ADP3050 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... switch and all control, logic, and protection functions. It uses a unique compensation scheme allowing the use of any type of output capacitor (tantalum, ceramic, electrolytic, OS-CON). Unlike some buck regulators, the design is not restricted to using a specific type of output capacitor or ESR valu ...
... switch and all control, logic, and protection functions. It uses a unique compensation scheme allowing the use of any type of output capacitor (tantalum, ceramic, electrolytic, OS-CON). Unlike some buck regulators, the design is not restricted to using a specific type of output capacitor or ESR valu ...
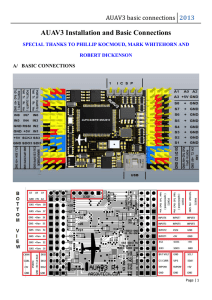
AUAV3 basic connections
... Please note all analog inputs have 1:1 resistor dividers + 10nF filter capacitors. The maximum measured voltage can be +6.6V. If you need to measure higher voltages, please do connect an appropriate resistor in series with the input used. 6. THE CONNECTORS UNDER THE SERVO OUTPUTS There are 3 connect ...
... Please note all analog inputs have 1:1 resistor dividers + 10nF filter capacitors. The maximum measured voltage can be +6.6V. If you need to measure higher voltages, please do connect an appropriate resistor in series with the input used. 6. THE CONNECTORS UNDER THE SERVO OUTPUTS There are 3 connect ...
LT1789-1/LT1789-10 - Micropower, Single Supply Rail-to-Rail Output Instrumentation Amplifier
... The high accuracy of the LT1789-1 (40ppm maximum nonlinearity and 0.25% max gain error) is unmatched by other micropower instrumentation amplifiers. The LT1789-10 maximizes both the input common mode range and dynamic output range when an amplification of 10 or greater is required, allowing precise ...
... The high accuracy of the LT1789-1 (40ppm maximum nonlinearity and 0.25% max gain error) is unmatched by other micropower instrumentation amplifiers. The LT1789-10 maximizes both the input common mode range and dynamic output range when an amplification of 10 or greater is required, allowing precise ...
TPS40020 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... The device controls the delays from main switch off to rectifier turn on and from rectifier turn off to main switch turn on in a way that minimizes diode losses (both conduction and recovery) in the synchronous rectifier. The reduction in these losses is significant and can mean that for a given con ...
... The device controls the delays from main switch off to rectifier turn on and from rectifier turn off to main switch turn on in a way that minimizes diode losses (both conduction and recovery) in the synchronous rectifier. The reduction in these losses is significant and can mean that for a given con ...
AN2835
... rectifier bridge with a capacitor filter, has an unregulated DC bus from the AC mains. The filter capacitor must be large enough to have a relatively low ripple superimposed on the DC level. The current from the mains is a series of narrow pulses with very high amplitude. A consequence of this condi ...
... rectifier bridge with a capacitor filter, has an unregulated DC bus from the AC mains. The filter capacitor must be large enough to have a relatively low ripple superimposed on the DC level. The current from the mains is a series of narrow pulses with very high amplitude. A consequence of this condi ...
TPS40200-HT 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... The TPS40200 is a nonsynchronous controller with a built-in 200-mA driver, designed to drive high-speed P-channel FETS up to 500 kHz. Its small size combined with complete functionality makes the part both versatile and easy to use. The controller uses a low-value current-sensing resistor in series ...
... The TPS40200 is a nonsynchronous controller with a built-in 200-mA driver, designed to drive high-speed P-channel FETS up to 500 kHz. Its small size combined with complete functionality makes the part both versatile and easy to use. The controller uses a low-value current-sensing resistor in series ...
MAX5037 VRM 9.0, Dual-Phase, Parallelable, Average Current-Mode Controller General Description
... provides optimum transient response. An internal regulator enables operation with either +5V or +12V input voltage without the need for additional voltage sources. The high switching frequency, up to 500kHz per phase, and dual-phase operation allow the use of low output inductor values and input cap ...
... provides optimum transient response. An internal regulator enables operation with either +5V or +12V input voltage without the need for additional voltage sources. The high switching frequency, up to 500kHz per phase, and dual-phase operation allow the use of low output inductor values and input cap ...
Transistor–transistor logic

Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a class of digital circuits built from bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and resistors. It is called transistor–transistor logic because both the logic gating function (e.g., AND) and the amplifying function are performed by transistors (contrast with RTL and DTL).TTL is notable for being a widespread integrated circuit (IC) family used in many applications such as computers, industrial controls, test equipment and instrumentation, consumer electronics, synthesizers, etc. The designation TTL is sometimes used to mean TTL-compatible logic levels, even when not associated directly with TTL integrated circuits, for example as a label on the inputs and outputs of electronic instruments.After their introduction in integrated circuit form in 1963 by Sylvania, TTL integrated circuits were manufactured by several semiconductor companies, with the 7400 series (also called 74xx) by Texas Instruments becoming particularly popular. TTL manufacturers offered a wide range of logic gate, flip-flops, counters, and other circuits. Several variations from the original bipolar TTL concept were developed, giving circuits with higher speed or lower power dissipation to allow optimization of a design. TTL circuits simplified design of systems compared to earlier logic families, offering superior speed to resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and easier design layout than emitter-coupled logic (ECL). The design of the input and outputs of TTL gates allowed many elements to be interconnected.TTL became the foundation of computers and other digital electronics. Even after much larger scale integrated circuits made multiple-circuit-board processors obsolete, TTL devices still found extensive use as the ""glue"" logic interfacing more densely integrated components. TTL devices were originally made in ceramic and plastic dual-in-line (DIP) packages, and flat-pack form. TTL chips are now also made in surface-mount packages. Successors to the original bipolar TTL logic often are interchangeable in function with the original circuits, but with improved speed or lower power dissipation.