Chapter 15 Invertebrates
... particles from the water – Each collar cell digests its own particles of ...
... particles from the water – Each collar cell digests its own particles of ...
Part A. What makes up soil? Part B. Soil Formation
... 2. Why would you NOT find soils on Mars or Venus? Not all materials that make up soil can be found on other planets, such as water, organic materials 3. Where do the minerals (inorganic materials) that form soil come from? From the weathering and erosion of rocks 4. How is the air found in soils dif ...
... 2. Why would you NOT find soils on Mars or Venus? Not all materials that make up soil can be found on other planets, such as water, organic materials 3. Where do the minerals (inorganic materials) that form soil come from? From the weathering and erosion of rocks 4. How is the air found in soils dif ...
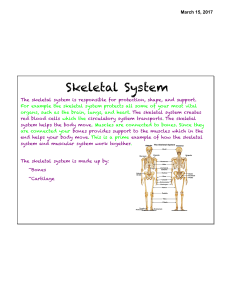
Skeletal System
... muscular system relies on the digestive for energy. It relies on the respiratory to help provide it with the oxygen the muscles need. The cardiovascular and circulatory system pump and transport the blood to the muscles which they also need. The nervous system also works with the muscular system by ...
... muscular system relies on the digestive for energy. It relies on the respiratory to help provide it with the oxygen the muscles need. The cardiovascular and circulatory system pump and transport the blood to the muscles which they also need. The nervous system also works with the muscular system by ...
Introduction to Animals - Kent City School District
... sessile (attached & non-moving) • Animals that move very little are said to be sedentary (clam) • Animals that can move are motile • Have muscular tissue to provide energy for movement ...
... sessile (attached & non-moving) • Animals that move very little are said to be sedentary (clam) • Animals that can move are motile • Have muscular tissue to provide energy for movement ...
Here is a list of soil tests
... As you saw in the first section on Soil classification, the Gradational group in the Northcote System is subdivided according to whether the soil is calcareous or not. Calcareous means that a form of calcium carbonate is present. This may come from some sort of limestone parent material or it may be ...
... As you saw in the first section on Soil classification, the Gradational group in the Northcote System is subdivided according to whether the soil is calcareous or not. Calcareous means that a form of calcium carbonate is present. This may come from some sort of limestone parent material or it may be ...
Chapter 7 Weathering and Soil
... At many places of Earth, land is covered by a thick layer of sediment that is deposited by glaciers. -This material is an unsorted mixture of clay, silt, sand, and boulders that were left after the glacial ice melted. It is extremely fertile. ...
... At many places of Earth, land is covered by a thick layer of sediment that is deposited by glaciers. -This material is an unsorted mixture of clay, silt, sand, and boulders that were left after the glacial ice melted. It is extremely fertile. ...
Making Soil - How Does Soil Form?
... 1. Have learners identify the components of soil. 2. To represent mechanical weathering, the learners can crush rocks and sand with the hammer as parent material for the mineral portion of the soil. Keep the rocks and particles inside the cloth bag to prevent injuries from flying pieces. Explain the ...
... 1. Have learners identify the components of soil. 2. To represent mechanical weathering, the learners can crush rocks and sand with the hammer as parent material for the mineral portion of the soil. Keep the rocks and particles inside the cloth bag to prevent injuries from flying pieces. Explain the ...
Science – Grade6
... Identify the safety precautions we need to take so that we are not affected by harmful microbes. Describe how food must be stored correctly. Recall the characteristics of all plants. Know that plants are divided into flowering and non flowering and state a few examples. Classify plants further with ...
... Identify the safety precautions we need to take so that we are not affected by harmful microbes. Describe how food must be stored correctly. Recall the characteristics of all plants. Know that plants are divided into flowering and non flowering and state a few examples. Classify plants further with ...
PSEUDOCOELOMATE LABORATORY Phylum Gastrotricha 1
... intestine. Trace out the alimentary canal: mouth, esophagus, pharynx, intestine, and anus. Note the relatively straight-tube construction of the gut that is nonmuscular except for the pharynx. The esophagus is highly glandular. In the living Ascaris the gut is under high pressure due to the coelomic ...
... intestine. Trace out the alimentary canal: mouth, esophagus, pharynx, intestine, and anus. Note the relatively straight-tube construction of the gut that is nonmuscular except for the pharynx. The esophagus is highly glandular. In the living Ascaris the gut is under high pressure due to the coelomic ...
Soil color – a window for public and educators to understands soils
... (OSDs). A color calculator developed in R and ArcMap were used to spatially display the soil colors. Soil colors showed vertical trends related to soil depth and horizontal trends related to parent material and climate. Soil colors represent development processes depending upon environment and time ...
... (OSDs). A color calculator developed in R and ArcMap were used to spatially display the soil colors. Soil colors showed vertical trends related to soil depth and horizontal trends related to parent material and climate. Soil colors represent development processes depending upon environment and time ...
