fahime_sheikhzadeh
... matching and learning processes within the What and Where cortical streams • Laminar Computing: cerebral cortex is organized into layered circuits which undergo characteristic bottom-up, top-down, and horizontal interactions ...
... matching and learning processes within the What and Where cortical streams • Laminar Computing: cerebral cortex is organized into layered circuits which undergo characteristic bottom-up, top-down, and horizontal interactions ...
Lecture 3
... •The cortex is a folded sheet of cells, about 2 mm thick. •The cells form layers (6 layers in primary visual cortex). •If move perpendicular to the surface of the cortex, cells will respond primarily to input from one eye (ocular dominance). •The pattern of responses forms columns of ocular dominanc ...
... •The cortex is a folded sheet of cells, about 2 mm thick. •The cells form layers (6 layers in primary visual cortex). •If move perpendicular to the surface of the cortex, cells will respond primarily to input from one eye (ocular dominance). •The pattern of responses forms columns of ocular dominanc ...
A1984TF19600002
... time, Ted Jones arrived in Oxford from Otago and together they worked through the material, and added some; and so the paper was written. It gave anatomical support to contemporary work on the visual cortex, using an accurate and relatively reliable technique. The superior colliculus was emphasized ...
... time, Ted Jones arrived in Oxford from Otago and together they worked through the material, and added some; and so the paper was written. It gave anatomical support to contemporary work on the visual cortex, using an accurate and relatively reliable technique. The superior colliculus was emphasized ...
Visual pathways cortical and sub
... some patients can scale grip and rotate wrist when reaching for objects in blind field Accuracy and latency of blindsight affected by nature of response ...
... some patients can scale grip and rotate wrist when reaching for objects in blind field Accuracy and latency of blindsight affected by nature of response ...
Ch 4 V Cortexb - Texas A&M University
... Single cell recording of neurons in the temporal lobe An electrode is inserted here, and neural responses are measured when stimuli are changed gradually ...
... Single cell recording of neurons in the temporal lobe An electrode is inserted here, and neural responses are measured when stimuli are changed gradually ...
The Brain - Academic Computer Center
... Processes and relays olfactory information, integrates the ANS, release hormones (ADH and Oxytocin), control over heart rate, digestive tract activity, rage and aggression, body temperature regulation, water balance and thirst, hunger and satiety centers and sleep pattern (Fig 12.13) ...
... Processes and relays olfactory information, integrates the ANS, release hormones (ADH and Oxytocin), control over heart rate, digestive tract activity, rage and aggression, body temperature regulation, water balance and thirst, hunger and satiety centers and sleep pattern (Fig 12.13) ...
Does History Repeat Itself? The case of cortical columns
... (VZ) migrate along radial glia to form vertical minicolumns in the cortical plate (CP) From Horton and Adams, 2005 ...
... (VZ) migrate along radial glia to form vertical minicolumns in the cortical plate (CP) From Horton and Adams, 2005 ...
Basic Brain Structure and Function
... – involved in speaking and muscle movements and in making plans and judgments – the “executive” ...
... – involved in speaking and muscle movements and in making plans and judgments – the “executive” ...
Association Cortex, Consciousness, and other topics that Embarrass
... • The concept that different parts of the brain did different things started with Spurzheim and Gall, whose phrenology became quite fashionable: • The phrenologist said that a given area of the brain increases in size, as does the overlying skull, when its function is exercised, and a good clinician ...
... • The concept that different parts of the brain did different things started with Spurzheim and Gall, whose phrenology became quite fashionable: • The phrenologist said that a given area of the brain increases in size, as does the overlying skull, when its function is exercised, and a good clinician ...
Neuroanatomy 18 [4-20
... => postcommisural fornix => medial and lateral mamillary nuclei, => precommisural fornix => lateral septal nuclues, => or anterior thalamic nucleus ...
... => postcommisural fornix => medial and lateral mamillary nuclei, => precommisural fornix => lateral septal nuclues, => or anterior thalamic nucleus ...
Visual Brain
... What and How Pathways - Further Evidence • Rod and frame illusion – Observers perform two tasks: matching and grasping • Matching task involves ventral (what) pathway • Grasping task involves dorsal (how) pathway – Results show that the frame orientation affects the matching task but not the ...
... What and How Pathways - Further Evidence • Rod and frame illusion – Observers perform two tasks: matching and grasping • Matching task involves ventral (what) pathway • Grasping task involves dorsal (how) pathway – Results show that the frame orientation affects the matching task but not the ...
primary visual cortex
... By the end of today’s class, you should be able to: 1. distinguish between cones and rods. 2. explain how an action potential is generated in the retinal cells of the visual system. 3. review the pathway by which visual information is transmitted from receptors to the brain. 4. identify the locatio ...
... By the end of today’s class, you should be able to: 1. distinguish between cones and rods. 2. explain how an action potential is generated in the retinal cells of the visual system. 3. review the pathway by which visual information is transmitted from receptors to the brain. 4. identify the locatio ...
Lecture 2
... et al., 2001) Can we assume humans are just morphed monkeys? In some areas the human cortical surface area is slightly larger than in the macaque (e.g., visual cortex: 2X); in others it is considerably larger (e.g., parietal cortex: 20X) Are individual areas larger? Are there more areas? ...
