Anatomy of the Upper Cervical Spine
... for the vertebral arteries seems to be full contralateral rotation of the atlas upon the axis when the occiput has been sideflexed upon the atlas. In order to determine why the vertebral arteries were apparently more strained in full lateral rotation than in what appeared to be much more stressful p ...
... for the vertebral arteries seems to be full contralateral rotation of the atlas upon the axis when the occiput has been sideflexed upon the atlas. In order to determine why the vertebral arteries were apparently more strained in full lateral rotation than in what appeared to be much more stressful p ...
Concise Guide to HUMAN ANATOMY 2
... Ⅲ. The Ventral Rami of the Thoracic Nerves………………………………………102 Ⅳ. The Lumbar Plexus……………………………………………………………..102 Ⅴ. The Sacral Plexus……………………………………………………………….103 Section 2 The Cranial Nerves……………………………………………………………104 Ⅰ. The Olfactory Nerve……………………………………………………………106 Ⅱ. The Optic Nerve………………………………………………… ...
... Ⅲ. The Ventral Rami of the Thoracic Nerves………………………………………102 Ⅳ. The Lumbar Plexus……………………………………………………………..102 Ⅴ. The Sacral Plexus……………………………………………………………….103 Section 2 The Cranial Nerves……………………………………………………………104 Ⅰ. The Olfactory Nerve……………………………………………………………106 Ⅱ. The Optic Nerve………………………………………………… ...
Anatomy 103 OSCE Chart
... • has holes for nerve/artery supply to pass through • connects the two bones along their entire length by this flat, flexible ligament ...
... • has holes for nerve/artery supply to pass through • connects the two bones along their entire length by this flat, flexible ligament ...
BIOL241articulations8JUL2012
... • Two types of movement – Hinge – depression and eleva3on of mandible – Side to side – (lateral excursion) grinding of teeth ...
... • Two types of movement – Hinge – depression and eleva3on of mandible – Side to side – (lateral excursion) grinding of teeth ...
Anterior jugular vein
... surrounds the thyroid and the parathyroid glands, forming a sheath for them, and encloses the infrahyoid muscles. ...
... surrounds the thyroid and the parathyroid glands, forming a sheath for them, and encloses the infrahyoid muscles. ...
ARTICULAR SYSTEM
... the contrary, peripheral regions of the mesenchyme, which surround the cavity, condense, giving rise to the fibrous capsule and ligaments of the joint. Cartilaginous epiphyses ossify in such away that a thin layer of articular cartilage remains on their surfaces for life, which provides the smoothne ...
... the contrary, peripheral regions of the mesenchyme, which surround the cavity, condense, giving rise to the fibrous capsule and ligaments of the joint. Cartilaginous epiphyses ossify in such away that a thin layer of articular cartilage remains on their surfaces for life, which provides the smoothne ...
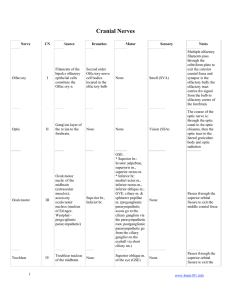
Cranial Nerves
... and projects into the pons to the primary sensory nucleus of V or more inferiorly to the nucleus of the spinal root of V (medulla and upper spinal ...
... and projects into the pons to the primary sensory nucleus of V or more inferiorly to the nucleus of the spinal root of V (medulla and upper spinal ...
Headache and vertigo of cervical origin
... that innervate the cerebral vessels and the dura and whose cell bodies are located in the trigeminal ganglion. This ganglion contains bipolar cells. Peripheral fibres innervate blood vessels in the meninges, the extracranial arteries, and those in the circle of Willis. These nerve fibres contain noc ...
... that innervate the cerebral vessels and the dura and whose cell bodies are located in the trigeminal ganglion. This ganglion contains bipolar cells. Peripheral fibres innervate blood vessels in the meninges, the extracranial arteries, and those in the circle of Willis. These nerve fibres contain noc ...
PELVIC BLOOD SUPPLY - University of Kansas Medical Center
... Abdominal sympathetic plexus. Inferior mesenteric ganglion. Superior hypogastric plexus: To uterine tubes in female. ...
