74VCX16374 Low Voltage 16-Bit D-Type Flip-Flops with 3.6V Tolerant Inputs and Outputs 7
... flip-flops with individual D-type inputs and 3-STATE true outputs. The device is byte controlled with each byte functioning identically, but independent of the other. The control pins can be shorted together to obtain full 16-bit operation. Each clock has a buffered clock and buffered Output Enable ...
... flip-flops with individual D-type inputs and 3-STATE true outputs. The device is byte controlled with each byte functioning identically, but independent of the other. The control pins can be shorted together to obtain full 16-bit operation. Each clock has a buffered clock and buffered Output Enable ...
Installation and Operating Instructions
... Although the battery charger is designed to operate with a battery, it can be connected to loads such as dc-to-dc power supplies or inverters. Ripple content is designed to be below 200 mVac rms, without the battery connected, on resistive load. The battery charger is designed to connect to a high c ...
... Although the battery charger is designed to operate with a battery, it can be connected to loads such as dc-to-dc power supplies or inverters. Ripple content is designed to be below 200 mVac rms, without the battery connected, on resistive load. The battery charger is designed to connect to a high c ...
MAX1844 High-Speed Step-Down Controller with Accurate Current Limit for Notebook Computers General Description
... constant-on-time PWM control scheme handles wide input/output voltage ratios with ease and provides 100ns “instant-on” response to load transients while maintaining a relatively constant switching frequency. Efficiency is enhanced by an ability to drive very large synchronous-rectifier MOSFETs. Accu ...
... constant-on-time PWM control scheme handles wide input/output voltage ratios with ease and provides 100ns “instant-on” response to load transients while maintaining a relatively constant switching frequency. Efficiency is enhanced by an ability to drive very large synchronous-rectifier MOSFETs. Accu ...
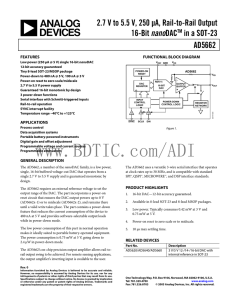
2.7 V to 5.5 V, 250 µA, Rail-to-Rail Output nano AD5662
... The power consumption is 0.75 mW at 5 V, going down to 2.4 µW in power-down mode. The AD5662’s on-chip precision output amplifier allows rail-torail output swing to be achieved. For remote sensing applications, the output amplifier’s inverting input is available to the user. ...
... The power consumption is 0.75 mW at 5 V, going down to 2.4 µW in power-down mode. The AD5662’s on-chip precision output amplifier allows rail-torail output swing to be achieved. For remote sensing applications, the output amplifier’s inverting input is available to the user. ...
Ohm`s Law - Parts 1 and 2
... order for it to be measured. If you use your finger to trace the path of a charge in Fig. 3.4(b) after it leaves the power supply, you will see that it must go through both the resistor and the ammeter. In contrast, tracing the path of a charge in Fig. 3.4(a) you will see that it has two “parallel” p ...
... order for it to be measured. If you use your finger to trace the path of a charge in Fig. 3.4(b) after it leaves the power supply, you will see that it must go through both the resistor and the ammeter. In contrast, tracing the path of a charge in Fig. 3.4(a) you will see that it has two “parallel” p ...
PTH04T240W,
... This control pin has an internal pull-up. Do not place an external pull-up on this pin. If it is left open-circuit, the module operates when input power is applied. A small, low-leakage (<100 nA) MOSFET is recommended for control. The open-circuit voltage is less than 3.5Vdc. For additional informat ...
... This control pin has an internal pull-up. Do not place an external pull-up on this pin. If it is left open-circuit, the module operates when input power is applied. A small, low-leakage (<100 nA) MOSFET is recommended for control. The open-circuit voltage is less than 3.5Vdc. For additional informat ...
NCP1219PRINTGEVB NCP1219 48 W Printer Evaluation Board User's Manual
... Throughout this application note, the minimum and maximum input voltages are referred as low and high line, respectively. The evaluation board schematic is provided in Figure 2 for reference to component values throughout the design procedure. ...
... Throughout this application note, the minimum and maximum input voltages are referred as low and high line, respectively. The evaluation board schematic is provided in Figure 2 for reference to component values throughout the design procedure. ...
AAT3604B 数据资料DataSheet下载
... ideal power solution to power OLED, LCD, and CCD applications. The step-up converter offers a true load disconnect feature which isolates the load from the power source when EN1 is pulled low. This eliminates leakage current and isolates the output while the device is disabled. The step-down DC/DC c ...
... ideal power solution to power OLED, LCD, and CCD applications. The step-up converter offers a true load disconnect feature which isolates the load from the power source when EN1 is pulled low. This eliminates leakage current and isolates the output while the device is disabled. The step-down DC/DC c ...
Low-noise Precision Variable Reference
... internally matched resistors that will contribute to low system gain and offset erros as well as good tracking over temperature in contrast to external passive components. The parallel interface of the DAC8820 can be easily replaced by an SPI interface. Usually parallel interfaces are used to provid ...
... internally matched resistors that will contribute to low system gain and offset erros as well as good tracking over temperature in contrast to external passive components. The parallel interface of the DAC8820 can be easily replaced by an SPI interface. Usually parallel interfaces are used to provid ...
