choice. It is about giving people the information to make up their own minds, and exploring alternatives for those who wish to do so.’ ...
... do so too. This book is about choice. It is about giving people the information to make up their own minds, and exploring alternatives for those who wish to do so.’ ...
Refractory Mood And Psychosis Mood disorders are common
... 33. ____________________ such as atropine and scopolamine, have been known to cause symptoms of restlessness, disorientation, mania, and hallucinations. a. b. c. d. ...
... 33. ____________________ such as atropine and scopolamine, have been known to cause symptoms of restlessness, disorientation, mania, and hallucinations. a. b. c. d. ...
Mapping synaptic pathology within cerebral cortical circuits in
... Primary auditory cortex offers another example of a cortical region in which convergent evidence implicates synaptic disruptions in the pathology of schizophrenia. In subjects with schizophrenia, the processing of sensory information within AI is impaired, manifest as the reduced ability to discrimi ...
... Primary auditory cortex offers another example of a cortical region in which convergent evidence implicates synaptic disruptions in the pathology of schizophrenia. In subjects with schizophrenia, the processing of sensory information within AI is impaired, manifest as the reduced ability to discrimi ...
Psychological Disorders
... Types of Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a cluster of disorders Positive Symptoms vs Negative Symptoms •disorganized/deluded vs toneless/expressionless •inappropriate emotions vs silence/catatonia Chronic vs Acute Schizophrenia • slow development/history of social inadequacy • rapid development/reac ...
... Types of Schizophrenia Schizophrenia is a cluster of disorders Positive Symptoms vs Negative Symptoms •disorganized/deluded vs toneless/expressionless •inappropriate emotions vs silence/catatonia Chronic vs Acute Schizophrenia • slow development/history of social inadequacy • rapid development/reac ...
SOCIAL SKILLS TRAINING FOR PEOPLE WITH SCHIZOPHRENIA
... & Collins, 2008). Many of these studies have also linked the severity of affective symptoms not only with poorer social functioning, but also with worsening of cognitive deficits (Lysaker & Salyers, 2007) and a marked decrease of the person’s self-esteem. The most common explanatory model for mental ...
... & Collins, 2008). Many of these studies have also linked the severity of affective symptoms not only with poorer social functioning, but also with worsening of cognitive deficits (Lysaker & Salyers, 2007) and a marked decrease of the person’s self-esteem. The most common explanatory model for mental ...
Describe antisocial personality disorder
... Environment can play a role, but is not a major cause. (EX: Case Study – Michael W. – disturbed home-life.) Schizophrenics seem to have an excess of dopamine, which causes neurons to fire too rapidly, which in turn leads to disturbances in speech patterns. Researchers feel that psychological problem ...
... Environment can play a role, but is not a major cause. (EX: Case Study – Michael W. – disturbed home-life.) Schizophrenics seem to have an excess of dopamine, which causes neurons to fire too rapidly, which in turn leads to disturbances in speech patterns. Researchers feel that psychological problem ...
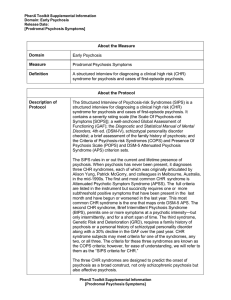
Microsoft Word
... subthreshold positive symptoms that have been present in the last month and have begun or worsened in the last year. This most common CHR syndrome is the one that maps onto DSM-5 APS. The second CHR syndrome, Brief Intermittent Psychosis Syndrome (BIPS), permits one or more symptoms at a psychotic i ...
... subthreshold positive symptoms that have been present in the last month and have begun or worsened in the last year. This most common CHR syndrome is the one that maps onto DSM-5 APS. The second CHR syndrome, Brief Intermittent Psychosis Syndrome (BIPS), permits one or more symptoms at a psychotic i ...
Psychological Disorder
... is during examination or waiting for interview results or maybe due to death of a loved one, anxiety is experienced by us. We also have our own way of coping with it but anxiety can take the form of a disorder if not treated properly at the correct time. Anxiety disorders are disorders which decreas ...
... is during examination or waiting for interview results or maybe due to death of a loved one, anxiety is experienced by us. We also have our own way of coping with it but anxiety can take the form of a disorder if not treated properly at the correct time. Anxiety disorders are disorders which decreas ...
“He`s a born worrier” CBT for GAD
... D. The symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning (including maintaining a safe environment for self and others). E. Hoarding symptoms not due to a general medical condition (e.g. brain injury, cerebrovascular disease ...
... D. The symptoms cause clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning (including maintaining a safe environment for self and others). E. Hoarding symptoms not due to a general medical condition (e.g. brain injury, cerebrovascular disease ...
Chapter 22: Mental Illness
... • Schizophrenia and the ventricle to-brain-size ratio • Other structural observation of the brains of ...
... • Schizophrenia and the ventricle to-brain-size ratio • Other structural observation of the brains of ...
The Garety et al. Model of CBT for Psychosis
... • May introduce coping strategies early on (engagement and can learn from behavioural change) – “There is something I can do that helps” “It isn’t all uncontrollable” • Formulation: • The formulation is the focal point for change and is an ongoing process • Aiming to “connect up” seemingly unconne ...
... • May introduce coping strategies early on (engagement and can learn from behavioural change) – “There is something I can do that helps” “It isn’t all uncontrollable” • Formulation: • The formulation is the focal point for change and is an ongoing process • Aiming to “connect up” seemingly unconne ...
File
... thoughts. Originally a vague general description that led to over diagnosis NOT “split personality” one personality that is ...
... thoughts. Originally a vague general description that led to over diagnosis NOT “split personality” one personality that is ...
Schizophrenia

Schizophrenia (/ˌskɪtsɵˈfrɛniə/ or /ˌskɪtsɵˈfriːniə/) is a mental disorder often characterized by abnormal social behavior and failure to recognize what is real. Common symptoms include false beliefs, unclear or confused thinking, auditory hallucinations, reduced social engagement and emotional expression, and lack of motivation. Diagnosis is based on observed behavior and the person's reported experiences.Genetics and early environment, as well as psychological and social processes, appear to be important contributory factors. Some recreational and prescription drugs appear to cause or worsen symptoms. The many possible combinations of symptoms have triggered debate about whether the diagnosis represents a single disorder or a number of separate syndromes. Despite the origin of the term, from Greek skhizein, meaning ""to split"", and phrēn, meaning ""mind"", schizophrenia does not imply a ""split personality"" or ""multiple personality disorder"" — a condition with which it is often confused in public perception. Rather, the term means a ""splitting of mental functions"", reflecting the presentation of the illness.The mainstay of treatment is antipsychotic medication, which primarily suppresses dopamine receptor activity. Counseling, job training and social rehabilitation are also important in treatment. In more serious cases—where there is risk to self or others—involuntary hospitalization may be necessary, although hospital stays are now shorter and less frequent than they once were.Symptoms begin typically in young adulthood, and about 0.3–0.7% of people are affected during their lifetime. In 2013 there was estimated to be 23.6 million cases globally. The disorder is thought to mainly affect the ability to think, but it also usually contributes to chronic problems with behavior and emotion. People with schizophrenia are likely to have additional conditions, including major depression and anxiety disorders; the lifetime occurrence of substance use disorder is almost 50%. Social problems, such as long-term unemployment, poverty, and homelessness are common. The average life expectancy of people with the disorder is ten to twenty five years less than the average life expectancy. This is the result of increased physical health problems and a higher suicide rate (about 5%). In 2013 an estimated 16,000 people died from behavior related-to or caused by schizophrenia.