... Abdominal sympathetic plexus. Inferior mesenteric ganglion. Superior hypogastric plexus: To uterine tubes in female. ...
the knee joint - Fisiokinesiterapia
... The patella moves the insertion of the quadriceps muscles further down the tibia. This increases the folcrum of the quads A longer folcrum increases the leverage of the quads making them a strong muscle group No patella: Folcrum ^__F_________R. Patella: Folcrum ^_____F______R. ...
... The patella moves the insertion of the quadriceps muscles further down the tibia. This increases the folcrum of the quads A longer folcrum increases the leverage of the quads making them a strong muscle group No patella: Folcrum ^__F_________R. Patella: Folcrum ^_____F______R. ...
THE KNEE JOINT
... The patella moves the insertion of the quadriceps muscles further down the tibia. This increases the folcrum of the quads A longer folcrum increases the leverage of the quads making them a strong muscle group No patella: Folcrum ^__F_________R. Patella: Folcrum ^_____F______R. ...
... The patella moves the insertion of the quadriceps muscles further down the tibia. This increases the folcrum of the quads A longer folcrum increases the leverage of the quads making them a strong muscle group No patella: Folcrum ^__F_________R. Patella: Folcrum ^_____F______R. ...
the knee joint - Fisiokinesiterapia
... The patella moves the insertion of the quadriceps muscles further down the tibia. This increases the folcrum of the quads A longer folcrum increases the leverage of the quads making them a strong muscle group No patella: Folcrum ^__F_________R. Patella: Folcrum ^_____F______R. ...
... The patella moves the insertion of the quadriceps muscles further down the tibia. This increases the folcrum of the quads A longer folcrum increases the leverage of the quads making them a strong muscle group No patella: Folcrum ^__F_________R. Patella: Folcrum ^_____F______R. ...
The development of the orbital region of Caretta caretta (Chelonia
... The orbit of Caretta develops inferolateral to the developing forebrain as an extracranial space. The walls of the orbit are composed of six irregularly shaped cartilages, each being a constituent of the neurocranium. The superior wall or roof of the orbit is composed of the taenia marginalis, the a ...
... The orbit of Caretta develops inferolateral to the developing forebrain as an extracranial space. The walls of the orbit are composed of six irregularly shaped cartilages, each being a constituent of the neurocranium. The superior wall or roof of the orbit is composed of the taenia marginalis, the a ...
WITH AUTOPSY GUIDE AND CLINICAL NOTES
... Epicranius muscle under the skin consists of the anterior (frontal) and the posterior (occipital) belly and the tendinous galea aponeurotica. Into the galea inserts also the temporoparietalis muscle which originates from the auricular cartilage. Galea is firmly attached to the skin, under the galea ...
... Epicranius muscle under the skin consists of the anterior (frontal) and the posterior (occipital) belly and the tendinous galea aponeurotica. Into the galea inserts also the temporoparietalis muscle which originates from the auricular cartilage. Galea is firmly attached to the skin, under the galea ...
SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE NASOPHARYNX
... - Arises from the lower part of the posterior margin of the medial pterygoid plate -Sphincter that prevents reflux into the nasopharynx and has a peristaltic function during swallowing ...
... - Arises from the lower part of the posterior margin of the medial pterygoid plate -Sphincter that prevents reflux into the nasopharynx and has a peristaltic function during swallowing ...
educational models for teaching pelvic floor disorders
... anthropoid (oval anteriorly/posteriorly): common in males, 20% of white females, 40% of black females platypelloid (oval transversely): rare in females ...
... anthropoid (oval anteriorly/posteriorly): common in males, 20% of white females, 40% of black females platypelloid (oval transversely): rare in females ...
Joints Of Upper Extremities
... Sternoclavicular Joint • 1. fibrous capsule - surrounds entire joint, reinforced by ligaments – a. synovial capsule - lines fibrous capsule & both sides of disc – b. lateral & medial synovial membranes line 2 cavities on either side of disc • 2. articular disc - mostly fibrocartilage - strong, thi ...