MAX15066/MAX15166 High-Efficiency, 4A, Step-Down DC-DC Regulators with Internal Power Switches EVALUATION KIT AVAILABLE
... The MAX15066/MAX15166 current-mode, synchronous, DC-DC buck converters deliver an output current up to 4A with high efficiency. The devices operate from an input voltage of 4.5V to 16V and provides an adjustable output voltage from 0.606V to 90% of the input voltage. The devices are ideal for distri ...
... The MAX15066/MAX15166 current-mode, synchronous, DC-DC buck converters deliver an output current up to 4A with high efficiency. The devices operate from an input voltage of 4.5V to 16V and provides an adjustable output voltage from 0.606V to 90% of the input voltage. The devices are ideal for distri ...
10A 4.5V-14V Input Non-Isolated Wide Output Adjustable Power
... of external output capacitors required to meet a target voltage deviation specification. Additionally, for a target output capacitor bank, TurboTrans can be used to significantly improve the regulators transient response by reducing the peak voltage deviation. SmartSync allows for switching frequenc ...
... of external output capacitors required to meet a target voltage deviation specification. Additionally, for a target output capacitor bank, TurboTrans can be used to significantly improve the regulators transient response by reducing the peak voltage deviation. SmartSync allows for switching frequenc ...
Module 1, Lesson 2 – Introduction to electricity Teacher 45 minutes
... test leads into the multimeter sockets. For DC voltage, connect the black test lead to the negative polarity point (ground) socket (usually colored black) and the red lead to the positive polarity test point (usually labeled with a “V”, although it may be labeled with other units in addition to the ...
... test leads into the multimeter sockets. For DC voltage, connect the black test lead to the negative polarity point (ground) socket (usually colored black) and the red lead to the positive polarity test point (usually labeled with a “V”, although it may be labeled with other units in addition to the ...
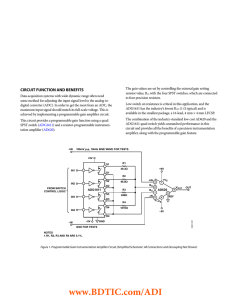
CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... (Continued from first page) "Circuits from the Lab" are intended only for use with Analog Devices products and are the intellectual property of Analog Devices or its licensors. While you may use the "Circuits from the Lab" in the design of your product, no other license is granted by implication or ...
... (Continued from first page) "Circuits from the Lab" are intended only for use with Analog Devices products and are the intellectual property of Analog Devices or its licensors. While you may use the "Circuits from the Lab" in the design of your product, no other license is granted by implication or ...
Unit 1 QN Questions Marks Unit No. BLOOMS Level (1
... constant resistance of 15 kΩ and supply voltage 10V, then find a. The minimum and maximum of output voltage, b. The range of output impedance, c. The range of power dissipated by the sensor. A Wheatstone bridge circuit has resistance of R1= R2= R3=5.00 KΩ and R4= 5.5 KΩ and a 10.00 V power supply. I ...
... constant resistance of 15 kΩ and supply voltage 10V, then find a. The minimum and maximum of output voltage, b. The range of output impedance, c. The range of power dissipated by the sensor. A Wheatstone bridge circuit has resistance of R1= R2= R3=5.00 KΩ and R4= 5.5 KΩ and a 10.00 V power supply. I ...
T L E 4 9 9 8 P 3 C ... Programmable Linear Hall Sensor S e n s o r s
... The output stage is an open-drain driver pulling the output pad to low only. Therefore, the high level must be obtained by an external pull-up resistor. This output type has the advantage that the receiver may use even a lower supply voltage (e.g. 3.3 V). In this case, the pull-up resistor must be c ...
... The output stage is an open-drain driver pulling the output pad to low only. Therefore, the high level must be obtained by an external pull-up resistor. This output type has the advantage that the receiver may use even a lower supply voltage (e.g. 3.3 V). In this case, the pull-up resistor must be c ...
Transistor–transistor logic

Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a class of digital circuits built from bipolar junction transistors (BJT) and resistors. It is called transistor–transistor logic because both the logic gating function (e.g., AND) and the amplifying function are performed by transistors (contrast with RTL and DTL).TTL is notable for being a widespread integrated circuit (IC) family used in many applications such as computers, industrial controls, test equipment and instrumentation, consumer electronics, synthesizers, etc. The designation TTL is sometimes used to mean TTL-compatible logic levels, even when not associated directly with TTL integrated circuits, for example as a label on the inputs and outputs of electronic instruments.After their introduction in integrated circuit form in 1963 by Sylvania, TTL integrated circuits were manufactured by several semiconductor companies, with the 7400 series (also called 74xx) by Texas Instruments becoming particularly popular. TTL manufacturers offered a wide range of logic gate, flip-flops, counters, and other circuits. Several variations from the original bipolar TTL concept were developed, giving circuits with higher speed or lower power dissipation to allow optimization of a design. TTL circuits simplified design of systems compared to earlier logic families, offering superior speed to resistor–transistor logic (RTL) and easier design layout than emitter-coupled logic (ECL). The design of the input and outputs of TTL gates allowed many elements to be interconnected.TTL became the foundation of computers and other digital electronics. Even after much larger scale integrated circuits made multiple-circuit-board processors obsolete, TTL devices still found extensive use as the ""glue"" logic interfacing more densely integrated components. TTL devices were originally made in ceramic and plastic dual-in-line (DIP) packages, and flat-pack form. TTL chips are now also made in surface-mount packages. Successors to the original bipolar TTL logic often are interchangeable in function with the original circuits, but with improved speed or lower power dissipation.