The Field Effect Transistor
... for the pinch-off voltage with the rather liberal limits given on the data page for “GateSource Cutoff Voltage”. Common-source transfer characteristics The program measures the current by measuring the voltage drop across the 1k drain resistor. Make a copy of the computer plot of drain current vs. ...
... for the pinch-off voltage with the rather liberal limits given on the data page for “GateSource Cutoff Voltage”. Common-source transfer characteristics The program measures the current by measuring the voltage drop across the 1k drain resistor. Make a copy of the computer plot of drain current vs. ...
The Comparator
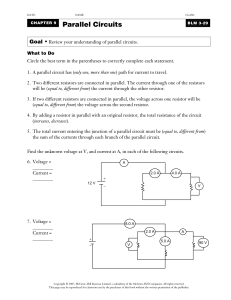
... A voltage divider is a circuit that produces an output voltage (Vout) that is a fraction of its input Vout is the voltage across the R2 Worked out by the resistor ratio ...
... A voltage divider is a circuit that produces an output voltage (Vout) that is a fraction of its input Vout is the voltage across the R2 Worked out by the resistor ratio ...
Application Note 956-1 The Criterion for the Tangential Sensitivity Measurement
... The Criterion for the Tangential Sensitivity Measurement ...
... The Criterion for the Tangential Sensitivity Measurement ...
07-NileshJoshi
... System is said to be causal if the present value of the output signal depends only on the present and or the past value of the input signal. Such a system is often referred to as being nonanticipatory, as the output doesn’t anticipate future value of the input. The if the resistor and capacitor are ...
... System is said to be causal if the present value of the output signal depends only on the present and or the past value of the input signal. Such a system is often referred to as being nonanticipatory, as the output doesn’t anticipate future value of the input. The if the resistor and capacitor are ...
Experiment No 2: BJT Characteristics Theory
... The transistor is used as a switch in Cut-off (OFF) and Saturation (ON) regions and as an amplifier in Active region. Reverse Active mode is rarely used (it is used as input stage in TTL gates in digital circuits). The transistor can be considered as a two port network. Three configurations are poss ...
... The transistor is used as a switch in Cut-off (OFF) and Saturation (ON) regions and as an amplifier in Active region. Reverse Active mode is rarely used (it is used as input stage in TTL gates in digital circuits). The transistor can be considered as a two port network. Three configurations are poss ...
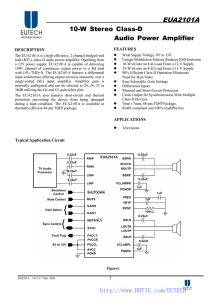
EUA2101A 10-W Stereo Class-D Audio Power Amplifier
... The EUA2101A is a high efficiency, 2 channel bridged-tied load (BTL), class-D audio power amplifier. Operating from a 12V power supply, EUA2101A is capable of delivering 10W/ channel of continuous output power to a 8Ω load with 10% THD+N. The EUA2101A features a differential input architecture offer ...
... The EUA2101A is a high efficiency, 2 channel bridged-tied load (BTL), class-D audio power amplifier. Operating from a 12V power supply, EUA2101A is capable of delivering 10W/ channel of continuous output power to a 8Ω load with 10% THD+N. The EUA2101A features a differential input architecture offer ...
Test Procedure for the NCP1013LED Evaluation Board Introduction:
... 3. Turn on the AC source and the power supply demo board the open circuit output voltage should be in the range of 8.6 +1.5 volt/‐ 0.5 volts on the DVM. 4. Adjust the electronic load from no current load (high impedance) slowly until the output voltage measures 7.5V. The output current should m ...
... 3. Turn on the AC source and the power supply demo board the open circuit output voltage should be in the range of 8.6 +1.5 volt/‐ 0.5 volts on the DVM. 4. Adjust the electronic load from no current load (high impedance) slowly until the output voltage measures 7.5V. The output current should m ...
Transistor–transistor logic

Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a class of digital circuits built from bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and resistors. It is called transistor–transistor logic because both the logic gating function (e.g., AND) and the amplifying function are performed by transistors (contrast with RTL and DTL).TTL is notable for being a widespread integrated circuit (IC) family used in many applications such as computers, industrial controls, test equipment and instrumentation, consumer electronics, synthesizers, etc. The designation TTL is sometimes used to mean TTL-compatible logic levels, even when not associated directly with TTL integrated circuits, for example as a label on the inputs and outputs of electronic instruments.After their introduction in integrated circuit form in 1963 by Sylvania, TTL integrated circuits were manufactured by several semiconductor companies, with the 7400 series (also called 74xx) by Texas Instruments becoming particularly popular. TTL manufacturers offered a wide range of logic gate, flip-flops, counters, and other circuits. Several variations from the original bipolar TTL concept were developed, giving circuits with higher speed or lower power dissipation to allow optimization of a design. TTL circuits simplified design of systems compared to earlier logic families, offering superior speed to resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and easier design layout than emitter-coupled logic (ECL). The design of the input and outputs of TTL gates allowed many elements to be interconnected.TTL became the foundation of computers and other digital electronics. Even after much larger scale integrated circuits made multiple-circuit-board processors obsolete, TTL devices still found extensive use as the ""glue"" logic interfacing more densely integrated components. TTL devices were originally made in ceramic and plastic dual-in-line (DIP) packages, and flat-pack form. TTL chips are now also made in surface-mount packages. Successors to the original bipolar TTL logic often are interchangeable in function with the original circuits, but with improved speed or lower power dissipation.