SUMMARY TERMS-Thoracic Cavity
... with posterior wall of the chest being much longer than the anterior wall; bounded by xiphoid process, costal arch from costal cartilages 7-10 and the 12th rib, and the 12th thoracic vertebra Vertebra, Body Pedicle Lamina Transverse process: Upper vertebrae-have deep, cup-shaped facets that permit r ...
... with posterior wall of the chest being much longer than the anterior wall; bounded by xiphoid process, costal arch from costal cartilages 7-10 and the 12th rib, and the 12th thoracic vertebra Vertebra, Body Pedicle Lamina Transverse process: Upper vertebrae-have deep, cup-shaped facets that permit r ...
Head - 山东大学医学院人体解剖学教研室
... and submandibular gland Loops around mandible (where it is palpable), at anterior border of masseter, to enter the face Follows a tortuous course to medial angle of eye Lies deep to most facial muscles ...
... and submandibular gland Loops around mandible (where it is palpable), at anterior border of masseter, to enter the face Follows a tortuous course to medial angle of eye Lies deep to most facial muscles ...
Interesting info Region supply Origin Vessel`s name Internal Carotid
... the terminal branches of the internal carotid, and the most continuous of the parent. It runs deep in the lateral sulcus, the central arteries arise from its proximal part, entering the base of hemisphere. Also a temporal, frontal and parietal branches emerge from the lateral sulcus supplying ++. It ...
... the terminal branches of the internal carotid, and the most continuous of the parent. It runs deep in the lateral sulcus, the central arteries arise from its proximal part, entering the base of hemisphere. Also a temporal, frontal and parietal branches emerge from the lateral sulcus supplying ++. It ...
Surface anatomy of the lungs - University of Nottingham
... Both cross the midclavicular line at the 8th cc Both cross the midaxillary line at the 10th cc ...
... Both cross the midclavicular line at the 8th cc Both cross the midaxillary line at the 10th cc ...
Chapter 8 - White Plains Public Schools
... margins of the joint capsule on the tibia. They are easily torn. These are an example of a hinge joint. ...
... margins of the joint capsule on the tibia. They are easily torn. These are an example of a hinge joint. ...
medial - Perkins Science
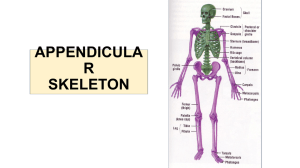
... • Attaches the lower limbs to the trunk • Upper and lower limbs differ in function • BUT: Share the same structural plan ...
... • Attaches the lower limbs to the trunk • Upper and lower limbs differ in function • BUT: Share the same structural plan ...
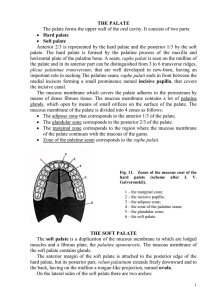
the palate
... larynx from another one. In the pharynx the respiratory and alimentary canal intersects with each other. The pharynx extends from the base of the skull to the level of the VI-VIIth cervical vertebrae. Its length is about 15 cm. In front of the pharynx are situated the nasal and oral cavities, and th ...
... larynx from another one. In the pharynx the respiratory and alimentary canal intersects with each other. The pharynx extends from the base of the skull to the level of the VI-VIIth cervical vertebrae. Its length is about 15 cm. In front of the pharynx are situated the nasal and oral cavities, and th ...
HADUnitIReview
... that exits at that level is spared, while the nerve root one segment below is often compressed For lumbar roots, that means a herniation of IV disc L2/L3 will compress the L3 root The rule applies the same for cervical vertebrae: C5/C6 C6 root For cervical vertebrae, however, it is the nerve ...
... that exits at that level is spared, while the nerve root one segment below is often compressed For lumbar roots, that means a herniation of IV disc L2/L3 will compress the L3 root The rule applies the same for cervical vertebrae: C5/C6 C6 root For cervical vertebrae, however, it is the nerve ...
anatomy_lab8_27_3_2011
... It passes through hypoglossal canal, entering the submandibular triangle then passing below 2 muscles ( posterior belly of digastric and stylohyoid) then entering the carotid triangle . ** it carries C1 nerve. ** sandwiched between 2 muscles ( mylohyoid and ...
... It passes through hypoglossal canal, entering the submandibular triangle then passing below 2 muscles ( posterior belly of digastric and stylohyoid) then entering the carotid triangle . ** it carries C1 nerve. ** sandwiched between 2 muscles ( mylohyoid and ...
