13.2 NOTES What factors determine climate? Objective: Identify and
... Ocean currents have an effect on the climate of areas along the seacoast. Some ocean currents are warm, and some are cold. Winds passing over ocean currents are either warmed or cooled by them. When these winds reach nearby land areas, they heat or cool the land. ...
... Ocean currents have an effect on the climate of areas along the seacoast. Some ocean currents are warm, and some are cold. Winds passing over ocean currents are either warmed or cooled by them. When these winds reach nearby land areas, they heat or cool the land. ...
Ocean Zones - Earth Science With Mrs. Locke
... volume of your lungs has been reduced to 1/3rd their capacity at sea level. You will also notice that it is much darker at 100 feet and COLD. The lack of sunlight at that depth also means the ocean is not getting warmed by sunlight, either. At a depth of about 180 feet you’ve pretty much reached the ...
... volume of your lungs has been reduced to 1/3rd their capacity at sea level. You will also notice that it is much darker at 100 feet and COLD. The lack of sunlight at that depth also means the ocean is not getting warmed by sunlight, either. At a depth of about 180 feet you’ve pretty much reached the ...
Lesson 2.1 Continental Drift
... Closed when India moved into Asia Panthalassic Ocean: Huge ocean surrounding Pangea Became the Pacific Atlantic Ocean: Formed when North America separated from Eurasia Indian Ocean: Formed when Gondwanaland broke apart ...
... Closed when India moved into Asia Panthalassic Ocean: Huge ocean surrounding Pangea Became the Pacific Atlantic Ocean: Formed when North America separated from Eurasia Indian Ocean: Formed when Gondwanaland broke apart ...
Ocean Topography presentation
... wedge of sediments. How do submarine canyons form? Thought to be fast moving currents and underwater landslides. ...
... wedge of sediments. How do submarine canyons form? Thought to be fast moving currents and underwater landslides. ...
Ocean Currents
... Consequences of Global Warming to Thermohaline Circulation • Ice cap melts creating an excess of floating fresh water in the Arctic Ocean • Permafrost and glaciers, particularly in Siberia, melt, causing huge flux of warm fresh water into Arctic Ocean via northward draining rivers. • Low density wa ...
... Consequences of Global Warming to Thermohaline Circulation • Ice cap melts creating an excess of floating fresh water in the Arctic Ocean • Permafrost and glaciers, particularly in Siberia, melt, causing huge flux of warm fresh water into Arctic Ocean via northward draining rivers. • Low density wa ...
Seafloor Spreading Notes Harry Hess He was a geology Professor
... Stretches about 12,000 miles from the Tip of Africa to the Arctic Ocean Can reach nearly 1000 miles wide Over 1 mile high in certain spots Mariana Trench The Mariana Trench lies near the Philippines in the Pacific Ocean It is a crescent-shaped scar in the Earth’s crust that measures more t ...
... Stretches about 12,000 miles from the Tip of Africa to the Arctic Ocean Can reach nearly 1000 miles wide Over 1 mile high in certain spots Mariana Trench The Mariana Trench lies near the Philippines in the Pacific Ocean It is a crescent-shaped scar in the Earth’s crust that measures more t ...
Gr.8-Ch.2-Review-Sheet-2014
... 20. Water on earth came from_____ and _____. 21. Water collected in the lowest parts of the Earth’s surface known as the _____. 22. A tumble of water when a wave collapses onshore is called _____. 23. Giant waves that can be sent in motion by earthquakes on the ocean floor, landslides or volcanic er ...
... 20. Water on earth came from_____ and _____. 21. Water collected in the lowest parts of the Earth’s surface known as the _____. 22. A tumble of water when a wave collapses onshore is called _____. 23. Giant waves that can be sent in motion by earthquakes on the ocean floor, landslides or volcanic er ...
Biome: Ocean - Ohio County Schools
... The ocean has the most biodiversity of all the biomes. The Mariana Trench is the deepest of the ocean and is 12,400 feet. Over 90% of the life on Earth lives in the ocean. Around 90% of all volcanic activity takes place in the world’s oceans. ...
... The ocean has the most biodiversity of all the biomes. The Mariana Trench is the deepest of the ocean and is 12,400 feet. Over 90% of the life on Earth lives in the ocean. Around 90% of all volcanic activity takes place in the world’s oceans. ...
File - Science by Shaw
... Illustrate the three water profiles into which the ocean water is divided based on temperature. Describe the pelagic zones of the water column. Which is denser, cold seawater or warm seawater? Why? At what depth can the main thermocline be found? ...
... Illustrate the three water profiles into which the ocean water is divided based on temperature. Describe the pelagic zones of the water column. Which is denser, cold seawater or warm seawater? Why? At what depth can the main thermocline be found? ...
mysask.com - National News
... VANCOUVER - Canada, Russia and the United States have drastically underestimated the size of their fisheries in the Arctic, says a new study from the University of British Columbia. And as climate change opens up the northern ocean, the pressure will only increase on this delicate and neglected ecos ...
... VANCOUVER - Canada, Russia and the United States have drastically underestimated the size of their fisheries in the Arctic, says a new study from the University of British Columbia. And as climate change opens up the northern ocean, the pressure will only increase on this delicate and neglected ecos ...
