Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole`s Human Anatomy and Physiology
... 10. Teeth occupy cavities in this arch. 11. The palatine bones are L shaped. 12. The palatine bones are located behind the maxillae. 13. The horizontal portions of the palatine bones form the posterior section of the hard palate and the floor of the nasal cavity. 14. The perpendicular portions of th ...
... 10. Teeth occupy cavities in this arch. 11. The palatine bones are L shaped. 12. The palatine bones are located behind the maxillae. 13. The horizontal portions of the palatine bones form the posterior section of the hard palate and the floor of the nasal cavity. 14. The perpendicular portions of th ...
scapula - FIT College
... • Transverse processes of thoracic or cervical vertebrae and to ribs superior to ...
... • Transverse processes of thoracic or cervical vertebrae and to ribs superior to ...
Protection Of The Spinal Cord
... External Anatomy of Spinal Cord • Flattened cylinder • 16-18 Inches long & 3/4 inch diameter • In adult ends at L2 • In newborn ends at L4 • Growth of cord stops at age 5 • Cervical enlargement – upper limbs ...
... External Anatomy of Spinal Cord • Flattened cylinder • 16-18 Inches long & 3/4 inch diameter • In adult ends at L2 • In newborn ends at L4 • Growth of cord stops at age 5 • Cervical enlargement – upper limbs ...
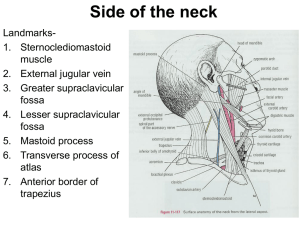
Side of the neck
... lymph nodes. Lipoma, cystic hygroma or lymphangioma, pharyngeal pouch or a cervical rib. Supraclavicular lymph nodes are commonly enlarged in tuberculosis, Hodgkin’s disease and in malignant growth of the breast, arm or chest. 2. Left supraclavicular nodes or Virchow’s or Scalene nodes are mostly in ...
... lymph nodes. Lipoma, cystic hygroma or lymphangioma, pharyngeal pouch or a cervical rib. Supraclavicular lymph nodes are commonly enlarged in tuberculosis, Hodgkin’s disease and in malignant growth of the breast, arm or chest. 2. Left supraclavicular nodes or Virchow’s or Scalene nodes are mostly in ...
5. Cat Superficial Abdomen
... three layers gives the abdominal wall its strength. Below the transverses abdominis lies the thin glistening membrane, the pariental peritoneum which lines the abdominal cavity. Rectus Abdominis- In the mid-ventral area, on either side of the line alba, lie two parallel muscles. They extend from the ...
... three layers gives the abdominal wall its strength. Below the transverses abdominis lies the thin glistening membrane, the pariental peritoneum which lines the abdominal cavity. Rectus Abdominis- In the mid-ventral area, on either side of the line alba, lie two parallel muscles. They extend from the ...
Chapter 3
... II. SPINAL NERVES • Distribution – plexuses • network of interlacing, adjacent axons • do not directly connect to structures they innervate • 5 plexuses – cervical: skin/muscles of head/neck/upper chest – brachial: shoulders/upper limbs – lumbar: lower limbs/abdominal wall – sacral: buttocks/perine ...
... II. SPINAL NERVES • Distribution – plexuses • network of interlacing, adjacent axons • do not directly connect to structures they innervate • 5 plexuses – cervical: skin/muscles of head/neck/upper chest – brachial: shoulders/upper limbs – lumbar: lower limbs/abdominal wall – sacral: buttocks/perine ...
Mitra Yari MD HEAD AND NECK BLOCK
... For diagnostic block 1-1.5 ml LA be used for distinguish neuralgia from myofascial pain. Complication is bleeding LON is in two third the distance between occipital protuberance and mastoid process. ...
... For diagnostic block 1-1.5 ml LA be used for distinguish neuralgia from myofascial pain. Complication is bleeding LON is in two third the distance between occipital protuberance and mastoid process. ...
Medial surface Central sulcus on axial imaging cs cs pM pocs
... area) (acoustic portion of Cr. N. VIII) cavities and chemoreceptors in the taste buds on Figure 5-7 Right internal auditory canal (porus acusticus) & nerves the anterior 2/3 of * NI = nervus intermedius the tongue 3. acoustic portion of the VIII nerve (mnemonic: “Coke down” for cochlear portion) 4. ...
... area) (acoustic portion of Cr. N. VIII) cavities and chemoreceptors in the taste buds on Figure 5-7 Right internal auditory canal (porus acusticus) & nerves the anterior 2/3 of * NI = nervus intermedius the tongue 3. acoustic portion of the VIII nerve (mnemonic: “Coke down” for cochlear portion) 4. ...