Bones
... • The brain and cranial nerves develop before the skull, so when the chondrocranium develops, its components form around the nerves and form foramina. • The chondrocranium ossifies from a number of centers. • The last piece of cartilage to ossify is between the body of the sphenoid bone and the occi ...
... • The brain and cranial nerves develop before the skull, so when the chondrocranium develops, its components form around the nerves and form foramina. • The chondrocranium ossifies from a number of centers. • The last piece of cartilage to ossify is between the body of the sphenoid bone and the occi ...
F. The Knee - Crestwood Local Schools
... ligament- lateral surface of the femur connects to the lateral surface of the fibula h. Intracapsular ligaments: 1. Anterior cructiate ligament (ACL)- goes from the anterior of the tibia to the posterior medial portion of the femur 2. Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)- goes from the posterior of tib ...
... ligament- lateral surface of the femur connects to the lateral surface of the fibula h. Intracapsular ligaments: 1. Anterior cructiate ligament (ACL)- goes from the anterior of the tibia to the posterior medial portion of the femur 2. Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)- goes from the posterior of tib ...
Pterygoid muscles: function of lateral vs. medial
... Carotid sheath contents "I See 10 CC's in the IV": I See (I.C.) = Internal Carotid artery 10 = CN 10 (Vagus nerve) CC = Common Carotid artery IV = Internal Jugular Vein ...
... Carotid sheath contents "I See 10 CC's in the IV": I See (I.C.) = Internal Carotid artery 10 = CN 10 (Vagus nerve) CC = Common Carotid artery IV = Internal Jugular Vein ...
Practical Class 4 BLOOD SUPPL BLOOD SUPPLY TO THE TRUNK
... The paired visceral branches of the thoracic aorta are the bronchial arteries which form part of the systemic circulation to the lungs (remind yourself of the distinction between the pulmonary and systemic circulations). In a previous practical you should have identified the bronchial arteries as th ...
... The paired visceral branches of the thoracic aorta are the bronchial arteries which form part of the systemic circulation to the lungs (remind yourself of the distinction between the pulmonary and systemic circulations). In a previous practical you should have identified the bronchial arteries as th ...
Scapular and Deltoid Regions Bony Landmarks
... Levator Scapulae Rhomboid Major Rhomboid Minor (all elevate medial border and downwardly rotate scapula; Dorsal Scapular nerve;) ...
... Levator Scapulae Rhomboid Major Rhomboid Minor (all elevate medial border and downwardly rotate scapula; Dorsal Scapular nerve;) ...
Characterizing the combined effects of force, repetition and posture
... force was scaled to run from a minimum of −0.001 N to the desired peak load (i.e. 10, 20, and 40% of each FSU's predicted UCT). Similar to research conducted by Parkinson and Callaghan (2009), dynamic flexion/extension was synchronously applied during each loading cycle using a motion profile recorded ...
... force was scaled to run from a minimum of −0.001 N to the desired peak load (i.e. 10, 20, and 40% of each FSU's predicted UCT). Similar to research conducted by Parkinson and Callaghan (2009), dynamic flexion/extension was synchronously applied during each loading cycle using a motion profile recorded ...
Muscles of the Arm and Cubital Fossa
... • Biceps tendon posterior part of radial tuberosity • Medial side of biceps tendon Biceps brachii ...
... • Biceps tendon posterior part of radial tuberosity • Medial side of biceps tendon Biceps brachii ...
Dr Nimr Resp Thoracic Wall (1)
... Origin: Floor of costal groove Insertion: Inner lip of upper border of rib below Fibers are directed from above downwards & backward Begins from anterior end of space close to the sternum. Ends at the angle of the rib, where it is replaced by post. or internal Intercostal membrane. Actio ...
... Origin: Floor of costal groove Insertion: Inner lip of upper border of rib below Fibers are directed from above downwards & backward Begins from anterior end of space close to the sternum. Ends at the angle of the rib, where it is replaced by post. or internal Intercostal membrane. Actio ...
Effective Treatments for the Neck
... Review of the basics As we continue to unravel this complex region, let us see what has been discussed so far. • Most conditions of the neck from can be traced back to previous trauma or imbalance. • Improper posture over time will cause the postural muscles to become ineffective and gradually beco ...
... Review of the basics As we continue to unravel this complex region, let us see what has been discussed so far. • Most conditions of the neck from can be traced back to previous trauma or imbalance. • Improper posture over time will cause the postural muscles to become ineffective and gradually beco ...
