Differential Diagnosis of the Cervical Spine
... The inferior surface of the R atlas is moving downwards and backwards The inferior surface of the L atlas is moving downwards and forwards ...
... The inferior surface of the R atlas is moving downwards and backwards The inferior surface of the L atlas is moving downwards and forwards ...
35-rectum_&_urinary_..
... It bends downwards and backwards at its junction with the anal canal. It is pulled forwards by the puborectalis part of the levator ani. The anal canal moves in a posterior direction. ...
... It bends downwards and backwards at its junction with the anal canal. It is pulled forwards by the puborectalis part of the levator ani. The anal canal moves in a posterior direction. ...
18 braim blood sup 124 Presentation
... groove of pons. Ends at upper border of pons by dividing into two posterior cerebral arteries. Branches; oPontine . oLabyrinthine . oAnterior inferior cerebellar. oSuperior cerebellar . oPosterior cerebral . ...
... groove of pons. Ends at upper border of pons by dividing into two posterior cerebral arteries. Branches; oPontine . oLabyrinthine . oAnterior inferior cerebellar. oSuperior cerebellar . oPosterior cerebral . ...
Resection of Bilateral C1 Neurofibromas Using a Unilateral
... junction with limited retraction. The first variation was the far lateral approach that included inferolateral bone removal of the foramen magnum towards the condylar fossa and partial removal of the C1 arch [7]. This approach was then further modified to include condylar resection for tumors when m ...
... junction with limited retraction. The first variation was the far lateral approach that included inferolateral bone removal of the foramen magnum towards the condylar fossa and partial removal of the C1 arch [7]. This approach was then further modified to include condylar resection for tumors when m ...
Frontal Bone
... hemimandible. The mandibular angle is formed by the intersection of the inferior rim of the body and the posterior rim of the ascending ramus. The superior ramus bifurcates into an anterior coronoid process and a posterior condylar process. The concavity between the 2 processes is called the mandibu ...
... hemimandible. The mandibular angle is formed by the intersection of the inferior rim of the body and the posterior rim of the ascending ramus. The superior ramus bifurcates into an anterior coronoid process and a posterior condylar process. The concavity between the 2 processes is called the mandibu ...
Considered a bone of both shoulder girdle and shoulder joint. The
... shoulder level by allowing the shoulderblade to move up to increase the range of motion (ROM). The clavicle helps increase the ROM because it acts as a strut maintaining the upper limb away from the thorax, which allows the greater ROM to occur. ...
... shoulder level by allowing the shoulderblade to move up to increase the range of motion (ROM). The clavicle helps increase the ROM because it acts as a strut maintaining the upper limb away from the thorax, which allows the greater ROM to occur. ...
File
... - there are eight paired bones (bilateral) b. temporal - below parietal on the side of the skull - lambdoid suture - separates occipital bone from parietal & temporal bones0- temporal bone (2) mandibular fossa - articulates with the head of the condylar process (3) articular tubercle - at the anteri ...
... - there are eight paired bones (bilateral) b. temporal - below parietal on the side of the skull - lambdoid suture - separates occipital bone from parietal & temporal bones0- temporal bone (2) mandibular fossa - articulates with the head of the condylar process (3) articular tubercle - at the anteri ...
FEMUR 2:
... CLOSED - The skin in the fracture area is not broken, and the break is not exposed to the outside. OPEN (COMPOUND) - The skin over the fracture is broken, exposing the broken bone. PATHOLOGICAL - The bone has been weakened or destroyed by disease so that it breaks easily. STRESS - There is a hairlin ...
... CLOSED - The skin in the fracture area is not broken, and the break is not exposed to the outside. OPEN (COMPOUND) - The skin over the fracture is broken, exposing the broken bone. PATHOLOGICAL - The bone has been weakened or destroyed by disease so that it breaks easily. STRESS - There is a hairlin ...
CEREBRAL VASCULAR SUPPLY
... Largest branches of internal carotid arteries. Run between temporal and frontal lobes. To most of lateral surfaces of cerebrum. Give off striate arteries: To internal capsule and adjacent structures. Stroke: Contralateral upper motor-neuron paralysis of face and UE/LE as well as sensory ...