Soil Organic Matter
... Adding Fresh OM • In a soil which at first has no readily decomposable materials, adding fresh tissue under favorable conditions: • 1) immediately starts rapid multiplication of bacteria, fungi, and actinomycetes, • 2) which are soon actively decomposing the fresh tissue. ...
... Adding Fresh OM • In a soil which at first has no readily decomposable materials, adding fresh tissue under favorable conditions: • 1) immediately starts rapid multiplication of bacteria, fungi, and actinomycetes, • 2) which are soon actively decomposing the fresh tissue. ...
File
... 1. ___________________________ 2. ___________________________ 3. ___________________________ 4. ___________________________ 9. The rock and mineral fragments found in soils come from rocks that have been ___________________________. Most of these fragments are small particles of sediment such as ___ ...
... 1. ___________________________ 2. ___________________________ 3. ___________________________ 4. ___________________________ 9. The rock and mineral fragments found in soils come from rocks that have been ___________________________. Most of these fragments are small particles of sediment such as ___ ...
Animilia - Paxon Biology
... - Class Oligochaeta - Class Polychaeta - Class Hirundinea - Class Oligochaeta: - Earthworms - Regular segments: true metamerism (the serial duplication of body parts) - Special segments for reproduction, nervous system, and circulatory systems. - They have a mouth, pharynx (suction pump) esophagus, ...
... - Class Oligochaeta - Class Polychaeta - Class Hirundinea - Class Oligochaeta: - Earthworms - Regular segments: true metamerism (the serial duplication of body parts) - Special segments for reproduction, nervous system, and circulatory systems. - They have a mouth, pharynx (suction pump) esophagus, ...
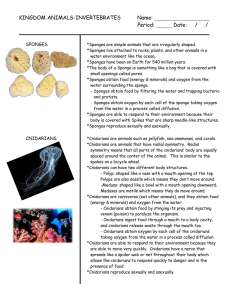
Period: ______ Date
... spaced around the center of the animal. This is similar to the spokes on a bicycle wheel. *Cnidarians can have two different body structures. - Polyp: shaped like a vase with a mouth opening at the top. Polyps are also sessile which means they don’t move around. -Medusa: shaped like a bowl with a mo ...
... spaced around the center of the animal. This is similar to the spokes on a bicycle wheel. *Cnidarians can have two different body structures. - Polyp: shaped like a vase with a mouth opening at the top. Polyps are also sessile which means they don’t move around. -Medusa: shaped like a bowl with a mo ...
HORTICULTURE_files/Unit 8
... • Lower plant forms such as lichens, moss, and fungi grow on rock matter • Organic matter: The decay of plants and animals which is essential for soil formation ...
... • Lower plant forms such as lichens, moss, and fungi grow on rock matter • Organic matter: The decay of plants and animals which is essential for soil formation ...
The Group of Plant Nutrition and the Laboratory of
... PhD position in soil organic matter/phosphorus biogeochemistry Soil organic matter is one of the most important components regulating the transfer of nutrients in terrestrial ecosystems. An innate constituent of soil organic matter is that it contains carbon, nitrogen, sulfur and phosphorus. However ...
... PhD position in soil organic matter/phosphorus biogeochemistry Soil organic matter is one of the most important components regulating the transfer of nutrients in terrestrial ecosystems. An innate constituent of soil organic matter is that it contains carbon, nitrogen, sulfur and phosphorus. However ...
Chapter 14 Final Review Weathering and Erosion
... the different layers of the soil • The layers of soil are called horizons and there are normally 3 main horizons. • Top soil is on top and has a mixture of small rock and any organic material, subsoil contains minerals that were from the topsoil and some humus, the bedrock is a solid rock layer and ...
... the different layers of the soil • The layers of soil are called horizons and there are normally 3 main horizons. • Top soil is on top and has a mixture of small rock and any organic material, subsoil contains minerals that were from the topsoil and some humus, the bedrock is a solid rock layer and ...
Phylum Arthropoda Non
... Adaptations for a predatory life on land Book lungs = paired sacs in the abdomen with many parallel folds that resemble the pages of a book. The folds in a book lung provide a large surface area for gas exchange. (and/or) Tracheae = a system of tubes that carry air directly to the tissues from spira ...
... Adaptations for a predatory life on land Book lungs = paired sacs in the abdomen with many parallel folds that resemble the pages of a book. The folds in a book lung provide a large surface area for gas exchange. (and/or) Tracheae = a system of tubes that carry air directly to the tissues from spira ...
Uint 2 lesson 5 soil
... b. B Horizon= below A where water carries minerals less humus leeching= water carrying materials through soil has a reddish or brownish color c. C. Horizon= below B and least developed contains large rock fragments directly above parent rock material (rock form which soil formed from) ...
... b. B Horizon= below A where water carries minerals less humus leeching= water carrying materials through soil has a reddish or brownish color c. C. Horizon= below B and least developed contains large rock fragments directly above parent rock material (rock form which soil formed from) ...
