Diffraction Intensity, resolving power, Xray diffraction
... Ans: It is produced by a circular aperture and has rings Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. ...
... Ans: It is produced by a circular aperture and has rings Copyright © 2012 Pearson Education Inc. ...
Introduction to Optics Frank L. Pedrotti Leno M. Pedrotti Leno S
... Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk © Pearson Education Limited 2014 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, e ...
... Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk © Pearson Education Limited 2014 All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted in any form or by any means, e ...
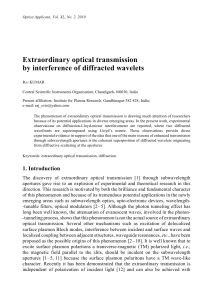
Extraordinary optical transmission by interference of diffracted
... subwavelength apertures and the peak intensity will reduce with increase in slit width due to sharp decrease in amplitude of boundary diffraction wave away from the geometrically illuminated to geometrically shadowed transition boundary. Here we have considered a single diffraction only but, actuall ...
... subwavelength apertures and the peak intensity will reduce with increase in slit width due to sharp decrease in amplitude of boundary diffraction wave away from the geometrically illuminated to geometrically shadowed transition boundary. Here we have considered a single diffraction only but, actuall ...
n 1n d
... The corresponding modulation of the coherent scattering length density b1 is two orders of magnitude larger than in the best PNR materials reported up to now!! b1 = (bN), due to phase separation of the constituent compounds (b) can be large even if (N) is relatively small !!! M. Fally, I. Dreve ...
... The corresponding modulation of the coherent scattering length density b1 is two orders of magnitude larger than in the best PNR materials reported up to now!! b1 = (bN), due to phase separation of the constituent compounds (b) can be large even if (N) is relatively small !!! M. Fally, I. Dreve ...
CMock exam IV paper 2
... (d) Between the plates, there is an acceleration/ force on the electron directed upward. (1M) With an initial constant horizontal velocity, the resulting path is parabolic between the plates.(1M) Outside the plates, there is no electric field, and no force acts on the electron, because of inertia, t ...
... (d) Between the plates, there is an acceleration/ force on the electron directed upward. (1M) With an initial constant horizontal velocity, the resulting path is parabolic between the plates.(1M) Outside the plates, there is no electric field, and no force acts on the electron, because of inertia, t ...
two-slit interference,one photon at a time
... Two-slit interference,one photon at a time 一、目的:encounter Wave-Particle Duality with photons 二、理論:refer to modern physics or optics physics 三、方法:Decreasing the light output of a given incandescent bulb shifts the spectrum toward the longer, red wavelengths. So,by turning down the bulb intensity and ...
... Two-slit interference,one photon at a time 一、目的:encounter Wave-Particle Duality with photons 二、理論:refer to modern physics or optics physics 三、方法:Decreasing the light output of a given incandescent bulb shifts the spectrum toward the longer, red wavelengths. So,by turning down the bulb intensity and ...
Laboratory 2 Thomas Young and the Wave
... in your experiment, L is the total distance from slit-to-mirror-to-image. CAUTION: Do not look into the laser beam or even at a directly reflected beam. Laser light is very intense and can damage your eyes more than you think. Handle optical devices in such a way that your fingers do not touch the o ...
... in your experiment, L is the total distance from slit-to-mirror-to-image. CAUTION: Do not look into the laser beam or even at a directly reflected beam. Laser light is very intense and can damage your eyes more than you think. Handle optical devices in such a way that your fingers do not touch the o ...
Purdue University PHYS 221 EXAM II 11/6/03
... A spherical concave mirror has a radius of curvature of 6.0 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a 6.0-cm object be placed to obtain an image that is 48 cm tall? (10 points) ...
... A spherical concave mirror has a radius of curvature of 6.0 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a 6.0-cm object be placed to obtain an image that is 48 cm tall? (10 points) ...
Light-More-interference
... The water drops act like prisms. Light enters near the top of the drop on one side, is reflected (total internal reflection), which means it undergoes two refractions. (Refraction as it enters the water drop and refraction when it leaves the water drop.) The colors are therefore dispersed . Violet l ...
... The water drops act like prisms. Light enters near the top of the drop on one side, is reflected (total internal reflection), which means it undergoes two refractions. (Refraction as it enters the water drop and refraction when it leaves the water drop.) The colors are therefore dispersed . Violet l ...
X‐ray diffraction: Determining lattice constants of crystal structure
... A schematic of the experiment is shown in Figure 2. The x-ray tube has a molybdenum anode so that the emitted x-rays have the following characteristic wavelengths: Kα = 71.08 pm and Kβ = 63.09 pm. These xrays are collimated into a beam by the collimating slit and the incident beam makes an angle θ w ...