... Largest branches of internal carotid arteries. Run between temporal and frontal lobes. To most of lateral surfaces of cerebrum. Give off striate arteries: To internal capsule and adjacent structures. Stroke: Contralateral upper motor-neuron paralysis of face and UE/LE as well as sensory ...
Lab 4 part 2 Shoulder 3
... Insertion: scapula (medial border) Innervation: long thoracic nerve Function: • Abduction of the scapula • Medial rotation of scapula • Keeps medial border and inferior angle of scapula opposed to thoracic wall ...
... Insertion: scapula (medial border) Innervation: long thoracic nerve Function: • Abduction of the scapula • Medial rotation of scapula • Keeps medial border and inferior angle of scapula opposed to thoracic wall ...
Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. 03.January.2014 Friday
... the only bony attachment between the trunk and the upper limb palpable along its entire length S-shaped contour forward-facing convex part medial forward-facing concave part lateral ...
... the only bony attachment between the trunk and the upper limb palpable along its entire length S-shaped contour forward-facing convex part medial forward-facing concave part lateral ...
Physiology Ch 5
... - disklike; bears weight arch - arch extending from the body foramen - spinal cord passes through transverse processes - lateral projections from arch spinous process - projection from posterior part of arch articular processes - allow vertebra to form joints with adjacent vertebrae cervical vertebr ...
... - disklike; bears weight arch - arch extending from the body foramen - spinal cord passes through transverse processes - lateral projections from arch spinous process - projection from posterior part of arch articular processes - allow vertebra to form joints with adjacent vertebrae cervical vertebr ...
Sacrum and pelvis
... In this position: The anterior surface of the Sacrum is directed forward and downward while the pelvic surface of symphysis pubis faces upward and ...
... In this position: The anterior surface of the Sacrum is directed forward and downward while the pelvic surface of symphysis pubis faces upward and ...
Skull and Face - Faculty of Science, Mahidol University
... – supplies all except lateral rectus and superior oblique • Trochlear Nerve (CN IV) – superior oblique • Abducens Nerve (CN VI) – lateral rectus ...
... – supplies all except lateral rectus and superior oblique • Trochlear Nerve (CN IV) – superior oblique • Abducens Nerve (CN VI) – lateral rectus ...
Ch 8 PPT - Rock Hill High School
... Sharp, pointed, posterior, and medial projection Can be felt through the skin of the back TRANSVERSE PROCESSES Sharp, pointed, and lateral projections 2 (left and right) • Note: These are markings that are common to most vertebrae ...
... Sharp, pointed, posterior, and medial projection Can be felt through the skin of the back TRANSVERSE PROCESSES Sharp, pointed, and lateral projections 2 (left and right) • Note: These are markings that are common to most vertebrae ...
Biology 210 Skeletal Tissues
... Sharp, pointed, posterior, and medial projection Can be felt through the skin of the back TRANSVERSE PROCESSES Sharp, pointed, and lateral projections 2 (left and right) • Note: These are markings that are common to most vertebrae ...
... Sharp, pointed, posterior, and medial projection Can be felt through the skin of the back TRANSVERSE PROCESSES Sharp, pointed, and lateral projections 2 (left and right) • Note: These are markings that are common to most vertebrae ...
Document
... 6. _____ The Alar ligaments provide stability at the base of the skull by preventing excessive rotation of the head. Which of the following describes the bones to which the alar ligaments are attached? A. Dens of axis (C2) to the occipital bone B. Body of the axis (C2) to the occipital bone C. Atlas ...
... 6. _____ The Alar ligaments provide stability at the base of the skull by preventing excessive rotation of the head. Which of the following describes the bones to which the alar ligaments are attached? A. Dens of axis (C2) to the occipital bone B. Body of the axis (C2) to the occipital bone C. Atlas ...
Summary of the structures, which have to be known by dentistry
... - name of the big toes in Latin (hallux). Sternum: - manubrium, body, angle (= level of 2nd rib!), xyphoid process. Costa: - true, false and floating ribs, - head, neck, tubercle of rib, costal groove (sulcus), - costal cartilages. ...
