text
... all the individual retinal positions provide branches that converge on individual temporal cortex neurons. This means that retinotopy is lost, that information about the spatial location of an object on the retina is no longer present, and that single temporal neurons respond to objects located any ...
... all the individual retinal positions provide branches that converge on individual temporal cortex neurons. This means that retinotopy is lost, that information about the spatial location of an object on the retina is no longer present, and that single temporal neurons respond to objects located any ...
Microsoft PowerPoint - NCRM EPrints Repository
... types and stages of work that went into the refurbishment of the façade of the building It is especially useful to draw attention to forms of work that ‘cover their tracks’ such that the product of labour conceals the labour that went into it Collage can be used both as a mode of analysis to gen ...
... types and stages of work that went into the refurbishment of the façade of the building It is especially useful to draw attention to forms of work that ‘cover their tracks’ such that the product of labour conceals the labour that went into it Collage can be used both as a mode of analysis to gen ...
Special Senses
... The information will be sent to vestibular nuclei between the pons and medulla and to the cerebellum. With information about equilibrium, vision and proprioception, appropriate motor outputs to maintain balance can be coordinated. *Equilibrium information may also be routed to the cortex, in the ins ...
... The information will be sent to vestibular nuclei between the pons and medulla and to the cerebellum. With information about equilibrium, vision and proprioception, appropriate motor outputs to maintain balance can be coordinated. *Equilibrium information may also be routed to the cortex, in the ins ...
primary visual cortex - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
... segregated into distinct pathways that project to areas of the secondary visual cortex and, then, the association visual cortex. ...
... segregated into distinct pathways that project to areas of the secondary visual cortex and, then, the association visual cortex. ...
Slide ()
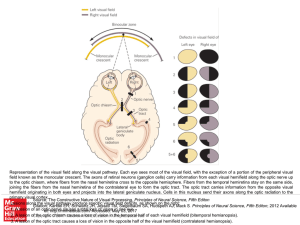
... field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the optic nerve up to the optic chiasm, where fibers from the nasal hemiretina cross to the opposite hemisphere. Fibers from the temporal hemiretina stay on the sam ...
... field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the optic nerve up to the optic chiasm, where fibers from the nasal hemiretina cross to the opposite hemisphere. Fibers from the temporal hemiretina stay on the sam ...
Slide ()
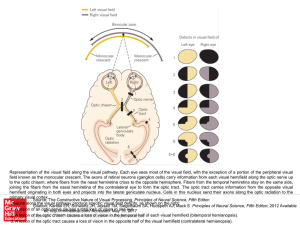
... field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the optic nerve up to the optic chiasm, where fibers from the nasal hemiretina cross to the opposite hemisphere. Fibers from the temporal hemiretina stay on the sam ...
... field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the optic nerve up to the optic chiasm, where fibers from the nasal hemiretina cross to the opposite hemisphere. Fibers from the temporal hemiretina stay on the sam ...
16. Taste, smell
... proximity with medial lemniscal fibers carrying somatosensory signals from tongue to lateral post central gyrus); third order fibers from thalamus terminate in cortex of anterior insular lobe (ppts. 5 & 6) • smell: olfactory sense informs of presence of other animals even recognition of individuals ...
... proximity with medial lemniscal fibers carrying somatosensory signals from tongue to lateral post central gyrus); third order fibers from thalamus terminate in cortex of anterior insular lobe (ppts. 5 & 6) • smell: olfactory sense informs of presence of other animals even recognition of individuals ...
Chemical Senses
... The 3-D model shown on the right (from Couto & Dickson, 2005) is that of a fly antennal lobe (AL), the equivalent of the vertebrate olfactory bulb. As you can see, the AL is composed of spheroidal structures, the glomeruli. While vertebrate olfactory bulbs may contain thousands of glomeruli, th ...
... The 3-D model shown on the right (from Couto & Dickson, 2005) is that of a fly antennal lobe (AL), the equivalent of the vertebrate olfactory bulb. As you can see, the AL is composed of spheroidal structures, the glomeruli. While vertebrate olfactory bulbs may contain thousands of glomeruli, th ...
ap-ii-lab-quiz-1-answers
... B) Sound waves (hearing) and head location/movements in space (equilibrium) are both detected by hair receptor cells that are neurons. C) Both mechanisms require vibrations. D) Both require the movement of fluid, and both require vibrations. Answer: A 4) Which of the structures below report head acc ...
... B) Sound waves (hearing) and head location/movements in space (equilibrium) are both detected by hair receptor cells that are neurons. C) Both mechanisms require vibrations. D) Both require the movement of fluid, and both require vibrations. Answer: A 4) Which of the structures below report head acc ...
Hair cells
... The organ of Corti, which transduces sound in the cochlea, consists of: -Basilar membrane: Bottom of cochlear duct -Hair cells with associated sensory neurons & stereocilia -Tectorial membrane: Overhanging, gelatinous membrane (holds top of stereocilia in place) Stereocilia of hair cells bend in res ...
... The organ of Corti, which transduces sound in the cochlea, consists of: -Basilar membrane: Bottom of cochlear duct -Hair cells with associated sensory neurons & stereocilia -Tectorial membrane: Overhanging, gelatinous membrane (holds top of stereocilia in place) Stereocilia of hair cells bend in res ...