BACK AND LIMBS - OUTLINES INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMICAL
... iii. intervertebral foramen: spinal nerves exit laterally via these holes; foramen formed by vertebral arch and zygapophyseal joint iv. only 7 cervical vertebra, but 8 spinal nerves nerve C7 comes out foramen above C7, and C8 comes out below (btw C7 and T1) v. spinal cord ends at lumbar region l ...
... iii. intervertebral foramen: spinal nerves exit laterally via these holes; foramen formed by vertebral arch and zygapophyseal joint iv. only 7 cervical vertebra, but 8 spinal nerves nerve C7 comes out foramen above C7, and C8 comes out below (btw C7 and T1) v. spinal cord ends at lumbar region l ...
1 Anatomy - Upper Limb – Bones
... Spine → acromion (articulates with clavicle) Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres major, minor, Trapezius, Deltoid Glenoid (articulates with head humerus), neck Supraglenoid tubercle → long head biceps; Infra → long head triceps Coracoid process anterolaterally, superior to glenoid Pec minor, short h ...
... Spine → acromion (articulates with clavicle) Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres major, minor, Trapezius, Deltoid Glenoid (articulates with head humerus), neck Supraglenoid tubercle → long head biceps; Infra → long head triceps Coracoid process anterolaterally, superior to glenoid Pec minor, short h ...
notes#10 - DENTISTRY 2012
... - Hitting the pterion area by a stone causes bleeding from the middle meningeal artery, that will be collected between dura an periosteum, therefore compressing the soft tissue of the brain (medially) specifically anterior cerebral gyrus (motor area). - this collection of blood called “extra dural ...
... - Hitting the pterion area by a stone causes bleeding from the middle meningeal artery, that will be collected between dura an periosteum, therefore compressing the soft tissue of the brain (medially) specifically anterior cerebral gyrus (motor area). - this collection of blood called “extra dural ...
Unit 24: Cranial Cavity and Contents
... spinal cord and brainstem. Those filaments arising from the upper cervical spinal cord segments ascend along the spinal cord, enter the posterior cranial fossa through the foramen magnum and join with the fibers that arise from the brainstem. Identify both parts of the accessory nerve. The hypogloss ...
... spinal cord and brainstem. Those filaments arising from the upper cervical spinal cord segments ascend along the spinal cord, enter the posterior cranial fossa through the foramen magnum and join with the fibers that arise from the brainstem. Identify both parts of the accessory nerve. The hypogloss ...
Sonographic Evaluation of Neck Vasculature. Common Carotid, ICA
... After coursing anteriorly to the transverse processes of the first three cervical vertebrae (C1 –C3), it enters the carotid canal of the petrous portion of the temporal bone. The intra-petrous portion of the ICA is also referred to as the cavernous portion of the ICA. After coursing through the base ...
... After coursing anteriorly to the transverse processes of the first three cervical vertebrae (C1 –C3), it enters the carotid canal of the petrous portion of the temporal bone. The intra-petrous portion of the ICA is also referred to as the cavernous portion of the ICA. After coursing through the base ...
anatomy exam 1 review – muscles, innervations, vasculature
... o Anterior – femoral nerve (exception = iliopsoas – femoral n. & lumbar pexus; pectineus = femoral n. & obturator n.) o Medial – obturator nerve (exception = adductor magnus – obturator n. & tibial n.) o Posterior – sciatic nerve - Femoral triangle: NAVL – anterior view – lateral to medial ...
... o Anterior – femoral nerve (exception = iliopsoas – femoral n. & lumbar pexus; pectineus = femoral n. & obturator n.) o Medial – obturator nerve (exception = adductor magnus – obturator n. & tibial n.) o Posterior – sciatic nerve - Femoral triangle: NAVL – anterior view – lateral to medial ...
Vertebra

In the vertebrate spinal column, each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, the proportions of which vary according to the segment of the backbone and the species of vertebrate animal.The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the large part is the body, and the central part is the centrum. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles, two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava. There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conducts for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebra and the vertebral arch form the vertebral foramen, the larger, central opening that accommodates the spinal canal, which encloses and protects the spinal cord.Vertebrae articulate with each other to give strength and flexibility to the spinal column, and the shape at their back and front aspects determines the range of movement. Structurally, vertebrae are essentially alike across the vertebrate species, with the greatest difference seen between an aquatic animal and other vertebrate animals. As such, vertebrates take their name from the vertebrae that compose the vertebral column.