Computed Tomography of the Sacral Plexus and Sciatic Nerve in
... Axial sections through the inferior part of the greaten sciatic fonamen include the sacrospinous ligament but not the pinform muscle. This structure appears as a thin line running in an oblique direction from the anterior lateral borden of the sacrum to the ischial spine and is a reliable landmark f ...
... Axial sections through the inferior part of the greaten sciatic fonamen include the sacrospinous ligament but not the pinform muscle. This structure appears as a thin line running in an oblique direction from the anterior lateral borden of the sacrum to the ischial spine and is a reliable landmark f ...
Glossary of Osteopathic Terminology - AVT
... of the cervical vertebrae. 2. Those parts of the lateral arches of the cervical vertebrae that contain a superior and inferior articular facet. articulation: 1. The place of union or junction between two or more bones of the skeleton. 2. The active or passive process of moving a joint through its pe ...
... of the cervical vertebrae. 2. Those parts of the lateral arches of the cervical vertebrae that contain a superior and inferior articular facet. articulation: 1. The place of union or junction between two or more bones of the skeleton. 2. The active or passive process of moving a joint through its pe ...
anatomic variations and references of the sphenopalatine foramen
... The medical literature reports an incidence of accessory foramens of < 2%. Padúa6 reports an incidence of accessory foramens of 2% in his study. Localization of the vidian nerve in relation to the sphenopalatine foramen in 90% of the cases was found posterosuperior to it, similar to what is reported ...
... The medical literature reports an incidence of accessory foramens of < 2%. Padúa6 reports an incidence of accessory foramens of 2% in his study. Localization of the vidian nerve in relation to the sphenopalatine foramen in 90% of the cases was found posterosuperior to it, similar to what is reported ...
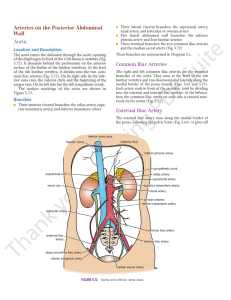
Common Iliac Arteries External Iliac Artery EMBRYOLOGIC NOTES
... Common Iliac Arteries The right and left common iliac arteries are the terminal branches of the aorta. They arise at the level of the 4th lumbar vertebra and run downward and laterally along the medial border of the psoas muscle (Figs. 5.63 and 5.72). Each artery ends in front of the sacroiliac join ...
... Common Iliac Arteries The right and left common iliac arteries are the terminal branches of the aorta. They arise at the level of the 4th lumbar vertebra and run downward and laterally along the medial border of the psoas muscle (Figs. 5.63 and 5.72). Each artery ends in front of the sacroiliac join ...
Abdomen - Kalam Books
... which contains acid phosphatase, hyaluronidase, neuraminidase and proteases necessary for fertilisation ♦ In the centre of the neck, is a well - formed centriole, corresponding to the proximal centriole of the spermatid from which it differentiated ♦ The axonemal complex is derived from the distal c ...
... which contains acid phosphatase, hyaluronidase, neuraminidase and proteases necessary for fertilisation ♦ In the centre of the neck, is a well - formed centriole, corresponding to the proximal centriole of the spermatid from which it differentiated ♦ The axonemal complex is derived from the distal c ...
VESSELS OF FORE ARM AND HAND
... It arises from the brachial artery It is continuation of the brachial artery It is one of the terminal branch of the brachial artery It arise from the brachial artery at the level of the neck of the radius It travels along the radial side of the forearm It winds backward around the carpu ...
... It arises from the brachial artery It is continuation of the brachial artery It is one of the terminal branch of the brachial artery It arise from the brachial artery at the level of the neck of the radius It travels along the radial side of the forearm It winds backward around the carpu ...
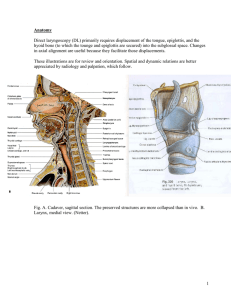
1 Anatomy Direct laryngoscopy (DL) primarily requires displacement
... Fig. Lifting force in DL can be directly opposed by SHL tension.. The hyoid bone is visible at the juncture of the chin and the neck. The greater horns of the hyoid (Strut) rest against the posterior pharyngeal wall. For DL the tongue and epiglottis, both secured to the hyoid, must be lifted above t ...
... Fig. Lifting force in DL can be directly opposed by SHL tension.. The hyoid bone is visible at the juncture of the chin and the neck. The greater horns of the hyoid (Strut) rest against the posterior pharyngeal wall. For DL the tongue and epiglottis, both secured to the hyoid, must be lifted above t ...
topography of the anterior lateral wallof the abdomen
... 6. The operation which completely removes the cause of the disease (pathological area) is 1) The radical 2) The palliative 3) The simultaneous 4) The urgent 7. The operation which is aimed at either making the condition of the patient better or to eliminate any life-threatening symptoms is 1) The ra ...
