theoretical eye models comparison based on mtf evolution
... influenced is the eye lens [1-3]. Most early eye models such as Emsley’s reduced eye, Gullstrand simplified or Gullstrand-le Grand eye, Swiegerling eye can be described as ideal theoretical models due to their assumptions valid in the paraxial domain [5], [8-9], [11-12]. The Arizona eye model that w ...
... influenced is the eye lens [1-3]. Most early eye models such as Emsley’s reduced eye, Gullstrand simplified or Gullstrand-le Grand eye, Swiegerling eye can be described as ideal theoretical models due to their assumptions valid in the paraxial domain [5], [8-9], [11-12]. The Arizona eye model that w ...
COMPUTER GRAPHICS OPTIQUE Optical Superposition of
... Beyond increased brightness, we believe optical superposition augmented by some optical effects like blurring (available in most projectors), can be used in modern computer graphics to replace expensive computation, to increase rendering speed, to achieve flexibility, and to increase intensity range ...
... Beyond increased brightness, we believe optical superposition augmented by some optical effects like blurring (available in most projectors), can be used in modern computer graphics to replace expensive computation, to increase rendering speed, to achieve flexibility, and to increase intensity range ...
CONTENTS Optic Axis Principal Section of a Crystal Geometry of
... the optic axis of the crystal. Since the speed of light wave in a medium is the ratio of its speed in vacuum and the index of refraction for that wavelength, an E-ray can move either faster or slower than an O-ray. • However, the velocity of O-ray inside the crystal is same in all the directions whi ...
... the optic axis of the crystal. Since the speed of light wave in a medium is the ratio of its speed in vacuum and the index of refraction for that wavelength, an E-ray can move either faster or slower than an O-ray. • However, the velocity of O-ray inside the crystal is same in all the directions whi ...
BMS 631 - Lecture 4
... Scatter - Rayleigh Scatter - directly proportional to property of the scattering molecule called molecular polarizability (ie dipole formation), inversely proportional to the fourth power of the wavelength of the incident light (blue light has highest scatter - thus blue sky!) Scatter - Raman Scatte ...
... Scatter - Rayleigh Scatter - directly proportional to property of the scattering molecule called molecular polarizability (ie dipole formation), inversely proportional to the fourth power of the wavelength of the incident light (blue light has highest scatter - thus blue sky!) Scatter - Raman Scatte ...
High refractive index Fresnel lens on a fiber fabricated by
... The lens master mold was fabricated using a gallium FIB integrated into a Zeiss Orion NanoFab microscope. First and a second generation replicas of the master mold were created with a commercial UV-curable polymer (Ormocomp, Micro Resist Technology) [19]. The second replica, which has the same litho ...
... The lens master mold was fabricated using a gallium FIB integrated into a Zeiss Orion NanoFab microscope. First and a second generation replicas of the master mold were created with a commercial UV-curable polymer (Ormocomp, Micro Resist Technology) [19]. The second replica, which has the same litho ...
Telescope Quiz Review
... Review the parts of the telescope. Know what each term describes Tripod ‐ The support for the telescope. The number on one leg is directed South (toward Igor’s tower). Optical Tube ‐ Large tube which holds the pieces of the telescope in place. The main body of the telescope. Finder scope (spotter ...
... Review the parts of the telescope. Know what each term describes Tripod ‐ The support for the telescope. The number on one leg is directed South (toward Igor’s tower). Optical Tube ‐ Large tube which holds the pieces of the telescope in place. The main body of the telescope. Finder scope (spotter ...
Nonconfocal Differential Interferometry Sensing Scheme for
... the focal length of the object beam leading to a situation in which the reference beam focuses on the chip base and the object beam focuses on the cantilever. Notably, the method to expand the focal length of object beam is rather simple. When a laser beam travers a glass plate with plane surfaces t ...
... the focal length of the object beam leading to a situation in which the reference beam focuses on the chip base and the object beam focuses on the cantilever. Notably, the method to expand the focal length of object beam is rather simple. When a laser beam travers a glass plate with plane surfaces t ...
