Chapter 1: Primitive Java
... Fourier Transform(frequency spectrum dB versus kHz) of the data plotted on the left. Ramesh Yerraballi ...
... Fourier Transform(frequency spectrum dB versus kHz) of the data plotted on the left. Ramesh Yerraballi ...
Automatic Routine Speeds Power-Supply
... introduced by the current-sense-resistor tolerance can be trimmed out to produce an accurate share-bus voltage. The common-mode errors have already been removed by the common-mode trim performed earlier. Share-bus specifications vary from design to design. The ability to calibrate the share bus thro ...
... introduced by the current-sense-resistor tolerance can be trimmed out to produce an accurate share-bus voltage. The common-mode errors have already been removed by the common-mode trim performed earlier. Share-bus specifications vary from design to design. The ability to calibrate the share bus thro ...
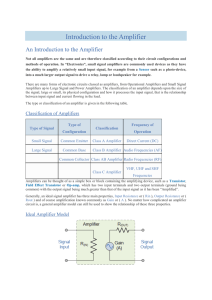
Introduction in to Amplifiers File
... twice as much power as 10dB because of the log scale. Also, a positive value of dB represents a Gain and a negative value of dB represents a Loss within the amplifier. For example, an amplifier gain of +3dB indicates that the amplifiers output signal has “doubled”, (x2) while an amplifier gain of -3 ...
... twice as much power as 10dB because of the log scale. Also, a positive value of dB represents a Gain and a negative value of dB represents a Loss within the amplifier. For example, an amplifier gain of +3dB indicates that the amplifiers output signal has “doubled”, (x2) while an amplifier gain of -3 ...
Core Technology Group Application Note 5
... A broad range of systems include components with very low resistance/impedance values such as current meters, force measurement devices, temperature sensors, battery/fuel cells, etc. Such impedance values can be in the range of 0.001 ohm to 0.1 ohm (maybe even smaller). In many cases, it is necessar ...
... A broad range of systems include components with very low resistance/impedance values such as current meters, force measurement devices, temperature sensors, battery/fuel cells, etc. Such impedance values can be in the range of 0.001 ohm to 0.1 ohm (maybe even smaller). In many cases, it is necessar ...
3-A Step-Down Converter with Hiccup Short
... once the output is above 95% of the nominal voltage, and is driven low once the output voltage falls below typically 90% of the nominal voltage. The PG pin is an open-drain output and is specified to sink up to 1 mA. The power good output requires a pullup resistor connecting to any voltage rail les ...
... once the output is above 95% of the nominal voltage, and is driven low once the output voltage falls below typically 90% of the nominal voltage. The PG pin is an open-drain output and is specified to sink up to 1 mA. The power good output requires a pullup resistor connecting to any voltage rail les ...
OPA567 Rail-to-Rail I/O, 2A POWER AMPLIFIER DESCRIPTION
... Voltage(2) ............................................... (V–) – 0.5V to (V+) + 0.5V Current(2) ................................................................................ ±10mA Output Short-Circuit(3) ........ Continuous when thermal protection enabled Enable Pin (pin 11) .................... ...
... Voltage(2) ............................................... (V–) – 0.5V to (V+) + 0.5V Current(2) ................................................................................ ±10mA Output Short-Circuit(3) ........ Continuous when thermal protection enabled Enable Pin (pin 11) .................... ...
Switched-capacitor power electronics circuits
... where VD is the forward voltage of a diode in conduction, r is the ESR of a capacitor, and r1 and r2 are the on-resistances of the p-type and n-type transistors, respectively. The circuit is operated at fs = 87KHz. Ideally, Vo = Vi / 2. It was designed for a 12 / 5 V converter of 12.5 W. If one requ ...
... where VD is the forward voltage of a diode in conduction, r is the ESR of a capacitor, and r1 and r2 are the on-resistances of the p-type and n-type transistors, respectively. The circuit is operated at fs = 87KHz. Ideally, Vo = Vi / 2. It was designed for a 12 / 5 V converter of 12.5 W. If one requ ...
download
... A passive differentiator is used to ”shorten” the pulse width of a square wave by sending the differentiated signal to a ”level detector” circuit, which outputs a ”high” signal (+5 volts) whenever the input exceeds 3.5 volts and a ”low” signal (0 volts) whenever the input drops below 3.5 volts: ...
... A passive differentiator is used to ”shorten” the pulse width of a square wave by sending the differentiated signal to a ”level detector” circuit, which outputs a ”high” signal (+5 volts) whenever the input exceeds 3.5 volts and a ”low” signal (0 volts) whenever the input drops below 3.5 volts: ...
3-5 units Question Bank
... A. X-OR B. Analog multiplier C. Sequential Circuit D. All 33. Charge pump PLL can be used to improve______ A. Stability B. Frequency C. Voltage D. None 34. Current source deposits charge in capacitor is called ______ A. Pump up B. Pump down C. Stabilizing D. All 35. Current source drawn charge from ...
... A. X-OR B. Analog multiplier C. Sequential Circuit D. All 33. Charge pump PLL can be used to improve______ A. Stability B. Frequency C. Voltage D. None 34. Current source deposits charge in capacitor is called ______ A. Pump up B. Pump down C. Stabilizing D. All 35. Current source drawn charge from ...
Experiment P44: LR Circuit (Power Amplifier, Voltage Sensor)
... Subtract the time for the peak voltage from the time for the half-max voltage to get the time for the voltage to reach half-max. Record this time in the Data Table. ...
... Subtract the time for the peak voltage from the time for the half-max voltage to get the time for the voltage to reach half-max. Record this time in the Data Table. ...
Chapter 18
... Resistors in Series • When two or more resistors are connected end-to-end, they are said to be in series • The current is the same in all resistors because any charge that flows through one resistor flows through the other • The sum of the potential differences across the resistors is equal to the ...
... Resistors in Series • When two or more resistors are connected end-to-end, they are said to be in series • The current is the same in all resistors because any charge that flows through one resistor flows through the other • The sum of the potential differences across the resistors is equal to the ...
Transistor–transistor logic

Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a class of digital circuits built from bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and resistors. It is called transistor–transistor logic because both the logic gating function (e.g., AND) and the amplifying function are performed by transistors (contrast with RTL and DTL).TTL is notable for being a widespread integrated circuit (IC) family used in many applications such as computers, industrial controls, test equipment and instrumentation, consumer electronics, synthesizers, etc. The designation TTL is sometimes used to mean TTL-compatible logic levels, even when not associated directly with TTL integrated circuits, for example as a label on the inputs and outputs of electronic instruments.After their introduction in integrated circuit form in 1963 by Sylvania, TTL integrated circuits were manufactured by several semiconductor companies, with the 7400 series (also called 74xx) by Texas Instruments becoming particularly popular. TTL manufacturers offered a wide range of logic gate, flip-flops, counters, and other circuits. Several variations from the original bipolar TTL concept were developed, giving circuits with higher speed or lower power dissipation to allow optimization of a design. TTL circuits simplified design of systems compared to earlier logic families, offering superior speed to resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and easier design layout than emitter-coupled logic (ECL). The design of the input and outputs of TTL gates allowed many elements to be interconnected.TTL became the foundation of computers and other digital electronics. Even after much larger scale integrated circuits made multiple-circuit-board processors obsolete, TTL devices still found extensive use as the ""glue"" logic interfacing more densely integrated components. TTL devices were originally made in ceramic and plastic dual-in-line (DIP) packages, and flat-pack form. TTL chips are now also made in surface-mount packages. Successors to the original bipolar TTL logic often are interchangeable in function with the original circuits, but with improved speed or lower power dissipation.