... 6. The operation which completely removes the cause of the disease (pathological area) is 1) The radical 2) The palliative 3) The simultaneous 4) The urgent 7. The operation which is aimed at either making the condition of the patient better or to eliminate any life-threatening symptoms is 1) The ra ...
Bilateral alar thoracic artery
... During a routine dissection a superficial artery was observed coursing subcutaneously at the anterior border of the axillary base towards the thoracic wall and bilaterally at the lower border of the pectoralis major muscle. On the right side it originated from the 3rd part of the axillary artery but ...
... During a routine dissection a superficial artery was observed coursing subcutaneously at the anterior border of the axillary base towards the thoracic wall and bilaterally at the lower border of the pectoralis major muscle. On the right side it originated from the 3rd part of the axillary artery but ...
The Glossary of Osteopathic Terminology
... arrangement of the articular portions of the cervical vertebrae. 2. Those parts of the lateral arches of the cervical vertebrae that contain a superior and inferior articular facet. ...
... arrangement of the articular portions of the cervical vertebrae. 2. Those parts of the lateral arches of the cervical vertebrae that contain a superior and inferior articular facet. ...
Computed Tomography of the Sacral Plexus and Sciatic Nerve in
... be seen in all cases in which the piriform muscle and sacrospinous ligament were visualized. The greater sciatic foramen is identified on axial images of the pelvis just inferior to the sacroiliac articulation . The posterior border is formed by the lateral margin of the sacrum; the anterior border ...
... be seen in all cases in which the piriform muscle and sacrospinous ligament were visualized. The greater sciatic foramen is identified on axial images of the pelvis just inferior to the sacroiliac articulation . The posterior border is formed by the lateral margin of the sacrum; the anterior border ...
THEME 1
... The program on human anatomy for the higher medical educational establishments of Ukraine III-IV of levels of accreditation is made for a speciality 7.110101 - “General medicine” directions of preparation 1101 «Medicine» according to Educational-Qualifying Characteristics (EQC) and Educational-Profe ...
... The program on human anatomy for the higher medical educational establishments of Ukraine III-IV of levels of accreditation is made for a speciality 7.110101 - “General medicine” directions of preparation 1101 «Medicine» according to Educational-Qualifying Characteristics (EQC) and Educational-Profe ...
2 m – 25. Aorta. External carotid artery
... into the right common carotid and right subclavian arteries. These arteries supply the right side of the head and neck, and the right upper limb. • Left common carotid artery: Supplies the left side of the head and neck. Left subclavian artery: Supplies the left upper limb. The right common carotid ...
... into the right common carotid and right subclavian arteries. These arteries supply the right side of the head and neck, and the right upper limb. • Left common carotid artery: Supplies the left side of the head and neck. Left subclavian artery: Supplies the left upper limb. The right common carotid ...
Chapter 1 - Mpilo Central Hospital
... that occasionally the strap muscles must be cut to facilitate thyroid surgery. They should be cut across the upper third of their length to avoid sacrificing their nerve supply. The Posterior Cervical Triangle The posterior cervical triangle is sometimes considered to be two triangles, occipital and ...
... that occasionally the strap muscles must be cut to facilitate thyroid surgery. They should be cut across the upper third of their length to avoid sacrificing their nerve supply. The Posterior Cervical Triangle The posterior cervical triangle is sometimes considered to be two triangles, occipital and ...
Word - Geometrical Anatomy
... be as much as 3 to 4 millimeters less at the end of range. The gap between the two vertebrae can be computed from x-ray images and it is probably between 2 and 3.5 millimeters in neutral position ( from Grants's Atlas[Fig. 4.16] and Grays Anatomy [Fig. 6.96 ]), therefore it is hard to see how 3 to 4 ...
... be as much as 3 to 4 millimeters less at the end of range. The gap between the two vertebrae can be computed from x-ray images and it is probably between 2 and 3.5 millimeters in neutral position ( from Grants's Atlas[Fig. 4.16] and Grays Anatomy [Fig. 6.96 ]), therefore it is hard to see how 3 to 4 ...
The Larynx
... The external branch (external laryngeal nerve) descends along the lateral wall of the pharynx to supply the inferior constrictor of the pharynx and ends by supplying the cricothyroid muscle; ...
... The external branch (external laryngeal nerve) descends along the lateral wall of the pharynx to supply the inferior constrictor of the pharynx and ends by supplying the cricothyroid muscle; ...
slide_3
... to the angle of the thyroid cartilage • Projects posterosuperiorly from its attachment to the thyroid cartilage. • The attachment is via the thyro-epiglottic ligament in the midline between the laryngeal prominence and the inferior thyroid notch • The upper margin of the epiglottis is behind t ...
