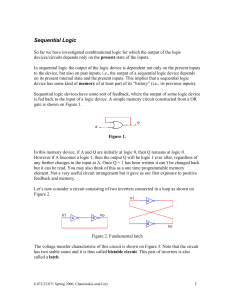
Direct Current Measurement and Ohm`s Law
... When preparing to draw a graph the first thing to do is pick a scale to use on your graph paper. Unless you are merely making a rough graph to visualize the trend of data, the scales should be picked so that the graph fills between a half and a whole sheet of paper. A graph that is too small is usel ...
... When preparing to draw a graph the first thing to do is pick a scale to use on your graph paper. Unless you are merely making a rough graph to visualize the trend of data, the scales should be picked so that the graph fills between a half and a whole sheet of paper. A graph that is too small is usel ...
50 dB GSM PA Controller AD8315 FEATURES
... True integration function in control loop Low power: 20 mW at 2.7 V, 38 mW at 5 V Power-down to 10.8 μW ...
... True integration function in control loop Low power: 20 mW at 2.7 V, 38 mW at 5 V Power-down to 10.8 μW ...
MAX7036 300MHz to 450MHz ASK Receiver with Internal IF Filter General Description
... The MAX7036 is available in a 20-pin thin QFN package with an exposed pad and is specified over the AEC-Q100 Level 2 (-40°C to +105°C) temperature range. ...
... The MAX7036 is available in a 20-pin thin QFN package with an exposed pad and is specified over the AEC-Q100 Level 2 (-40°C to +105°C) temperature range. ...
Formulas - Brown Book Shop
... Peak Amperes = Effective (RMS) Amperes x Power Factor (PF) = Watts/VA VA (apparent power) = Volts x Ampere or Watts/Power Factor VA 1-Phase = Volts x Amperes VA 3-Phase = Volts x Amperes x 3 Watts (real power) Single-Phase = Volts x Amperes x Power Factor Watts (real power) Three-Phase = Volts x Amp ...
... Peak Amperes = Effective (RMS) Amperes x Power Factor (PF) = Watts/VA VA (apparent power) = Volts x Ampere or Watts/Power Factor VA 1-Phase = Volts x Amperes VA 3-Phase = Volts x Amperes x 3 Watts (real power) Single-Phase = Volts x Amperes x Power Factor Watts (real power) Three-Phase = Volts x Amp ...
ADR391 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... The ADR39x family of micropower, low dropout voltage references provides a stable output voltage from a minimum supply of 300 mV above the output. Their advanced design eliminates the need for external capacitors, which further reduces board space and system cost. The combination of low power operat ...
... The ADR39x family of micropower, low dropout voltage references provides a stable output voltage from a minimum supply of 300 mV above the output. Their advanced design eliminates the need for external capacitors, which further reduces board space and system cost. The combination of low power operat ...
Multi Stage Amplifiers
... The first cut off frequency lies in low frequency range, in which the impedance by coupling capacitor Cc is comparable to the collector resistance Rc. Thus it largely the current amplification. The second cut-off frequency lies in the high frequency range where the area offered by coupling capacitor ...
... The first cut off frequency lies in low frequency range, in which the impedance by coupling capacitor Cc is comparable to the collector resistance Rc. Thus it largely the current amplification. The second cut-off frequency lies in the high frequency range where the area offered by coupling capacitor ...
AD811
... AD811 is limited by the associated rise in junction temperature. For the plastic packages, the maximum safe junction temperature is 145°C. For the CERDIP and LCC packages, the maximum junction temperature is 175°C. If these maximums are exceeded momentarily, proper circuit operation is restored as s ...
... AD811 is limited by the associated rise in junction temperature. For the plastic packages, the maximum safe junction temperature is 145°C. For the CERDIP and LCC packages, the maximum junction temperature is 175°C. If these maximums are exceeded momentarily, proper circuit operation is restored as s ...
Laboratory 1 Ohm`s Law
... First set channel A to read GND. You should see a straight line trace. (If you cannot find the trace, push the "beam find" button, and adjust the x-pos and y-pos knobs to center the trace.) Adjust the focus and intensity knobs till you have a focused, reasonably intense (but not overly bright) trace ...
... First set channel A to read GND. You should see a straight line trace. (If you cannot find the trace, push the "beam find" button, and adjust the x-pos and y-pos knobs to center the trace.) Adjust the focus and intensity knobs till you have a focused, reasonably intense (but not overly bright) trace ...
LINEAR VARIABLE DIFFERENTIAL TRANSFORMERS
... armature will then move the flux field into one secondary and out of the other. This results in an increase in the voltage induced in one secondary and a corresponding decrease in the other. The secondary coils are normally connected in series with opposing phase. The net output of the LVDT is the d ...
... armature will then move the flux field into one secondary and out of the other. This results in an increase in the voltage induced in one secondary and a corresponding decrease in the other. The secondary coils are normally connected in series with opposing phase. The net output of the LVDT is the d ...
Transistor–transistor logic

Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a class of digital circuits built from bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and resistors. It is called transistor–transistor logic because both the logic gating function (e.g., AND) and the amplifying function are performed by transistors (contrast with RTL and DTL).TTL is notable for being a widespread integrated circuit (IC) family used in many applications such as computers, industrial controls, test equipment and instrumentation, consumer electronics, synthesizers, etc. The designation TTL is sometimes used to mean TTL-compatible logic levels, even when not associated directly with TTL integrated circuits, for example as a label on the inputs and outputs of electronic instruments.After their introduction in integrated circuit form in 1963 by Sylvania, TTL integrated circuits were manufactured by several semiconductor companies, with the 7400 series (also called 74xx) by Texas Instruments becoming particularly popular. TTL manufacturers offered a wide range of logic gate, flip-flops, counters, and other circuits. Several variations from the original bipolar TTL concept were developed, giving circuits with higher speed or lower power dissipation to allow optimization of a design. TTL circuits simplified design of systems compared to earlier logic families, offering superior speed to resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and easier design layout than emitter-coupled logic (ECL). The design of the input and outputs of TTL gates allowed many elements to be interconnected.TTL became the foundation of computers and other digital electronics. Even after much larger scale integrated circuits made multiple-circuit-board processors obsolete, TTL devices still found extensive use as the ""glue"" logic interfacing more densely integrated components. TTL devices were originally made in ceramic and plastic dual-in-line (DIP) packages, and flat-pack form. TTL chips are now also made in surface-mount packages. Successors to the original bipolar TTL logic often are interchangeable in function with the original circuits, but with improved speed or lower power dissipation.