Operational Transconductance Amplifier Design for A 16
... transistor is turned on, the other will turn off. The current through one leg will be sourced to the output while the other leg will sink current from the load. The input transistors were sized with a very large W/L ratio to provide the high transconductance required to quickly move charge onto the ...
... transistor is turned on, the other will turn off. The current through one leg will be sourced to the output while the other leg will sink current from the load. The input transistors were sized with a very large W/L ratio to provide the high transconductance required to quickly move charge onto the ...
LTC6405
... Note 4: The LTC6405C/LTC6405I are guaranteed functional over the operating temperature range –40°C to 85°C. Note 5: The LTC6405C is guaranteed to meet specified performance from 0°C to 70°C. The LTC6405C is designed, characterized, and expected to meet specified performance from –40°C to 85°C but is n ...
... Note 4: The LTC6405C/LTC6405I are guaranteed functional over the operating temperature range –40°C to 85°C. Note 5: The LTC6405C is guaranteed to meet specified performance from 0°C to 70°C. The LTC6405C is designed, characterized, and expected to meet specified performance from –40°C to 85°C but is n ...
TPS2375-1 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... DET: Connect a resistor, R(DET), between DET and VDD. This resistor should equal 24.9 kΩ, ±1% for most applications. R(DET) is connected across the input line when V(VDD) lies between 1.4 V and 11.3 V, and is disconnected when the line voltage exceeds this range to conserve power. This voltage range ...
... DET: Connect a resistor, R(DET), between DET and VDD. This resistor should equal 24.9 kΩ, ±1% for most applications. R(DET) is connected across the input line when V(VDD) lies between 1.4 V and 11.3 V, and is disconnected when the line voltage exceeds this range to conserve power. This voltage range ...
AVOP-ELEKTRO-BER-003
... This is why the left ends of the resistors are more positive than their right ends. We can draw small plus signs to the left ends, minus signs to the right ends of the resistors. VR2 = 10 V R2 ...
... This is why the left ends of the resistors are more positive than their right ends. We can draw small plus signs to the left ends, minus signs to the right ends of the resistors. VR2 = 10 V R2 ...
HIGH-VOLTAGE, LOW-DISTORTION, CURRENT-FEEDBACK OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS THS3092 THS3096
... range of ±5 V to ±15 V for applications requiring large, linear output signals such as Pin, Power FET, and VDSL line drivers. The THS3096 features a power-down pin (PD) that puts the amplifier in low power standby mode, and lowers the quiescent current from 9.5 mA to 500 µA. The wide supply range co ...
... range of ±5 V to ±15 V for applications requiring large, linear output signals such as Pin, Power FET, and VDSL line drivers. The THS3096 features a power-down pin (PD) that puts the amplifier in low power standby mode, and lowers the quiescent current from 9.5 mA to 500 µA. The wide supply range co ...
AD8048
... Additionally, the balanced high impedance inputs of the voltage feedback architecture allow maximum flexibility when designing active filters. ...
... Additionally, the balanced high impedance inputs of the voltage feedback architecture allow maximum flexibility when designing active filters. ...
VCA810 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... Operating from ±5V supplies, the gain control voltage for the VCA810 will adjust the gain from –40dB at 0V input to +40dB at –2V input. Increasing the control voltage above ground will attenuate the signal path to greater than 80dB. Signal bandwidth and slew rate remain constant over the entire gain ...
... Operating from ±5V supplies, the gain control voltage for the VCA810 will adjust the gain from –40dB at 0V input to +40dB at –2V input. Increasing the control voltage above ground will attenuate the signal path to greater than 80dB. Signal bandwidth and slew rate remain constant over the entire gain ...
AN4075
... Jumpers J3, J5 and J7 allow I2C interface address configuration. CON2 is used to provide input/output voltages from/to external circuits. The C/Q channel is used for communication (transceiver line), L+ is used to supply an IO-Link device, L- is shorted to GND and the I/Q channel is used as an addit ...
... Jumpers J3, J5 and J7 allow I2C interface address configuration. CON2 is used to provide input/output voltages from/to external circuits. The C/Q channel is used for communication (transceiver line), L+ is used to supply an IO-Link device, L- is shorted to GND and the I/Q channel is used as an addit ...
a Complete 8-Bit, 32 MSPS, 95 mW CMOS A/D Converter AD9280
... The AD9280 implements a pipelined multistage architecture to achieve high sample rate with low power. The AD9280 distributes the conversion over several smaller A/D subblocks, refining the conversion with progressively higher accuracy as it passes the results from stage to stage. As a consequence of ...
... The AD9280 implements a pipelined multistage architecture to achieve high sample rate with low power. The AD9280 distributes the conversion over several smaller A/D subblocks, refining the conversion with progressively higher accuracy as it passes the results from stage to stage. As a consequence of ...