BDS Ist YEAR EXAMINATION 2008-09
... During development the midgut undergoes rotation through: a) ...
... During development the midgut undergoes rotation through: a) ...
Anatomy nose bones external: nasal processes of frontal bones
... Hyoid bone above, firmly attached by 3 thyrohyoid ligaments and thyrohyoid membrane Three unpaired midline cartilages Thyroid cartilage Two laminae, fused in midline Superior border attached to hyoid Posterior borders attached to stylopharyngeus and palatopharyngeus External surface attached to ster ...
... Hyoid bone above, firmly attached by 3 thyrohyoid ligaments and thyrohyoid membrane Three unpaired midline cartilages Thyroid cartilage Two laminae, fused in midline Superior border attached to hyoid Posterior borders attached to stylopharyngeus and palatopharyngeus External surface attached to ster ...
Anatomy and Physiology - futurefittraining.co.uk
... located towards the centre or point of attachment. The proximal end of a bone is the top of the bone. See distal see bone marrow movement of a body part backwards on a plane parallel to the ground rotating about the longitudinal axis, as with the twisting of the spine a triangular bone formed from f ...
... located towards the centre or point of attachment. The proximal end of a bone is the top of the bone. See distal see bone marrow movement of a body part backwards on a plane parallel to the ground rotating about the longitudinal axis, as with the twisting of the spine a triangular bone formed from f ...
spinal nerve
... • The spinal cord extends inferiorly from the medulla oblongata to the lumbar region • Along its length there are two notably thicker regions: The Cervical and Lumbosacral enlargements – These are sites where the nerves serving the limbs emerge • Conus medullaris – the end of the spinal cord in the ...
... • The spinal cord extends inferiorly from the medulla oblongata to the lumbar region • Along its length there are two notably thicker regions: The Cervical and Lumbosacral enlargements – These are sites where the nerves serving the limbs emerge • Conus medullaris – the end of the spinal cord in the ...
Anatomy in Practice: Lumbar Zygapophysial Joint Palpation
... low back pain. Some approaches to the assessment of the lumbar spine therefore advocate that palpation of the zygapophysial joints is useful in determining the side and level of their involvement. This commentary was undertaken to describe the clinical anatomy of the lumbar spine as it relates to pa ...
... low back pain. Some approaches to the assessment of the lumbar spine therefore advocate that palpation of the zygapophysial joints is useful in determining the side and level of their involvement. This commentary was undertaken to describe the clinical anatomy of the lumbar spine as it relates to pa ...
Coding Companion for Neurosurgery/Neurology
... cancer screening that uses a static photographic image of the ectocervix, taken with a specially designed camera for evaluation purposes and to provide photo documentation. The physician inserts a speculum for visualization of the cervix. A Pap smear is obtained and the cervix is cleaned using an ac ...
... cancer screening that uses a static photographic image of the ectocervix, taken with a specially designed camera for evaluation purposes and to provide photo documentation. The physician inserts a speculum for visualization of the cervix. A Pap smear is obtained and the cervix is cleaned using an ac ...
VASCULARIZATION OF THE HEAD AND NECK
... gland, facial nerve, auricle, scalp, temporal bone structures Superficial Temporal: smaller of two teminal branches; begins deep to parotid, posterior to neck of mandible and passes anterior to ear -- gives off: transverse facial which supplies parotid gland/duct, masseter muscle, and skin of the fa ...
... gland, facial nerve, auricle, scalp, temporal bone structures Superficial Temporal: smaller of two teminal branches; begins deep to parotid, posterior to neck of mandible and passes anterior to ear -- gives off: transverse facial which supplies parotid gland/duct, masseter muscle, and skin of the fa ...
Slide 1 - mcstmf
... intercostal nerves. • The visceral pleura covering the lungs is sensitive to stretch but is insensitive to common sensations such as pain and ...
... intercostal nerves. • The visceral pleura covering the lungs is sensitive to stretch but is insensitive to common sensations such as pain and ...
Hip Introduction Bones, Ligaments and Other Structures
... • The Ilium is the largest aspect of the pelvic girdle and is the most superior of the bones that make up the pelvic girdle. • The Ilium is broken down into two portions. – The Body: The lower part of the Ilium which joins with both the pubis and ischium to form the acetabulum. – The “Ala”: Latin fo ...
... • The Ilium is the largest aspect of the pelvic girdle and is the most superior of the bones that make up the pelvic girdle. • The Ilium is broken down into two portions. – The Body: The lower part of the Ilium which joins with both the pubis and ischium to form the acetabulum. – The “Ala”: Latin fo ...