... - name of the big toes in Latin (hallux). Sternum: - manubrium, body, angle (= level of 2nd rib!), xyphoid process. Costa: - true, false and floating ribs, - head, neck, tubercle of rib, costal groove (sulcus), - costal cartilages. ...
MSK Answers - Mosaiced.org
... Infraspinatus – laterally rotates arm & stabilises shoulder, suprascapular nerve C5-C6 Palmar interossei – ulnar nerve, C8-T1 Pectoralis major – flexes, medially rotates & adducts humerus, lateral & medial pectoral nerves, C5-T1 Sartorius – flexes & laterally rotates hip & flexes knee, femor ...
... Infraspinatus – laterally rotates arm & stabilises shoulder, suprascapular nerve C5-C6 Palmar interossei – ulnar nerve, C8-T1 Pectoralis major – flexes, medially rotates & adducts humerus, lateral & medial pectoral nerves, C5-T1 Sartorius – flexes & laterally rotates hip & flexes knee, femor ...
Blue Boxes Back/Upper Limb – Jessica Magid 2011 1
... When examining a newborn, adjacent vertebrae should be palpated in sequence to be certain the vertebral arches are intact and continuous from the cervical to sacral regions o Spina bifida cystic is a severe type of spina bifida in which one or more vertebral arches fail to develop completely Ass ...
... When examining a newborn, adjacent vertebrae should be palpated in sequence to be certain the vertebral arches are intact and continuous from the cervical to sacral regions o Spina bifida cystic is a severe type of spina bifida in which one or more vertebral arches fail to develop completely Ass ...
Thyroid gland
... • At the middle of the back of the thyroid lobe, level with the first tracheal ring and above the inferior thyroid artery. ...
... • At the middle of the back of the thyroid lobe, level with the first tracheal ring and above the inferior thyroid artery. ...
가로막, 간, 쓸개
... inspiration, descends during inspiration; however, only its central part moves because its periphery, as the fixed origin of the muscle, attaches to the inferior margin of the thoracic cage and the superior lumbar vertebrae. - The muscular part of the diaphragm is situated peripherally with fibers t ...
... inspiration, descends during inspiration; however, only its central part moves because its periphery, as the fixed origin of the muscle, attaches to the inferior margin of the thoracic cage and the superior lumbar vertebrae. - The muscular part of the diaphragm is situated peripherally with fibers t ...
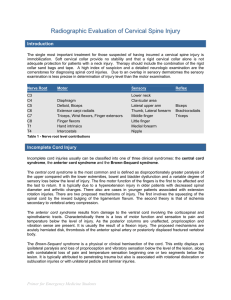
Radiographic Evaluation of Cervical Spine Injury
... Posterior Longitudinal Ligament - this narrow fibrous band located along the anterior surface of the spinal canal. it begins at C2 and extends to the sacrum, closely applied to the posterior margins of the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs. Annulus Fibrosus Capsular Ligaments - surrounds th ...
... Posterior Longitudinal Ligament - this narrow fibrous band located along the anterior surface of the spinal canal. it begins at C2 and extends to the sacrum, closely applied to the posterior margins of the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs. Annulus Fibrosus Capsular Ligaments - surrounds th ...
Module 2 - Stony Brook University School of Medicine
... 14. sphenoid sinus 15. frontal sinus 16. ethmoid air cells ...
... 14. sphenoid sinus 15. frontal sinus 16. ethmoid air cells ...
Vertebra

In the vertebrate spinal column, each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, the proportions of which vary according to the segment of the backbone and the species of vertebrate animal.The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the large part is the body, and the central part is the centrum. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles, two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava. There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conducts for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebra and the vertebral arch form the vertebral foramen, the larger, central opening that accommodates the spinal canal, which encloses and protects the spinal cord.Vertebrae articulate with each other to give strength and flexibility to the spinal column, and the shape at their back and front aspects determines the range of movement. Structurally, vertebrae are essentially alike across the vertebrate species, with the greatest difference seen between an aquatic animal and other vertebrate animals. As such, vertebrates take their name from the vertebrae that compose the vertebral column.