Neurotransmitters - Motivational Interviewing Network of Trainers
... that guide what follows next (including how we react to love or perceived threats). There are over 50 types and are secreted by neurons and various cells throughout the body. The internal & external environment, affects which transmitters are released. 2. Dopamine is neurotransmitter that helps with ...
... that guide what follows next (including how we react to love or perceived threats). There are over 50 types and are secreted by neurons and various cells throughout the body. The internal & external environment, affects which transmitters are released. 2. Dopamine is neurotransmitter that helps with ...
Neurologic Music Therapy: An Overview
... oscillating bodies lock into phase so that they vibrate in harmony, synchronizing rhythms ...
... oscillating bodies lock into phase so that they vibrate in harmony, synchronizing rhythms ...
Visual Queries
... Just-in-time & just-enough processing is provided by rapid scanning–-- eye movements within 100 milliseconds. Visual processing requires attention: “We are conscious of the field of information to which we have rapid access rather than being immediately conscious of the world.” ...
... Just-in-time & just-enough processing is provided by rapid scanning–-- eye movements within 100 milliseconds. Visual processing requires attention: “We are conscious of the field of information to which we have rapid access rather than being immediately conscious of the world.” ...
File - Dr. Jerry Cronin
... Primary visual area of cerebral cortex (area 17) in occipital lobe Left eye and its pathways ...
... Primary visual area of cerebral cortex (area 17) in occipital lobe Left eye and its pathways ...
Slide ()
... turns of the mouse cochlea. As indicated in the upper turn, the fluid spaces are the scala tympani and scala vestibuli filled with perilymph, and scala media filled with endolymph. They are separated by the thin Reissner membrane and by the basilar membrane on which the organ of Corti is located. Wh ...
... turns of the mouse cochlea. As indicated in the upper turn, the fluid spaces are the scala tympani and scala vestibuli filled with perilymph, and scala media filled with endolymph. They are separated by the thin Reissner membrane and by the basilar membrane on which the organ of Corti is located. Wh ...
septins were depleted Orai1 became sites. However, more work will be
... predominantly upon distal cues. These cell types include grid cells that respond when a rat visits a regular array of locations [7], head-direction cells that respond to allocentric head direction [8], and boundary-vector cells that respond to the location of barriers to movement [9,10]. In contrast ...
... predominantly upon distal cues. These cell types include grid cells that respond when a rat visits a regular array of locations [7], head-direction cells that respond to allocentric head direction [8], and boundary-vector cells that respond to the location of barriers to movement [9,10]. In contrast ...
Sensa1on and Percep1on
... sensory receptor neurons located in the nasal mucosa • When odourants enter the nose they bind to receptors located on olfactory sensory receptor neurons • An ac&on poten&al occurs in olfactory sensory receptor neurons when enough odourant molecules bind to receptors ...
... sensory receptor neurons located in the nasal mucosa • When odourants enter the nose they bind to receptors located on olfactory sensory receptor neurons • An ac&on poten&al occurs in olfactory sensory receptor neurons when enough odourant molecules bind to receptors ...
Chapter 4 – Sensation
... adjacent neurons’ response to help distinguish edges since the outermost visual cells won’t be inhibited as much Color can be described with three dimensions: hue, brightness, and saturation Hue is the attribute that distinguishes one color from another and varies with wavelength Brightness is ...
... adjacent neurons’ response to help distinguish edges since the outermost visual cells won’t be inhibited as much Color can be described with three dimensions: hue, brightness, and saturation Hue is the attribute that distinguishes one color from another and varies with wavelength Brightness is ...
Psychology Unit 2 over Chapters 3 and 4 Chapter 3 “Biological
... Clarify how the autonomic nervous system works in emergency and everyday situations Describe what hormones are and how they affect behavior Distinguish the parts of neurons and what they do Describe electrical responses of neurons and what makes them possible Explain how neurons use neurot ...
... Clarify how the autonomic nervous system works in emergency and everyday situations Describe what hormones are and how they affect behavior Distinguish the parts of neurons and what they do Describe electrical responses of neurons and what makes them possible Explain how neurons use neurot ...
Key Elements of Sensation
... Sound Localization • Involves interpretation by the brain of sound waves entering both ears in order to determine the direction the noise is coming from. • Possible because the sound waves arrive at one ear faster than they reach the other ear, and this information about timing is then interpre ...
... Sound Localization • Involves interpretation by the brain of sound waves entering both ears in order to determine the direction the noise is coming from. • Possible because the sound waves arrive at one ear faster than they reach the other ear, and this information about timing is then interpre ...
Here
... Which part of the ear is lined with cilia that are triggered by sound and sends nerve signals to transmit impulses to the brain? B 100 ...
... Which part of the ear is lined with cilia that are triggered by sound and sends nerve signals to transmit impulses to the brain? B 100 ...
Brain Day - No Regrets
... The ear is divided into three parts: outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. The outer ear (pinna) collects sound waves and sends them through the ear canal to the eardrum (tympanic membrane). The middle ear is air-filled space containing ossicles, the three smallest bones in the human body (malleus, ...
... The ear is divided into three parts: outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear. The outer ear (pinna) collects sound waves and sends them through the ear canal to the eardrum (tympanic membrane). The middle ear is air-filled space containing ossicles, the three smallest bones in the human body (malleus, ...
Cortical Representation
... – Coefficient for F(t) shows the correlation (a measure of similarity) between the signal and F(t) ...
... – Coefficient for F(t) shows the correlation (a measure of similarity) between the signal and F(t) ...