Nematodes
... disease cycles are sylvatic (wild carnivores and their prey) and urban (humans, rats, pigs) garbage plays an important role in the urban cycle trichinosis disease (humans are a dead end host) 1) penetration of adult females into mucosa - 12 hours to 2 days; abdominal pain, diarrhea, sweating, nausea ...
... disease cycles are sylvatic (wild carnivores and their prey) and urban (humans, rats, pigs) garbage plays an important role in the urban cycle trichinosis disease (humans are a dead end host) 1) penetration of adult females into mucosa - 12 hours to 2 days; abdominal pain, diarrhea, sweating, nausea ...
Genome Wide Association Study in Hap
... Arabidopsis ecotypes with naturally selected differences in sensitivity to soil carbonate provide an excellent material for investigating the physiological mechanisms that are behind this differential behaviour. The aim of this study is to identify genes related to adaptation to soil carbonate in Ar ...
... Arabidopsis ecotypes with naturally selected differences in sensitivity to soil carbonate provide an excellent material for investigating the physiological mechanisms that are behind this differential behaviour. The aim of this study is to identify genes related to adaptation to soil carbonate in Ar ...
forensic soil analysis ii
... CAPTAIN OF CIVIL GUARD IN CHARGE OF THE SOIL ANALYSIS SECTION CRIMINALISTIC SERVICE OF THE CIVIL GUARD ...
... CAPTAIN OF CIVIL GUARD IN CHARGE OF THE SOIL ANALYSIS SECTION CRIMINALISTIC SERVICE OF THE CIVIL GUARD ...
Compacted Zone In Soil - NRCS
... a constant source of carbon and relatively stable conditions in the soil. Under these conditions, more Glomalin is produced and more macro-aggregates are formed. Deep (10-12” or more) tillage is often assumed to break up hard pans. Deep tillage is really never a permanent fix for this problem. To be ...
... a constant source of carbon and relatively stable conditions in the soil. Under these conditions, more Glomalin is produced and more macro-aggregates are formed. Deep (10-12” or more) tillage is often assumed to break up hard pans. Deep tillage is really never a permanent fix for this problem. To be ...
Introduction to Soils
... • Rivers, glaciers, landslides and avalanches cause rock particles to grind against each other wearing them down. • Chemicals mix with water to further break the rocks down. • Plants began to grow in the weathered rocks and as they die, they add organic matter to the soil which attracts soil microor ...
... • Rivers, glaciers, landslides and avalanches cause rock particles to grind against each other wearing them down. • Chemicals mix with water to further break the rocks down. • Plants began to grow in the weathered rocks and as they die, they add organic matter to the soil which attracts soil microor ...
Nature of the parent material will greatly influence time it takes to
... Soil Science Taxonomy • Soil as a natural body • Each soil as a unique individual – Developed as a result of the 5 factors of soil formation ...
... Soil Science Taxonomy • Soil as a natural body • Each soil as a unique individual – Developed as a result of the 5 factors of soil formation ...
Earthworm

An earthworm is a tube-shaped, segmented worm found in the phylum Annelida. They are commonly found living in soil, feeding on live and dead organic matter. Its digestive system runs through the length of its body. It conducts respiration through its skin. An earthworm has a double transport system composed of coelomic fluid that moves within the fluid-filled coelom and a simple, closed blood circulatory system. It has a central and a peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system consists of two ganglia above the mouth, one on either side, connected to a nerve cord running back along its length to motor neurons and sensory cells in each segment. Large numbers of chemoreceptors are concentrated near its mouth. Circumferential and longitudinal muscles on the periphery of each segment enable the worm to move. Similar sets of muscles line the gut, and their actions move the digesting food toward the worm's anus.Earthworms are hermaphrodites—each individual carries both male and female sex organs. They lack either an internal skeleton or exoskeleton, but maintain their structure with fluid-filled coelom chambers that function as a hydrostatic skeleton.""Earthworm"" is the common name for the largest members of Oligochaeta (which is either a class or a subclass depending on the author). In classical systems, they were placed in the order Opisthopora, on the basis of the male pores opening posterior to the female pores, though the internal male segments are anterior to the female. Theoretical cladistic studies have placed them, instead, in the suborder Lumbricina of the order Haplotaxida, but this may again soon change. Folk names for the earthworm include ""dew-worm"", ""rainworm"", ""night crawler"", and ""angleworm"" (due to its use as fishing bait).Larger terrestrial earthworms are also called megadriles (or big worms), as opposed to the microdriles (or small worms) in the semiaquatic families Tubificidae, Lumbriculidae, and Enchytraeidae, among others. The megadriles are characterized by having a distinct clitellum (which is more extensive than that of microdriles) and a vascular system with true capillaries.Earthworms are far less abundant in disturbed environments and are typically active only if water is present.