Tyukhtin_RREPS13_presentation
... D is a square of cross-section of ray tube on the observation point. This calculation is related to Fock’s method for analyzing reflection of arbitrary non-plane waves from an arbitrary surface; analogous calculations are applied to elaborate different optical systems. At the second step, the incide ...
... D is a square of cross-section of ray tube on the observation point. This calculation is related to Fock’s method for analyzing reflection of arbitrary non-plane waves from an arbitrary surface; analogous calculations are applied to elaborate different optical systems. At the second step, the incide ...
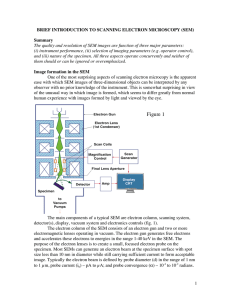
Microscope
... Is the useful limit of magnification, it is the ability of microscope, at specific magnification to distinguish two separate objects situated close to one another and the ability of the lens to reveal fine details. The smaller the distance between the two specific objects that can be distinguish ...
... Is the useful limit of magnification, it is the ability of microscope, at specific magnification to distinguish two separate objects situated close to one another and the ability of the lens to reveal fine details. The smaller the distance between the two specific objects that can be distinguish ...
Snell`s Law - Initial Set Up
... the light ray bend relative to the normal? When light travels from a more optically dense material to a less optically dense material, how does the light ray bend relative to the normal? ...
... the light ray bend relative to the normal? When light travels from a more optically dense material to a less optically dense material, how does the light ray bend relative to the normal? ...
Optical gratings: Nano-engineered lenses - MiNa
... which the phase shift is a quadratic function of the position. The authors showed that their fabricated lens, with a diameter of 300 μm, a focal length of 17.2 mm and for operation with 1,550 nm light, successfully focused light down to a 60 μm spot. This corresponds to a numerical aperture (NA) of ...
... which the phase shift is a quadratic function of the position. The authors showed that their fabricated lens, with a diameter of 300 μm, a focal length of 17.2 mm and for operation with 1,550 nm light, successfully focused light down to a 60 μm spot. This corresponds to a numerical aperture (NA) of ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
... the detector. Transverse aberration plots give an idea of image blur at the detector. The vertical axis of each plot gives the magnitude of the blur. The horizontal axis represents the beam diameter for any field angle and is effectively normalized so dimensions are not given. Thus the transverse ab ...
... the detector. Transverse aberration plots give an idea of image blur at the detector. The vertical axis of each plot gives the magnitude of the blur. The horizontal axis represents the beam diameter for any field angle and is effectively normalized so dimensions are not given. Thus the transverse ab ...
Electron
... • 1839, George Airy: there should be a natural limit to the optical microscopes. • 1872, both Ernst Abbe and Hermann von Helmholtz: Light is limited by the size of the wavelength. Resolution of the eyes 0.1-0.2 mm Resolution of a good VLM ~300 nm ...
... • 1839, George Airy: there should be a natural limit to the optical microscopes. • 1872, both Ernst Abbe and Hermann von Helmholtz: Light is limited by the size of the wavelength. Resolution of the eyes 0.1-0.2 mm Resolution of a good VLM ~300 nm ...
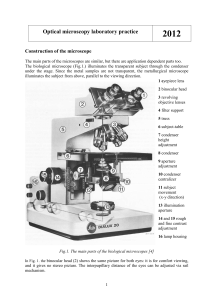
Optical microscopy laboratory practice 2012
... The depth of focus of an optical microscope is the range of image plane position at which the image may be viewed without appearing out of focus for an object or specimen The bigger the overall magnification, the lower the depth of focus. ...
... The depth of focus of an optical microscope is the range of image plane position at which the image may be viewed without appearing out of focus for an object or specimen The bigger the overall magnification, the lower the depth of focus. ...
Certified Optical Network Engineer Core Networks
... today. You’ll learn about the clever things that can be done with light to deliver higher data rates over longer distances at lower cost than ever before. You’ll also appreciate the supporting role played by recent advances in electronic communications technology in overcoming some of the impairment ...
... today. You’ll learn about the clever things that can be done with light to deliver higher data rates over longer distances at lower cost than ever before. You’ll also appreciate the supporting role played by recent advances in electronic communications technology in overcoming some of the impairment ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.