Digestive System
... • Gall stones – if bile is stored in gall bladder too long or too much water is removed, the cholesterol in it crystallizes forming gall stones – Can cause blockage of hepatic or bile ducts and bile begins is released into bloodstream instead • Bile in blood and eventually tissues causes jaundice • ...
... • Gall stones – if bile is stored in gall bladder too long or too much water is removed, the cholesterol in it crystallizes forming gall stones – Can cause blockage of hepatic or bile ducts and bile begins is released into bloodstream instead • Bile in blood and eventually tissues causes jaundice • ...
Digestion - District 128 Moodle
... 5. Large Intestine – All undigested material ends up here – Water is absorbed into the blood – Undigested material is stored, compacted. – The product is called feces or stool. – Fiber (cellulose) from whole grains, fruits and vegetables keep stool softer. ...
... 5. Large Intestine – All undigested material ends up here – Water is absorbed into the blood – Undigested material is stored, compacted. – The product is called feces or stool. – Fiber (cellulose) from whole grains, fruits and vegetables keep stool softer. ...
Digestion, Absorption, Metabolism, and Excretion
... Small intestine About 20 feet long Made up of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum 90% of the digestive action and nearly all end product absorption occur in the small intestine Emulsification – a process of breaking down non ...
... Small intestine About 20 feet long Made up of the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum 90% of the digestive action and nearly all end product absorption occur in the small intestine Emulsification – a process of breaking down non ...
Medical Terminology
... and to hold food and release it at a constant rate. The stomach is a highly acidic environment due to hydrochloric acid production and secretion which produces a pH range usually between 1 and 2. Combined with digestive enzymes, such an environment is able to break down large molecules to smaller on ...
... and to hold food and release it at a constant rate. The stomach is a highly acidic environment due to hydrochloric acid production and secretion which produces a pH range usually between 1 and 2. Combined with digestive enzymes, such an environment is able to break down large molecules to smaller on ...
Chapter 11.3: The Human Excretory System
... apocrine glands ; those that connect directly with the skin surface are called eccrine glands ...
... apocrine glands ; those that connect directly with the skin surface are called eccrine glands ...
B20 C6 Your Own Digestion Map
... 4) Sites of Chemical Digestion: Secretions labeled with arrows from site of production to site of action. Color code enzymes for the macromolecules they digest (starch, sugars, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids) ...
... 4) Sites of Chemical Digestion: Secretions labeled with arrows from site of production to site of action. Color code enzymes for the macromolecules they digest (starch, sugars, proteins, lipids, nucleic acids) ...
The Pancreas
... Secretion of Bile and the Role of Bile Acids in Digestion Bile is a complex fluid containing water, electrolytes and a battery of organic molecules including bile acids, cholesterol, phospholipids and bilirubin that flows through the biliary tract into the small intestine. There are two fundamentall ...
... Secretion of Bile and the Role of Bile Acids in Digestion Bile is a complex fluid containing water, electrolytes and a battery of organic molecules including bile acids, cholesterol, phospholipids and bilirubin that flows through the biliary tract into the small intestine. There are two fundamentall ...
Lecture 19
... Microvilli – Each cell of a villus has a fuzzy brush border of microvilli and 1 m high This wrinkling of the cell membrane increases the surface area by a factor of 20 ...
... Microvilli – Each cell of a villus has a fuzzy brush border of microvilli and 1 m high This wrinkling of the cell membrane increases the surface area by a factor of 20 ...
16 DIGESTION Presentation
... together and lubricating it for an easy passage. The undigested, unabsorbed substances called faeces enters into the caecum of the large intestine through ileo-caecal valve, which preventsthe back flow of the faecal matter. It is temporarily stored in the rectu till defaecation ...
... together and lubricating it for an easy passage. The undigested, unabsorbed substances called faeces enters into the caecum of the large intestine through ileo-caecal valve, which preventsthe back flow of the faecal matter. It is temporarily stored in the rectu till defaecation ...
Digestive System Part II
... Gross Anatomy of Pancreas • Endocrine and exocrine gland – secretes insulin and glucagon – secretes 1500 mL pancreatic juice/day • Pancreatic juice: – Water, zymogens, enzymes, and sodium bicarbonate Pancreatic lobules Pancreatic duct Common bile duct Body of ...
... Gross Anatomy of Pancreas • Endocrine and exocrine gland – secretes insulin and glucagon – secretes 1500 mL pancreatic juice/day • Pancreatic juice: – Water, zymogens, enzymes, and sodium bicarbonate Pancreatic lobules Pancreatic duct Common bile duct Body of ...
Digestive Enzymes and their Action
... surface tension and increase surface area, thus aiding in the emulsification of fats. They also increase the effectiveness of pancreatic lipase in its digestive action on emulsified fats, In addition, bile salts aid the absorption of fatty acids through the walls of the intestine. After absorption o ...
