ES145 - Systems Analysis & Physiology
... name was Tan. Tan could only say the word “Tan”. When asked what was his name, he would say Tan. When asked if he was hungry, he would say Tan. Tan could understand speech normally. These patients had no problems moving their mouth or tongue. They could whistle or sing a melody without difficulty. B ...
... name was Tan. Tan could only say the word “Tan”. When asked what was his name, he would say Tan. When asked if he was hungry, he would say Tan. Tan could understand speech normally. These patients had no problems moving their mouth or tongue. They could whistle or sing a melody without difficulty. B ...
Subthalamic High-frequency Deep Brain Stimulation Evaluated in a
... During the past decade, subthalamic high frequency deep brain stimulation (DBS) has proven effective in the treatment of Parkinson's disease complicated with motor fluctuations and L-dopa induced dyskinesias. The current claim holds that the electrical stimulation inhibits neural activity in the sub ...
... During the past decade, subthalamic high frequency deep brain stimulation (DBS) has proven effective in the treatment of Parkinson's disease complicated with motor fluctuations and L-dopa induced dyskinesias. The current claim holds that the electrical stimulation inhibits neural activity in the sub ...
Ch. 11 Notes
... • Consists of 31 segments • Each gives rise to a spinal nerve • Provides 2-way communication b/t brain & body • 2 main functions: ...
... • Consists of 31 segments • Each gives rise to a spinal nerve • Provides 2-way communication b/t brain & body • 2 main functions: ...
Lecture 7 Powerpoint file
... discrete regions of the brain in response to a sensory stimulus: What are the possible interpretations? 1. Area A “drives” area B 2. Area B “drives” area A 3. Area A and B are controlled by a third area independently and their activity is unrelated ...
... discrete regions of the brain in response to a sensory stimulus: What are the possible interpretations? 1. Area A “drives” area B 2. Area B “drives” area A 3. Area A and B are controlled by a third area independently and their activity is unrelated ...
Axial vs. Appendicular Skeleton
... Cervical spinal nerves (C1 to C8) control signals to the back of the head, the neck and shoulders, the arms and hands, and the diaphragm. Thoracic spinal nerves (T1 to T12) control signals to the chest muscles, some muscles of the back, and parts of the abdomen. Lumbar spinal nerves (L1 to L5) contr ...
... Cervical spinal nerves (C1 to C8) control signals to the back of the head, the neck and shoulders, the arms and hands, and the diaphragm. Thoracic spinal nerves (T1 to T12) control signals to the chest muscles, some muscles of the back, and parts of the abdomen. Lumbar spinal nerves (L1 to L5) contr ...
The Nervous System
... • Defects in vision (Visual Field Cuts). • Difficulty with locating objects in environment. • Difficulty with identifying colors (Color Agnosia). • Visual illusions - inaccurately seeing objects. • Word blindness - inability to recognize words. • Difficulty in recognizing drawn objects. • Inability ...
... • Defects in vision (Visual Field Cuts). • Difficulty with locating objects in environment. • Difficulty with identifying colors (Color Agnosia). • Visual illusions - inaccurately seeing objects. • Word blindness - inability to recognize words. • Difficulty in recognizing drawn objects. • Inability ...
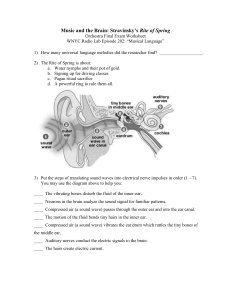
Music and the Brain: Stravinsky`s Rite of Spring
... b. Ibuprofen c. Dopamine d. a press release 7) As the Rite of Spring was being premiered, audience members became so agitated that: a. They booed the performers b. They threw punches c. Old women attacked one another with canes. d. All of the above 8) The auditory cortical fugal network adjusts neur ...
... b. Ibuprofen c. Dopamine d. a press release 7) As the Rite of Spring was being premiered, audience members became so agitated that: a. They booed the performers b. They threw punches c. Old women attacked one another with canes. d. All of the above 8) The auditory cortical fugal network adjusts neur ...
The Neural Control of Movement
... More motor units and faster rate of motor unit activitygreater EMG activity that can be recorded ...
... More motor units and faster rate of motor unit activitygreater EMG activity that can be recorded ...
Nervous System
... of serial sequences of information, visual & auditory details detailed activities required for motor control ...
... of serial sequences of information, visual & auditory details detailed activities required for motor control ...
Nervous System - Berlin High School
... of serial sequences of information, visual & auditory details detailed activities required for motor control ...
... of serial sequences of information, visual & auditory details detailed activities required for motor control ...
Central Nervous System
... information and generates involuntary somatic motor responses. Pons connects the cerebellum to the brain stem and is involved with somatic and visceral motor control Medulla oblongata: connects to spinal cord relays sensory information and regulates autonomic ...
... information and generates involuntary somatic motor responses. Pons connects the cerebellum to the brain stem and is involved with somatic and visceral motor control Medulla oblongata: connects to spinal cord relays sensory information and regulates autonomic ...
Chicurel2001NatureNV..
... neurons in an area of a monkey’s brain controlling limb movement, they could predict how the force exerted by the monkey’s wrist would change8. Subsequent multi-unit experiments have revealed how neurons in such ‘motor’ areas of the brain encode information about the direction of movement9, so that ...
... neurons in an area of a monkey’s brain controlling limb movement, they could predict how the force exerted by the monkey’s wrist would change8. Subsequent multi-unit experiments have revealed how neurons in such ‘motor’ areas of the brain encode information about the direction of movement9, so that ...
29-Audition-Percepti..
