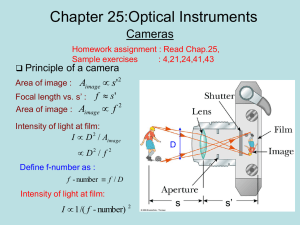
Stops, Pupils, Field Optics and Cameras
... The optical system above transfers an upright, one-to-one image Either lens 1, or lens 2 may be thought of as the aperture stop, since both define the same cone as seen from the image point A Lens 2 defines the field stop One can show that the diameter of the entrance window is 1/3 the diameter of ...
... The optical system above transfers an upright, one-to-one image Either lens 1, or lens 2 may be thought of as the aperture stop, since both define the same cone as seen from the image point A Lens 2 defines the field stop One can show that the diameter of the entrance window is 1/3 the diameter of ...
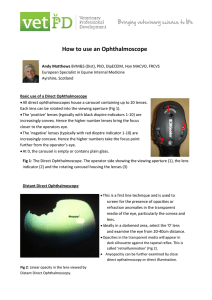
How to use an Ophthalmoscope
... instrument held 3-5cm from the horse’s eye, at 0 the optic disc can typically be brought into sharp focus (Fig 3). This will vary with the refraction of the operator’s eye and with the viewing distance selected. The fundic image is upright and magnified (Fig 2). With the pupil fully dilated (using ...
... instrument held 3-5cm from the horse’s eye, at 0 the optic disc can typically be brought into sharp focus (Fig 3). This will vary with the refraction of the operator’s eye and with the viewing distance selected. The fundic image is upright and magnified (Fig 2). With the pupil fully dilated (using ...
High-resolution retinal microscopy using MEMS
... Figure 2: Measured wavefront for Zernike modes 4-21, as obtained by closed-loop control with the µDM in the adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscope. Subsequently a reticle grid was positioned at the retinal plane of the model eye, and the eye was adjusted to introduce aberration through defocu ...
... Figure 2: Measured wavefront for Zernike modes 4-21, as obtained by closed-loop control with the µDM in the adaptive optics scanning laser ophthalmoscope. Subsequently a reticle grid was positioned at the retinal plane of the model eye, and the eye was adjusted to introduce aberration through defocu ...
Thin Lenses - Saddleback College
... the image screen.) Compare the experimental focal length to the actual focal length. 3. Select a converging lens and set up each of the three cases p>2f, f
... the image screen.) Compare the experimental focal length to the actual focal length. 3. Select a converging lens and set up each of the three cases p>2f, f
lens shape - CVI Laser Optics
... For imaging at unit magnification (s = s" = 2f), a similar analysis would show that a symmetric biconvex lens is the best shape. Not only is spherical aberration minimized, but coma, distortion, and lateral chromatic aberration exactly cancel each other out. These results are true regardless of mate ...
... For imaging at unit magnification (s = s" = 2f), a similar analysis would show that a symmetric biconvex lens is the best shape. Not only is spherical aberration minimized, but coma, distortion, and lateral chromatic aberration exactly cancel each other out. These results are true regardless of mate ...
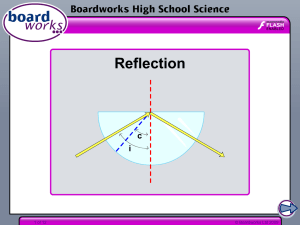
2 Reflection
... IO : reflected ray NI : normal at the point of incidence i : angle of incidence r : angle of reflection SI and NI define the plane of incidence ...
... IO : reflected ray NI : normal at the point of incidence i : angle of incidence r : angle of reflection SI and NI define the plane of incidence ...
Class10 CBSE Test paper Chapter: Reflection and Refraction of Light -...
... Solution: Light rays that are parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror converge at a specific point on its principal axis after reflecting from the mirror. This point is known as the principal focus of the concave mirror Question 2: The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm. W ...
... Solution: Light rays that are parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror converge at a specific point on its principal axis after reflecting from the mirror. This point is known as the principal focus of the concave mirror Question 2: The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm. W ...
Microscopy Basics
... combination of lenses of different refractive index (Achromat – 2 different wavelength focused to 1 point, Apochromat – 3 different wavelength focused to 1 point Flat-Field correction ensures planarity of the image – important for its projection on a chip of a camera ...
... combination of lenses of different refractive index (Achromat – 2 different wavelength focused to 1 point, Apochromat – 3 different wavelength focused to 1 point Flat-Field correction ensures planarity of the image – important for its projection on a chip of a camera ...
Wollaston and Nomarski Prisms
... prisms are composed of two precisely ground and polished wedge-shaped slabs produced from high-grade optical quartz, a uniaxial birefringent crystal. Two quartz wedges having perpendicular orientations of the optical axis must be fabricated to produce a single Wollaston (or Nomarski) prism. The wedg ...
... prisms are composed of two precisely ground and polished wedge-shaped slabs produced from high-grade optical quartz, a uniaxial birefringent crystal. Two quartz wedges having perpendicular orientations of the optical axis must be fabricated to produce a single Wollaston (or Nomarski) prism. The wedg ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.