... et al., 2001) Can we assume humans are just morphed monkeys? In some areas the human cortical surface area is slightly larger than in the macaque (e.g., visual cortex: 2X); in others it is considerably larger (e.g., parietal cortex: 20X) Are individual areas larger? Are there more areas? ...
Review 2 - Texas A&M University
... square stimulus creates a square image on the retina. However, this image could also have been created by the other two shapes and many other stimuli. This is why we say that the image on the retina is ambiguous. ...
... square stimulus creates a square image on the retina. However, this image could also have been created by the other two shapes and many other stimuli. This is why we say that the image on the retina is ambiguous. ...
Ch. 2 the LGN and Striate Cortex
... Single cell recording of neurons in the temporal lobe An electrode is inserted here, and neural responses are measured when stimuli are changed gradually ...
... Single cell recording of neurons in the temporal lobe An electrode is inserted here, and neural responses are measured when stimuli are changed gradually ...
Exam 1 Review - Central Connecticut State University
... • 27. What is the difference between a ganglion and a nucleus? • A. Size • B. Location in the nervous system • C. Number of cells • D. One is a cell body, the other is an axon ...
... • 27. What is the difference between a ganglion and a nucleus? • A. Size • B. Location in the nervous system • C. Number of cells • D. One is a cell body, the other is an axon ...
study notes quiz 1
... (a) Precentral gyrus: anterior to the central sulcus (i) controls motor commands from brain – nerves leave gyrus to innvervate muscles (ii) aka “PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX” (b) postcentral gyrus: posterior to the central sulcus (i) receives incoming sensory information from peripheral nerves (ii) aka “PRI ...
... (a) Precentral gyrus: anterior to the central sulcus (i) controls motor commands from brain – nerves leave gyrus to innvervate muscles (ii) aka “PRIMARY MOTOR CORTEX” (b) postcentral gyrus: posterior to the central sulcus (i) receives incoming sensory information from peripheral nerves (ii) aka “PRI ...
Orbitofrontal Cortex and Its Contribution to Decision
... Elliot was diagnosed with a brain tumor and had it successfully removed. The surgery left him with bilateral damage to his OFC. Neuropsychologist ran test on Elliot but found no evidence of brain damage. - Tested intelligence, memory, reading and writing comprehension, verbal fluency, visuospatial a ...
... Elliot was diagnosed with a brain tumor and had it successfully removed. The surgery left him with bilateral damage to his OFC. Neuropsychologist ran test on Elliot but found no evidence of brain damage. - Tested intelligence, memory, reading and writing comprehension, verbal fluency, visuospatial a ...
view - Scan. Vet. Press
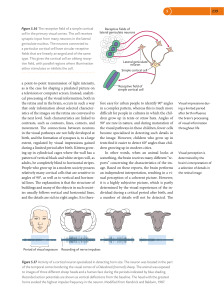
... something, the brain receives many different “reports” concerning the characteristics of the image. Based on these reports, the brain performs an independent interpretation, resulting in a visual perception of a coherent picture. However, it is a highly subjective picture, which is partly determined ...
... something, the brain receives many different “reports” concerning the characteristics of the image. Based on these reports, the brain performs an independent interpretation, resulting in a visual perception of a coherent picture. However, it is a highly subjective picture, which is partly determined ...
Objectives 31
... -other neurons are more concerned with color than with black/white contrast; they have circular receptive fields with antagonistic center-surround color properties 4. – visual cortex divided into hypercolumns; within hypercolumns all aspects of the information coming from a particular part of the co ...
... -other neurons are more concerned with color than with black/white contrast; they have circular receptive fields with antagonistic center-surround color properties 4. – visual cortex divided into hypercolumns; within hypercolumns all aspects of the information coming from a particular part of the co ...
Inferior temporal gyrus

The inferior temporal gyrus is placed below the middle temporal gyrus, and is connected behind with the inferior occipital gyrus; it also extends around the infero-lateral border on to the inferior surface of the temporal lobe, where it is limited by the inferior sulcus. This region is one of the higher levels of the ventral stream of visual processing, associated with the representation of complex object features, such as global shape. It may also be involved in face perception, and in the recognition of numbers.The inferior temporal gyrus is the anterior region of the temporal lobe located underneath the central temporal sulcus. The primary function of the inferior temporal gyrus - otherwise referenced as IT cortex - is associated with visual stimuli processing, namely visual object recognition, and has been suggested by recent experimental results as the final location of the ventral cortical visual system. The IT cortex in humans is also known as the Inferior Temporal Gyrus since it has been located to a specific region of the human temporal lobe. The IT processes visual stimuli of objects in our field of vision, and is involved with memory and memory recall to identify that object; it is involved with the processing and perception created by visual stimuli amplified in the V1, V2, V3, and V4 regions of the occipital lobe. This region processes the color and form of the object in the visual field and is responsible for producing the “what” from this visual stimuli, or in other words identifying the object based on the color and form of the object and comparing that processed information to stored memories of objects to identify that object.The IT cortex’s neurological significance is not just its contribution to the processing of visual stimuli in object recognition but also has been found to be a vital area with regards to simple processing of the visual field, difficulties with perceptual tasks and spatial awareness, and the location of unique single cells that possibly explain the IT cortex’s relation to memory.