A relation between partitions and the number of divisors
... called odd partitions, whereas the other three partitions are called even. Add the smallest numbers of the odd partitions, 1 + 7 = 8, and do the same for the smallest numbers of the even partitions, 1 + 2 + 3 = 6. The difference between these two sums, 8 − 6 = 2, is exactly the number of divisors of ...
... called odd partitions, whereas the other three partitions are called even. Add the smallest numbers of the odd partitions, 1 + 7 = 8, and do the same for the smallest numbers of the even partitions, 1 + 2 + 3 = 6. The difference between these two sums, 8 − 6 = 2, is exactly the number of divisors of ...
Medium Term Maths Plan (Topic)
... To recognise the value of each digit in numbers up to 100 000 ...
... To recognise the value of each digit in numbers up to 100 000 ...
EXPLORING INTEGERS ON THE NUMBER LINE
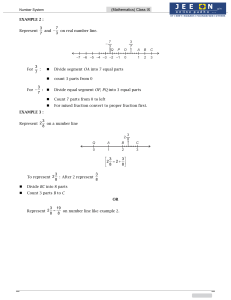
... Chapter 1 Exploring Integers on the Number Line Another way to represent numbers is to describe locations with the number line model, which is visually similar to a thermometer. To construct a number line, begin by drawing a straight line and picking some point on the line. We call this point the ...
... Chapter 1 Exploring Integers on the Number Line Another way to represent numbers is to describe locations with the number line model, which is visually similar to a thermometer. To construct a number line, begin by drawing a straight line and picking some point on the line. We call this point the ...
Lesson 01 - Purdue Math
... the expression involves a fraction, treat the numerator and denominator as if they were each a group. Grouping can include parentheses, brackets, a root, or absolute value bars. 2. Evaluate all exponential expressions. 3. Perform multiplication and/or division as they occur, working from left to rig ...
... the expression involves a fraction, treat the numerator and denominator as if they were each a group. Grouping can include parentheses, brackets, a root, or absolute value bars. 2. Evaluate all exponential expressions. 3. Perform multiplication and/or division as they occur, working from left to rig ...
4.2 Models for Greatest Common Factor and Least Common Multiple
... Abbreviated: GCF(a, b) Also called the Greatest Common Divisor or GCD(a, b) GCF can be found for two or more numbers GCF is the largest number that is a factor of ALL the numbers being tested Factorization or prime factorization of the numbers being tested is one way of determining the lar ...
... Abbreviated: GCF(a, b) Also called the Greatest Common Divisor or GCD(a, b) GCF can be found for two or more numbers GCF is the largest number that is a factor of ALL the numbers being tested Factorization or prime factorization of the numbers being tested is one way of determining the lar ...
4.2 Models for Greatest Common Factor and Least Common Multiple
... § Abbreviated: GCF(a, b) § Also called the Greatest Common Divisor or GCD(a, b) § GCF can be found for two or more numbers § GCF is the largest number that is a factor of ALL the numbers being tested § Factorization or prime factorization of the numbers being tested is one way of determining the lar ...
... § Abbreviated: GCF(a, b) § Also called the Greatest Common Divisor or GCD(a, b) § GCF can be found for two or more numbers § GCF is the largest number that is a factor of ALL the numbers being tested § Factorization or prime factorization of the numbers being tested is one way of determining the lar ...
Full text
... Our main result, Theorem 4.1, generalizes Theorem 1.1 to series of the form [H(2kx)J, where r is rational and 2k (k > 1) is the highest power of 2 dividing the denominator of r. A summary by sections follows. Section 2 is a preliminary section in which we state the basic definitions and lemmas that ...
... Our main result, Theorem 4.1, generalizes Theorem 1.1 to series of the form [H(2kx)J, where r is rational and 2k (k > 1) is the highest power of 2 dividing the denominator of r. A summary by sections follows. Section 2 is a preliminary section in which we state the basic definitions and lemmas that ...
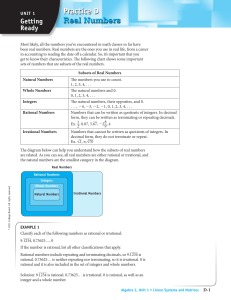
Practice D Real Numbers
... The numbers a and −a are called additive inverses or opposites. Similarly, the numbers a and __ a1 , where a ≠ 0, are called multiplicative inverses or reciprocals. Additive inverses have a special feature in common. They share the same absolute value. The absolute value of a given number can be ...
... The numbers a and −a are called additive inverses or opposites. Similarly, the numbers a and __ a1 , where a ≠ 0, are called multiplicative inverses or reciprocals. Additive inverses have a special feature in common. They share the same absolute value. The absolute value of a given number can be ...
1.3 - mathchick.net
... other words, the set of irrational numbers is the set of numbers whose _______ representations are neither ___________________ nor _________________. THE SET OF REAL NUMBERS All numbers that can be represented by _____________ on the number line are called _____________ numbers. THE SETS THAT MAKE U ...
... other words, the set of irrational numbers is the set of numbers whose _______ representations are neither ___________________ nor _________________. THE SET OF REAL NUMBERS All numbers that can be represented by _____________ on the number line are called _____________ numbers. THE SETS THAT MAKE U ...