152
... • surfaces are kidney shaped- flat/smooth • built for wt bearing • wider transversely & deeper in front • upper/lower borders of bodies give attachments to anterior/posterior longitudinal ligaments • attachment of crura of diaphragm (L1-L3) • superior= T/S • inferior= sacrum/ SIJ • pedicles do not o ...
... • surfaces are kidney shaped- flat/smooth • built for wt bearing • wider transversely & deeper in front • upper/lower borders of bodies give attachments to anterior/posterior longitudinal ligaments • attachment of crura of diaphragm (L1-L3) • superior= T/S • inferior= sacrum/ SIJ • pedicles do not o ...
Mechanism of change in the orientation of the articular process of
... above downwards, on paper (Fig. 1). This helped to indicate the changing pattern of orientation of the articular surfaces, at a glance, within a column. The inferior articular surfaces of the upper vertebrae were not drawn as they reciprocate the superior articular surfaces of the vertebrae below. I ...
... above downwards, on paper (Fig. 1). This helped to indicate the changing pattern of orientation of the articular surfaces, at a glance, within a column. The inferior articular surfaces of the upper vertebrae were not drawn as they reciprocate the superior articular surfaces of the vertebrae below. I ...
superiorly with the parietal bone by the squamosal suture anteriorly
... The styloid process a base, which is embedded between the petrous and tympanic part the free portion which is directed downward and forward and medially for a varying distance ...
... The styloid process a base, which is embedded between the petrous and tympanic part the free portion which is directed downward and forward and medially for a varying distance ...
1 Spine Joints and Joint Surfaces ATLAS • Superior articular facet
... l Joint injury: Including such conditions referred to as osteoarthrosis, instability and the after effects of sprains and strains, are impairments (dysfunctions) rather than diseases. l Impairments are manifest as either increases or decreases of motion from the expected normal or by the presence ...
... l Joint injury: Including such conditions referred to as osteoarthrosis, instability and the after effects of sprains and strains, are impairments (dysfunctions) rather than diseases. l Impairments are manifest as either increases or decreases of motion from the expected normal or by the presence ...
ULNA BONE:
... Has smooth ,convex articular surface on lateral part for articulation with ulnar notch of radius. Inferior surface is separated from carpal bones by articular disc of inferior radioulnar joint, attached by its apex to the area between articular surface & styloid process. Anterior & posterior m ...
... Has smooth ,convex articular surface on lateral part for articulation with ulnar notch of radius. Inferior surface is separated from carpal bones by articular disc of inferior radioulnar joint, attached by its apex to the area between articular surface & styloid process. Anterior & posterior m ...
D23-1 UNIT 23. DISSECTION: PHARYNX AND LARYNX
... 3. Step 2 (D23-2) Use a mallet, chisel and saw to make an opening through the floor of the cranial cavity into the retropharyngeal space. Using your chisel and hammer, chisel an opening approximately 1/2 inch in front of the foramen magnum; continue ...
... 3. Step 2 (D23-2) Use a mallet, chisel and saw to make an opening through the floor of the cranial cavity into the retropharyngeal space. Using your chisel and hammer, chisel an opening approximately 1/2 inch in front of the foramen magnum; continue ...
12_skeleton_upper_appendicular-29sept2016
... Scapula [“shovel”]: lies over 2nd to 7th ribs. 245 borders superior, axillary, vertebral (or medial and lateral) angles superior and inferior glenoid fossa [“socket-like”] articulates with head of humerus supra glenoid tubercle [“above” and “bump little”] anchor for biceps long head coracoid process ...
... Scapula [“shovel”]: lies over 2nd to 7th ribs. 245 borders superior, axillary, vertebral (or medial and lateral) angles superior and inferior glenoid fossa [“socket-like”] articulates with head of humerus supra glenoid tubercle [“above” and “bump little”] anchor for biceps long head coracoid process ...
Vertebra

In the vertebrate spinal column, each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, the proportions of which vary according to the segment of the backbone and the species of vertebrate animal.The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the large part is the body, and the central part is the centrum. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles, two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava. There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conducts for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebra and the vertebral arch form the vertebral foramen, the larger, central opening that accommodates the spinal canal, which encloses and protects the spinal cord.Vertebrae articulate with each other to give strength and flexibility to the spinal column, and the shape at their back and front aspects determines the range of movement. Structurally, vertebrae are essentially alike across the vertebrate species, with the greatest difference seen between an aquatic animal and other vertebrate animals. As such, vertebrates take their name from the vertebrae that compose the vertebral column.