... Sternoclavicular Joint • 1. fibrous capsule - surrounds entire joint, reinforced by ligaments – a. synovial capsule - lines fibrous capsule & both sides of disc – b. lateral & medial synovial membranes line 2 cavities on either side of disc • 2. articular disc - mostly fibrocartilage - strong, thi ...
internal medicine series
... sciatic nerve running through the belly of the piriformis. Piriformis hypertonicity can cause buttock pain that radiates down the thigh, but not usually below the knee. ...
... sciatic nerve running through the belly of the piriformis. Piriformis hypertonicity can cause buttock pain that radiates down the thigh, but not usually below the knee. ...
Anatomy of thyroid gland Introduction • Brownish
... Right and left lobes United by a narrow isthmus, which extends across the trachea anterior to second and third tracheal cartilages In some people a third “pyramidal lobe” exists, ascending from the ...
... Right and left lobes United by a narrow isthmus, which extends across the trachea anterior to second and third tracheal cartilages In some people a third “pyramidal lobe” exists, ascending from the ...
ch_06_lecture_presentation
... Checkpoint (6-2) 2. Identify the four general shapes of bones. 3. How would the strength of a bone be affected if the ratio of collagen to calcium increased? 4. A sample of a long bone shows concentric layers surrounding a central canal. Is it from the shaft or the end of the bone? 5. Mature bone c ...
... Checkpoint (6-2) 2. Identify the four general shapes of bones. 3. How would the strength of a bone be affected if the ratio of collagen to calcium increased? 4. A sample of a long bone shows concentric layers surrounding a central canal. Is it from the shaft or the end of the bone? 5. Mature bone c ...
The Skeletal System - Lewiston School District
... • CVertebral column - support for the trunk of the body. • It runs from the skull to the pelvis. • The bones that make up this column are known as vertebrae and are separated from each other by intervertebral discs. ...
... • CVertebral column - support for the trunk of the body. • It runs from the skull to the pelvis. • The bones that make up this column are known as vertebrae and are separated from each other by intervertebral discs. ...
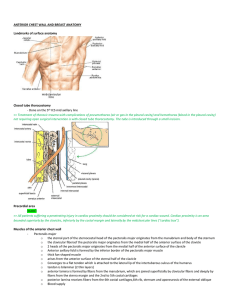
anterior chest wall and breast anatomy
... o they pass obliquely downwards and laterally parallel with the posterior borders of the external intercostals o each is attached to the upper edge and external surface of the rib immediately below the vertebra from which it takes its origin, between the tubercle and angle o each of the 4 lower musc ...
... o they pass obliquely downwards and laterally parallel with the posterior borders of the external intercostals o each is attached to the upper edge and external surface of the rib immediately below the vertebra from which it takes its origin, between the tubercle and angle o each of the 4 lower musc ...
Ch 6 notes-
... Checkpoint (6-2) 2. Identify the four general shapes of bones. 3. How would the strength of a bone be affected if the ratio of collagen to calcium increased? 4. A sample of a long bone shows concentric layers surrounding a central canal. Is it from the shaft or the end of the bone? 5. Mature bo ...
... Checkpoint (6-2) 2. Identify the four general shapes of bones. 3. How would the strength of a bone be affected if the ratio of collagen to calcium increased? 4. A sample of a long bone shows concentric layers surrounding a central canal. Is it from the shaft or the end of the bone? 5. Mature bo ...
Non-Muscular-Anatomy-Handout-4
... • Femur run in a medial and inferior oblique direction • Sits on a vertical tibia ...
... • Femur run in a medial and inferior oblique direction • Sits on a vertical tibia ...
Vertebra

In the vertebrate spinal column, each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, the proportions of which vary according to the segment of the backbone and the species of vertebrate animal.The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the large part is the body, and the central part is the centrum. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles, two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava. There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conducts for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebra and the vertebral arch form the vertebral foramen, the larger, central opening that accommodates the spinal canal, which encloses and protects the spinal cord.Vertebrae articulate with each other to give strength and flexibility to the spinal column, and the shape at their back and front aspects determines the range of movement. Structurally, vertebrae are essentially alike across the vertebrate species, with the greatest difference seen between an aquatic animal and other vertebrate animals. As such, vertebrates take their name from the vertebrae that compose the vertebral column.