Word
... The “memory” of thermohaline water masses tells scientists about the ________________ at the time the water was formed. (video) Antarctic Bottom Water is notable for retaining its integrity for nearly 1,600 years, while the time it takes most other deep water to form and rise to the surface is about ...
... The “memory” of thermohaline water masses tells scientists about the ________________ at the time the water was formed. (video) Antarctic Bottom Water is notable for retaining its integrity for nearly 1,600 years, while the time it takes most other deep water to form and rise to the surface is about ...
the ocean floor - NVHSEarthScienceKDudenhausen
... • Deep ocean trenches – formed by subduction, deepest known place on Earth is the Challenger Deep of the Mariana Trench, 11,022 meters deep • Abyssal plains – extremely flat, most level places • Seamounts – submerged volcanic peaks • Guyots – once active, now submerged, flat topped remnants of volca ...
... • Deep ocean trenches – formed by subduction, deepest known place on Earth is the Challenger Deep of the Mariana Trench, 11,022 meters deep • Abyssal plains – extremely flat, most level places • Seamounts – submerged volcanic peaks • Guyots – once active, now submerged, flat topped remnants of volca ...
Ocean Topography
... Has hills, valleys, canyons and other features. This is very wide off of Atlantic Canada. ...
... Has hills, valleys, canyons and other features. This is very wide off of Atlantic Canada. ...
3. Ocean Geography Notes
... When it meets the continental crust it subducts into the mantle because it is ...
... When it meets the continental crust it subducts into the mantle because it is ...
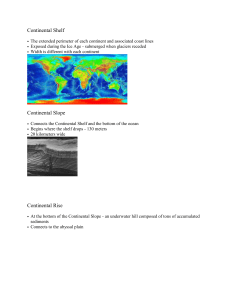
Continental Shelf • The extended perimeter of each continent and
... • The extended perimeter of each continent and associated coast lines • Exposed during the Ice Age - submerged when glaciers receded • Width is different with each continent ...
... • The extended perimeter of each continent and associated coast lines • Exposed during the Ice Age - submerged when glaciers receded • Width is different with each continent ...
Understanding Climate Change in Polar Regions Friday, Dec 19, 8
... interdisciplinary program of funded research aimed at developing a better understanding of the interactions between the ecosystem, atmosphere, and human dynamics in northern Eurasia in support of international science programs with particular relevance to Global climate change research interests and ...
... interdisciplinary program of funded research aimed at developing a better understanding of the interactions between the ecosystem, atmosphere, and human dynamics in northern Eurasia in support of international science programs with particular relevance to Global climate change research interests and ...
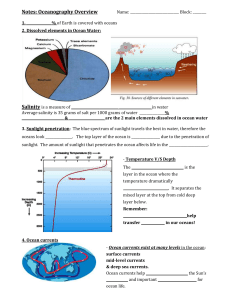
Oceanography Overview Notes
... mixed layer at the top from cold deep layer below. Remember: ______________________________________help transfer ______________ in our oceans! ...
... mixed layer at the top from cold deep layer below. Remember: ______________________________________help transfer ______________ in our oceans! ...
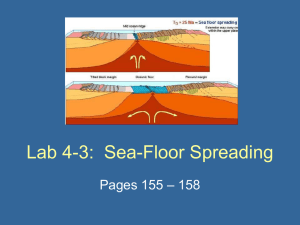
Lab 4-3: Sea-Floor Spreading
... – Ocean crust is created at a divergent boundary as plates pull apart and molten material rises from deep within the Earth. ...
... – Ocean crust is created at a divergent boundary as plates pull apart and molten material rises from deep within the Earth. ...
International Research Training Group ArcTrain: Processes
... North Atlantic Ocean and the Canadian Arctic ArcTrain is a collaborative project between the University of Bremen and the Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research in Germany, and a consortium of eight Canadian universities led by the Université du Québec à Montréal. F ...
... North Atlantic Ocean and the Canadian Arctic ArcTrain is a collaborative project between the University of Bremen and the Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research in Germany, and a consortium of eight Canadian universities led by the Université du Québec à Montréal. F ...
Arctic Ocean

The Arctic Ocean (also known as the Northern Ocean), located in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Arctic north polar region, is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceanic divisions. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, although some oceanographers call it the Arctic Mediterranean Sea or simply the Arctic Sea, classifying it a mediterranean sea or an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. Alternatively, the Arctic Ocean can be seen as the northernmost part of the all-encompassing World Ocean.Almost completely surrounded by Eurasia and North America, the Arctic Ocean is partly covered by sea ice throughout the year (and almost completely in winter). The Arctic Ocean's surface temperature and salinity vary seasonally as the ice cover melts and freezes; its salinity is the lowest on average of the five major oceans, due to low evaporation, heavy fresh water inflow from rivers and streams, and limited connection and outflow to surrounding oceanic waters with higher salinities. The summer shrinking of the ice has been quoted at 50%. The US National Snow and Ice Data Center (NSIDC) uses satellite data to provide a daily record of Arctic sea ice cover and the rate of melting compared to an average period and specific past years.