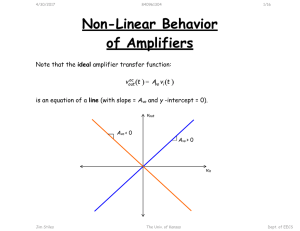
Circuit Theory Chapter 4
... every voltage source by 0V (or a short circuit), and every current source by 0A (or an open circuit). This way we obtain a simpler and more manageable circuit. – Dependent sources are left intact because they are controlled by circuit variables. ...
... every voltage source by 0V (or a short circuit), and every current source by 0A (or an open circuit). This way we obtain a simpler and more manageable circuit. – Dependent sources are left intact because they are controlled by circuit variables. ...
LTM4615 - Triple Output, Low Voltage DC/DC uModule Regulator
... are set by a single resistor for each output. Only bulk input and output capacitors are needed to complete the design. ...
... are set by a single resistor for each output. Only bulk input and output capacitors are needed to complete the design. ...
Interfacing LVPECL 3.3V Drivers with Xilinx 2.5V Differential Receivers Summary
... Inserting a series capacitor and biasing network into each leg of the differential receiver allows a reduction of the common mode voltage. This technique can provide protection against extreme DC voltages and can be useful for board-to-board or system-to-system interfaces. An example of such an inte ...
... Inserting a series capacitor and biasing network into each leg of the differential receiver allows a reduction of the common mode voltage. This technique can provide protection against extreme DC voltages and can be useful for board-to-board or system-to-system interfaces. An example of such an inte ...
MAX1717 Dynamically Adjustable, Synchronous Step-Down Controller for Notebook CPUs General Description
... accepts two 5-bit DAC settings with only five digital input pins. Output voltage transitions are accomplished with a proprietary precision slew-rate control† that minimizes surge currents to and from the battery while guaranteeing “just-in-time” arrival at the new DAC setting. High DC precision is e ...
... accepts two 5-bit DAC settings with only five digital input pins. Output voltage transitions are accomplished with a proprietary precision slew-rate control† that minimizes surge currents to and from the battery while guaranteeing “just-in-time” arrival at the new DAC setting. High DC precision is e ...
74VCX16373 Low Voltage 16-Bit Transparent Latch with 3.6V Tolerant Inputs and Outputs 7
... information that was present on the I inputs a setup time preceding the HIGH-to-LOW transition on LEn. The 3-STATE outputs are controlled by the Output Enable (OEn) input. When OEn is LOW the standard outputs are in the 2-state mode. When OEn is HIGH, the standard outputs are in the high impedance m ...
... information that was present on the I inputs a setup time preceding the HIGH-to-LOW transition on LEn. The 3-STATE outputs are controlled by the Output Enable (OEn) input. When OEn is LOW the standard outputs are in the 2-state mode. When OEn is HIGH, the standard outputs are in the high impedance m ...
EEE331-Exp-6
... The short circuit connection between gate and source in the NMOS circuit given in Fig. 6.1 guarantees the condition that NMOS is in SAT region as long as VGS ≥ VTN. ...
... The short circuit connection between gate and source in the NMOS circuit given in Fig. 6.1 guarantees the condition that NMOS is in SAT region as long as VGS ≥ VTN. ...
Transistor–transistor logic

Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a class of digital circuits built from bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and resistors. It is called transistor–transistor logic because both the logic gating function (e.g., AND) and the amplifying function are performed by transistors (contrast with RTL and DTL).TTL is notable for being a widespread integrated circuit (IC) family used in many applications such as computers, industrial controls, test equipment and instrumentation, consumer electronics, synthesizers, etc. The designation TTL is sometimes used to mean TTL-compatible logic levels, even when not associated directly with TTL integrated circuits, for example as a label on the inputs and outputs of electronic instruments.After their introduction in integrated circuit form in 1963 by Sylvania, TTL integrated circuits were manufactured by several semiconductor companies, with the 7400 series (also called 74xx) by Texas Instruments becoming particularly popular. TTL manufacturers offered a wide range of logic gate, flip-flops, counters, and other circuits. Several variations from the original bipolar TTL concept were developed, giving circuits with higher speed or lower power dissipation to allow optimization of a design. TTL circuits simplified design of systems compared to earlier logic families, offering superior speed to resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and easier design layout than emitter-coupled logic (ECL). The design of the input and outputs of TTL gates allowed many elements to be interconnected.TTL became the foundation of computers and other digital electronics. Even after much larger scale integrated circuits made multiple-circuit-board processors obsolete, TTL devices still found extensive use as the ""glue"" logic interfacing more densely integrated components. TTL devices were originally made in ceramic and plastic dual-in-line (DIP) packages, and flat-pack form. TTL chips are now also made in surface-mount packages. Successors to the original bipolar TTL logic often are interchangeable in function with the original circuits, but with improved speed or lower power dissipation.