... • New style: amplifies specific frequencies, based on a listener’s particular hearing capabilities. • More recently, profoundly deaf listeners may regain some hearing through the use of a cochlear implant (CI). • For listeners with nerve deafness. • However, CIs can only transmit a degraded signal t ...
... • New style: amplifies specific frequencies, based on a listener’s particular hearing capabilities. • More recently, profoundly deaf listeners may regain some hearing through the use of a cochlear implant (CI). • For listeners with nerve deafness. • However, CIs can only transmit a degraded signal t ...
B- Parietal
... C- Between Neurons– 40 pts. (the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of another) ...
... C- Between Neurons– 40 pts. (the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of another) ...
Research Interests: Reading neural codes Current:
... Past: I had previously engaged in reading neural codes in the early visual system, in a structure that receives directly from the retina known as the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN). We presented short videos of animals at the zoo to awake monkeys, and then attempted to calculate backwards what th ...
... Past: I had previously engaged in reading neural codes in the early visual system, in a structure that receives directly from the retina known as the lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN). We presented short videos of animals at the zoo to awake monkeys, and then attempted to calculate backwards what th ...
YG013807812
... response used and this is shown in studies of P300 signals. Patterns of P300 surfs are generated unwillingly. When people recognise and may allow BCIs to interpret groups of thoughts without exercise patients first. In 2000 Jessica Bayliss showed that volunteers tiring computer-generated reality hat ...
... response used and this is shown in studies of P300 signals. Patterns of P300 surfs are generated unwillingly. When people recognise and may allow BCIs to interpret groups of thoughts without exercise patients first. In 2000 Jessica Bayliss showed that volunteers tiring computer-generated reality hat ...
Chapter 11 - Central Nervous System
... arbor vitae - pattern of white and gray matter vermis connects hemispheres cerebellar cortex – gray matter Coordinates voluntary muscle movements • inferior peduncle receives proprioception • middle peduncle receives desired motion from cerebrum • cerebellum integrates a and b • superior pedun ...
... arbor vitae - pattern of white and gray matter vermis connects hemispheres cerebellar cortex – gray matter Coordinates voluntary muscle movements • inferior peduncle receives proprioception • middle peduncle receives desired motion from cerebrum • cerebellum integrates a and b • superior pedun ...
How Psychologists Study the Brain
... his patients during surgery to determine what functions the various parts of the brain perform so as to localize (focus on) the malfunctioning part for which surgery was required ...
... his patients during surgery to determine what functions the various parts of the brain perform so as to localize (focus on) the malfunctioning part for which surgery was required ...
Chapter 11
... • Sulci divide each cerebral hemisphere into 5 functional areas called lobes (named for skull ...
... • Sulci divide each cerebral hemisphere into 5 functional areas called lobes (named for skull ...
GUIDELINES FORTHE DIAGNOSIS OF BRAIN DEATH
... physician to determine the safety and validity of this test for apnea. Testing for apnea without passive oxygenation is not recommended. In addition to its potential deleterious effects on the brain, the resultant hypoxemia can occasionally cause complex movements of the limbs and trunk, presumably ...
... physician to determine the safety and validity of this test for apnea. Testing for apnea without passive oxygenation is not recommended. In addition to its potential deleterious effects on the brain, the resultant hypoxemia can occasionally cause complex movements of the limbs and trunk, presumably ...
Connecting cortex to machines: recent advances in brain interfaces
... humans1 and in behaving monkeys2 in the 1960s. Electrical stimulation has been used to influence brain function in alert monkeys and to treat neurological disorders in conscious humans since the 1950s (refs. 3,4). Today, implantation of physical devices into the brain is increasingly used to treat n ...
... humans1 and in behaving monkeys2 in the 1960s. Electrical stimulation has been used to influence brain function in alert monkeys and to treat neurological disorders in conscious humans since the 1950s (refs. 3,4). Today, implantation of physical devices into the brain is increasingly used to treat n ...
Unit 3B: The Brain Messing with the Brain Scientists can electrically
... Mind’s subsystems localized in particular brain regions yet brain acts as whole unit Brain divides mental functions (speaking, perceiving, thinking, remembering) into sub-functions o Ex: breaks vision into color, depth, movement, form Continuous stream of experience is actually subdivided info ...
... Mind’s subsystems localized in particular brain regions yet brain acts as whole unit Brain divides mental functions (speaking, perceiving, thinking, remembering) into sub-functions o Ex: breaks vision into color, depth, movement, form Continuous stream of experience is actually subdivided info ...
Nervous System
... • At the back portion of the frontal lobe, along the sulcus that separates it from the parietal lobe, is an area called the motor cortex. • In studies with brain surgery patients, stimulating areas of the motor cortex with tiny electrical probes caused movements. • It has been possible for researche ...
... • At the back portion of the frontal lobe, along the sulcus that separates it from the parietal lobe, is an area called the motor cortex. • In studies with brain surgery patients, stimulating areas of the motor cortex with tiny electrical probes caused movements. • It has been possible for researche ...
Chapter 2 Review Notes
... A neural impulse fires when the neuron is stimulated by pressure, heat, light, or chemical messages from adjacent neurons. Received signals trigger an impulse only if the excitatory signals minus the inhibitory signals exceeds a minimum intensity called the threshold. The neuron’s reaction is an all ...
... A neural impulse fires when the neuron is stimulated by pressure, heat, light, or chemical messages from adjacent neurons. Received signals trigger an impulse only if the excitatory signals minus the inhibitory signals exceeds a minimum intensity called the threshold. The neuron’s reaction is an all ...