SN75ALS056 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... loading to the bus. By using a 2-V pullup termination on the bus, the output signal swing is approximately 1 V, which reduces the power necessary to drive the bus load capacitance. The driver outputs generate trapezoidal waveforms that reduce crosstalk between channels. The drivers are capable of dr ...
... loading to the bus. By using a 2-V pullup termination on the bus, the output signal swing is approximately 1 V, which reduces the power necessary to drive the bus load capacitance. The driver outputs generate trapezoidal waveforms that reduce crosstalk between channels. The drivers are capable of dr ...
VUI30-12N1 - IXYS Power
... correction, set up as follows: • input from three phase mains - wide range of input voltage - mains currents approx. sinusoidal in phase with mains voltage - topology permits to control overcurrent such as in case of input voltage peaks • output - direct current link - buck type conve ...
... correction, set up as follows: • input from three phase mains - wide range of input voltage - mains currents approx. sinusoidal in phase with mains voltage - topology permits to control overcurrent such as in case of input voltage peaks • output - direct current link - buck type conve ...
Thermoelectricity from wasted heat of integrated circuits | SpringerLink
... Received: 31 July 2011 / Accepted: 24 April 2012 / Published online: 22 May 2012 Ó The Author(s) 2012. This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com ...
... Received: 31 July 2011 / Accepted: 24 April 2012 / Published online: 22 May 2012 Ó The Author(s) 2012. This article is published with open access at Springerlink.com ...
UC2577-ADJ: Simple Step-Up Voltage
... APPLICATIONS INFORMATION Step-up (Boost) Regulator The Block Diagram shows a step-up switching regulator utilizing the UC2577. The regulator produces an output voltage higher than the input voltage. The UC2577 turns its switch on and off at a fixed frequency of 52kHz, thus storing energy in the indu ...
... APPLICATIONS INFORMATION Step-up (Boost) Regulator The Block Diagram shows a step-up switching regulator utilizing the UC2577. The regulator produces an output voltage higher than the input voltage. The UC2577 turns its switch on and off at a fixed frequency of 52kHz, thus storing energy in the indu ...
A Modified CMOS Differential-Pair-Based Triangular-and-Trapezoidal-to-Sine Converter Kanitpong Pengwon and Ekachai Leelarasmee
... SFDR or better is acceptable while only -40 dBc one is required for instrument applications [2]. Many techniques to realize sinusoidal waveforms have been reported. Most of them, such as [1], [3] and [6], are based on nonlinear or picewiselinear approximations because it is difficult to directly gen ...
... SFDR or better is acceptable while only -40 dBc one is required for instrument applications [2]. Many techniques to realize sinusoidal waveforms have been reported. Most of them, such as [1], [3] and [6], are based on nonlinear or picewiselinear approximations because it is difficult to directly gen ...
Word Document - UCSD VLSI CAD Laboratory
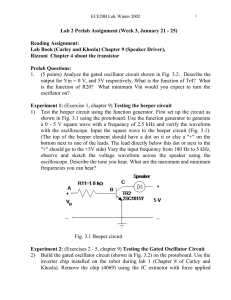
... Khosla). Remove the chip (4069) using the IC extractor with force applied ...
... Khosla). Remove the chip (4069) using the IC extractor with force applied ...
A Breakdown Voltage Multiplier for High Voltage Swing Drivers
... ). Conto satisfy the resistance required for the desired was set to 80 mA to achieve sequently, the current through . The voltage that turns on and off at the 1.8 V across node C is lowered with an emitter-follower and fed to the base and simultaneously switch on and of ; in this manner off. was Aft ...
... ). Conto satisfy the resistance required for the desired was set to 80 mA to achieve sequently, the current through . The voltage that turns on and off at the 1.8 V across node C is lowered with an emitter-follower and fed to the base and simultaneously switch on and of ; in this manner off. was Aft ...