... surface tension and increase surface area, thus aiding in the emulsification of fats. They also increase the effectiveness of pancreatic lipase in its digestive action on emulsified fats, In addition, bile salts aid the absorption of fatty acids through the walls of the intestine. After absorption o ...
ALIMENTARY CANAL 1. What happen to the food that we
... 3. What happen to the food that cannot be digested and cannot be absorbed? They are pass into the large intestine (Colon). In the colon: ‐ ABSORPTION of water, mineral salts and vitamins takes place. ‐ The undigested food / waste (faeces) is stored in the rectum and passed out through the anus (EGES ...
... 3. What happen to the food that cannot be digested and cannot be absorbed? They are pass into the large intestine (Colon). In the colon: ‐ ABSORPTION of water, mineral salts and vitamins takes place. ‐ The undigested food / waste (faeces) is stored in the rectum and passed out through the anus (EGES ...
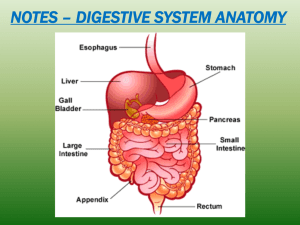
Digestive System
... From the esophagus food enters the stomach • What are the functions of the stomach? • What type of epithelial tissue is found ...
... From the esophagus food enters the stomach • What are the functions of the stomach? • What type of epithelial tissue is found ...
Chapter x – title of chapter
... Term 1. passive diffusion 2. lymphatic system 3. capillaries in villi 4. chylomicron 5. active/facilitated transport 6. membrane transporter ...
... Term 1. passive diffusion 2. lymphatic system 3. capillaries in villi 4. chylomicron 5. active/facilitated transport 6. membrane transporter ...
Digestive System Exam Review
... 18. What are the three functions of the liver? a. storage of glycogen, fatty acids, fat-soluble vitamins & minerals b. detoxification & removal of drugs, toxins & hormones c. phagocytosis of worn-out RBCs, bacteria & other pathogens 19. How is glucose stored in the liver? glycogen 20. What is the o ...
... 18. What are the three functions of the liver? a. storage of glycogen, fatty acids, fat-soluble vitamins & minerals b. detoxification & removal of drugs, toxins & hormones c. phagocytosis of worn-out RBCs, bacteria & other pathogens 19. How is glucose stored in the liver? glycogen 20. What is the o ...
a) digestive system functions
... -severe vomiting = void contents of stomach & sml. intestine only ...
... -severe vomiting = void contents of stomach & sml. intestine only ...
a) digestive system functions
... -severe vomiting = void contents of stomach & sml. intestine only ...
... -severe vomiting = void contents of stomach & sml. intestine only ...
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
... LARGE INTESTINE • ABOUT 5’ IN LENGTH • FOOD STAYS IN LARGE INTESTINE 18-24 HOURS • WATER IS ABSORBED • VITAMIN K AND B ABSORBED ...
... LARGE INTESTINE • ABOUT 5’ IN LENGTH • FOOD STAYS IN LARGE INTESTINE 18-24 HOURS • WATER IS ABSORBED • VITAMIN K AND B ABSORBED ...
Document
... • Bile production: 600-1000 mL/day. Bile salts (bilirubin), cholesterol, fats, fat-soluble hormones, lecithin – Neutralizes and dilutes stomach acid – Bile salts emulsify fats. Most are reabsorbed in the ileum. – Secretin (from the duodenum) stimulates bile secretions, increasing water and bicarbona ...
... • Bile production: 600-1000 mL/day. Bile salts (bilirubin), cholesterol, fats, fat-soluble hormones, lecithin – Neutralizes and dilutes stomach acid – Bile salts emulsify fats. Most are reabsorbed in the ileum. – Secretin (from the duodenum) stimulates bile secretions, increasing water and bicarbona ...
Study Guide Exam #2 1) What are the 2 stages of
... 1) What are the 2 stages of food consumption in animals? What is the difference between them? ...
... 1) What are the 2 stages of food consumption in animals? What is the difference between them? ...
Bile acid
Bile acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Different molecular forms of bile acids can be synthesized in the liver by different species. Bile acids are conjugated with taurine or glycine in the liver, forming bile salts.Primary bile acids are those synthesized by the liver. Secondary bile acids result from bacterial actions in the colon. In humans, taurocholic acid and glycocholic acid (derivatives of cholic acid) and taurochenodeoxycholic acid and glycochenodeoxycholic acid (derivatives of chenodeoxycholic acid) are the major bile salts in bile and are roughly equal in concentration. The conjugated salts of their 7-alpha-dehydroxylated derivatives, deoxycholic acid and lithocholic acid, are also found, with derivatives of cholic, chenodeoxycholic and deoxycholic acids accounting for over 90% of human biliary bile acids.Bile acids comprise about 80% of the organic compounds in bile (others are phospholipids and cholesterol). An increased secretion of bile acids produces an increase in bile flow. The main function of bile acids is to facilitate the formation of micelles, which promotes digestion and absorption of dietary fat, but they are increasingly being shown to have hormonal actions throughout the body.