... to the angle of the thyroid cartilage • Projects posterosuperiorly from its attachment to the thyroid cartilage. • The attachment is via the thyro-epiglottic ligament in the midline between the laryngeal prominence and the inferior thyroid notch • The upper margin of the epiglottis is behind t ...
Ahmed Refaat_Chapter1
... These meniscofemoral ligaments often constitute the sole attachments of the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus. The tendon of the popliteus muscle intervens between the lateral meniscus and the fibular collateral ligament (Figure 7). The more medial part of the tendon is inserted into the latera ...
... These meniscofemoral ligaments often constitute the sole attachments of the posterior horn of the lateral meniscus. The tendon of the popliteus muscle intervens between the lateral meniscus and the fibular collateral ligament (Figure 7). The more medial part of the tendon is inserted into the latera ...
Applied anatomy of the knee - A System of Orthopaedic Medicine
... of the tibial condyles are projected anteriorly, they coincide with the articular surface of the patella which corresponds to, and is almost congruent with, the anterior surfaces of the femoral condyles. If the intercondylar eminence of the tibia is projected anteriorly, its plane is continuous with ...
... of the tibial condyles are projected anteriorly, they coincide with the articular surface of the patella which corresponds to, and is almost congruent with, the anterior surfaces of the femoral condyles. If the intercondylar eminence of the tibia is projected anteriorly, its plane is continuous with ...
anatomy - Focus OKC
... compact or cancellous tissue. Nerves are distributed freely to the periosteum, and they accompany the artery into the interior of the bone; they are most numerous in the articular extremities of long bones, in the vertebrae and in large flat bones. The epiphysis is a plate of cartilage, developed fr ...
... compact or cancellous tissue. Nerves are distributed freely to the periosteum, and they accompany the artery into the interior of the bone; they are most numerous in the articular extremities of long bones, in the vertebrae and in large flat bones. The epiphysis is a plate of cartilage, developed fr ...
No. 11
... The kidneys, however, as the main excretory organs, are critically important in maintaining the balance of substances required for internal constancy. The kidneys eliminate from the body a variety of metabolic products, such as urea, uric acid, and creatinine. Further the kidneys conserve or excrete ...
... The kidneys, however, as the main excretory organs, are critically important in maintaining the balance of substances required for internal constancy. The kidneys eliminate from the body a variety of metabolic products, such as urea, uric acid, and creatinine. Further the kidneys conserve or excrete ...
Clinical Anatomy for Your Pocket
... Significance Bears 2 facets that articulate with vertebra of same number and the vertebra superior to it Joins head with body of rib • Articulates with transverse process of vertebra of same number • Located at junction of neck and body ...
... Significance Bears 2 facets that articulate with vertebra of same number and the vertebra superior to it Joins head with body of rib • Articulates with transverse process of vertebra of same number • Located at junction of neck and body ...
Vascular anatomy of the head and neck region, pictorial
... the X c.n., vagus nerve. It is so called "recurren" because it descends into the thorax before rising up between trachea and esophagus. The right nerve loops around the right subclavian artery, while he left has a longer course as it hooks the aortic arch Fig.3. The recurrent (inferior) laryngeal ne ...
... the X c.n., vagus nerve. It is so called "recurren" because it descends into the thorax before rising up between trachea and esophagus. The right nerve loops around the right subclavian artery, while he left has a longer course as it hooks the aortic arch Fig.3. The recurrent (inferior) laryngeal ne ...
Anterior
... Compression of the third part of this artery against the humerus may be necessary when profuse bleeding occurs ...
... Compression of the third part of this artery against the humerus may be necessary when profuse bleeding occurs ...
Lumbar spinal nerves
... fifth lumbar nerves merge into a single lumbosacral trunk, that descends to the lesser pelvis cavity and joins the sacral nerves. The lowest portion of the sacral plexus formed of the fifth sacral nerves and the coccygeal nerve is the coccygeal plexus. The sacral plexus appears as a thick triangular ...
... fifth lumbar nerves merge into a single lumbosacral trunk, that descends to the lesser pelvis cavity and joins the sacral nerves. The lowest portion of the sacral plexus formed of the fifth sacral nerves and the coccygeal nerve is the coccygeal plexus. The sacral plexus appears as a thick triangular ...
Vertebra

In the vertebrate spinal column, each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, the proportions of which vary according to the segment of the backbone and the species of vertebrate animal.The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the large part is the body, and the central part is the centrum. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles, two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava. There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conducts for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebra and the vertebral arch form the vertebral foramen, the larger, central opening that accommodates the spinal canal, which encloses and protects the spinal cord.Vertebrae articulate with each other to give strength and flexibility to the spinal column, and the shape at their back and front aspects determines the range of movement. Structurally, vertebrae are essentially alike across the vertebrate species, with the greatest difference seen between an aquatic animal and other vertebrate animals. As such, vertebrates take their name from the vertebrae that compose the vertebral column.