LT1880 - SOT-23, Rail-to-Rail Output, Picoamp Input Current Precision Op Amp
... The extremely low input bias currents, 150pA, allow high accuracy to be maintained with high impedance sources and feedback networks. The LT1880’s low input bias currents are obtained by using a cancellation circuit on-chip. This causes the resulting IBIAS+ and IBIAS– to be uncorrelated, as implied ...
... The extremely low input bias currents, 150pA, allow high accuracy to be maintained with high impedance sources and feedback networks. The LT1880’s low input bias currents are obtained by using a cancellation circuit on-chip. This causes the resulting IBIAS+ and IBIAS– to be uncorrelated, as implied ...
AN-6024 — FMS6xxx Product Series Understanding Analog Video Signal Clamps, Bias, Description
... known DC level and biased with a voltage swing in the range of 0 to 1.3V DC. There is no feedback control on the absolute DC level of the output voltage and may vary with system temperature and supply voltage. ...
... known DC level and biased with a voltage swing in the range of 0 to 1.3V DC. There is no feedback control on the absolute DC level of the output voltage and may vary with system temperature and supply voltage. ...
A Current-Mode Square-Rooting Circuit Using Negative Feedback Technique
... r.m.s. value of an arbitrary waveform[2]. In the past, squarerooting circuit was proposed by using operational amplifiers(op-amp) and bipolar junction transistors[3]. This approach provides the logarithmic principle to realize a squarerooting function. However the frequency performance is limited by ...
... r.m.s. value of an arbitrary waveform[2]. In the past, squarerooting circuit was proposed by using operational amplifiers(op-amp) and bipolar junction transistors[3]. This approach provides the logarithmic principle to realize a squarerooting function. However the frequency performance is limited by ...
TKN IEEE 802.15.4 Symbol Rate Timer for TelosB
... This is within the required accuracy of 125000 Hz ±40 ppm. In addition, we compared the board with the 32768 Hz oscillator of the TelosB mote once every 0.5 s and found that there are no short-term discontinuities, the frequency did neither increase nor decrease suddenly. We verified that the output ...
... This is within the required accuracy of 125000 Hz ±40 ppm. In addition, we compared the board with the 32768 Hz oscillator of the TelosB mote once every 0.5 s and found that there are no short-term discontinuities, the frequency did neither increase nor decrease suddenly. We verified that the output ...
Transistor–transistor logic

Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a class of digital circuits built from bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and resistors. It is called transistor–transistor logic because both the logic gating function (e.g., AND) and the amplifying function are performed by transistors (contrast with RTL and DTL).TTL is notable for being a widespread integrated circuit (IC) family used in many applications such as computers, industrial controls, test equipment and instrumentation, consumer electronics, synthesizers, etc. The designation TTL is sometimes used to mean TTL-compatible logic levels, even when not associated directly with TTL integrated circuits, for example as a label on the inputs and outputs of electronic instruments.After their introduction in integrated circuit form in 1963 by Sylvania, TTL integrated circuits were manufactured by several semiconductor companies, with the 7400 series (also called 74xx) by Texas Instruments becoming particularly popular. TTL manufacturers offered a wide range of logic gate, flip-flops, counters, and other circuits. Several variations from the original bipolar TTL concept were developed, giving circuits with higher speed or lower power dissipation to allow optimization of a design. TTL circuits simplified design of systems compared to earlier logic families, offering superior speed to resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and easier design layout than emitter-coupled logic (ECL). The design of the input and outputs of TTL gates allowed many elements to be interconnected.TTL became the foundation of computers and other digital electronics. Even after much larger scale integrated circuits made multiple-circuit-board processors obsolete, TTL devices still found extensive use as the ""glue"" logic interfacing more densely integrated components. TTL devices were originally made in ceramic and plastic dual-in-line (DIP) packages, and flat-pack form. TTL chips are now also made in surface-mount packages. Successors to the original bipolar TTL logic often are interchangeable in function with the original circuits, but with improved speed or lower power dissipation.