... A schematic of the experiment is shown in Figure 2. The x-ray tube has a molybdenum anode so that the emitted x-rays have the following characteristic wavelengths: Kα = 71.08 pm and Kβ = 63.09 pm. These xrays are collimated into a beam by the collimating slit and the incident beam makes an angle θ w ...
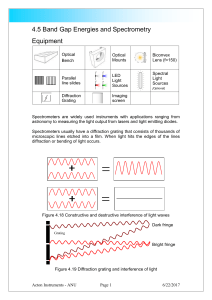
Diffraction of light by a single slit and gratings
... geometric ray optics the transmitted beam would have the same cross section as the slit, but what we indeed observe is a drastically different diffraction pattern. The main properties of the diffraction pattern can be understood with the aid of Fig. 2 and Fig. 3. For the case of Fraunhofer diffracti ...
... geometric ray optics the transmitted beam would have the same cross section as the slit, but what we indeed observe is a drastically different diffraction pattern. The main properties of the diffraction pattern can be understood with the aid of Fig. 2 and Fig. 3. For the case of Fraunhofer diffracti ...
hw08_assingnment
... What is the rate at which the electric field is changing between the plates if the square plates are 1.60 cm on a side? 3. If the magnetic field in a traveling EM wave has a peak magnitude of 17.5 nT at a given point, what is the peak magnitude of the electric field? ...
... What is the rate at which the electric field is changing between the plates if the square plates are 1.60 cm on a side? 3. If the magnetic field in a traveling EM wave has a peak magnitude of 17.5 nT at a given point, what is the peak magnitude of the electric field? ...
Electromagnetic radiation – the nature of light
... White light can be separated into different frequency waves (for example by a prism). ...
... White light can be separated into different frequency waves (for example by a prism). ...
Fraunhofer Diffraction
... 8. Close both slits so that only the (0, 0) diffraction order is transmitted. Observe the image on the wall. 9. Fully open one of the slits so diffraction orders (0, n) are transmitted. Observe the image on the wall. Repeat with the other slit. 10. Open and reposition one of the slits to transmit th ...
... 8. Close both slits so that only the (0, 0) diffraction order is transmitted. Observe the image on the wall. 9. Fully open one of the slits so diffraction orders (0, n) are transmitted. Observe the image on the wall. Repeat with the other slit. 10. Open and reposition one of the slits to transmit th ...
PSC1341 Chapter 4 Waves Waves • A wave is a repeating
... has either one curved surface or one flat surface or two curved surfaces. Lenses are either convex or concave. Convex lenses are thicker in the middle then the edges and concave are thicker at the edges then the middle. When light travels through lenses, refraction occurs. The light bends either out ...
... has either one curved surface or one flat surface or two curved surfaces. Lenses are either convex or concave. Convex lenses are thicker in the middle then the edges and concave are thicker at the edges then the middle. When light travels through lenses, refraction occurs. The light bends either out ...
Diffraction
Diffraction refers to various phenomena which occur when a wave encounters an obstacle or a slit. In classical physics, the diffraction phenomenon is described as the interference of waves according to the Huygens–Fresnel principle. These characteristic behaviors are exhibited when a wave encounters an obstacle or a slit that is comparable in size to its wavelength. Similar effects occur when a light wave travels through a medium with a varying refractive index, or when a sound wave travels through a medium with varying acoustic impedance. Diffraction occurs with all waves, including sound waves, water waves, and electromagnetic waves such as visible light, X-rays and radio waves.Since physical objects have wave-like properties (at the atomic level), diffraction also occurs with matter and can be studied according to the principles of quantum mechanics. Italian scientist Francesco Maria Grimaldi coined the word ""diffraction"" and was the first to record accurate observations of the phenomenon in 1660.While diffraction occurs whenever propagating waves encounter such changes, its effects are generally most pronounced for waves whose wavelength is roughly comparable to the dimensions of the diffracting object or slit. If the obstructing object provides multiple, closely spaced openings, a complex pattern of varying intensity can result. This is due to the addition, or interference, of different parts of a wave that travels to the observer by different paths, where different path lengths result in different phases (see diffraction grating and wave superposition). The formalism of diffraction can also describe the way in which waves of finite extent propagate in free space. For example, the expanding profile of a laser beam, the beam shape of a radar antenna and the field of view of an ultrasonic transducer can all be analyzed using diffraction equations.