Ecology notes - Bethlehem Central School District
... Tropical Forest (rain forest): found near the equator, temp varies little from 25 degrees C. and day light varies from 12 hours by less than one hour. Lowlands receive very little rain fall, and develop thorn forests. Nearer the equator regions have distinct wet and dry seasons and tropical deciduo ...
... Tropical Forest (rain forest): found near the equator, temp varies little from 25 degrees C. and day light varies from 12 hours by less than one hour. Lowlands receive very little rain fall, and develop thorn forests. Nearer the equator regions have distinct wet and dry seasons and tropical deciduo ...
Land and Food Resources I - University of Evansville
... Carefully managed, grazing can be sustained in grasslands (with the loss of a few grazing-intolerant plant species), because most species are tolerant of being grazed. ...
... Carefully managed, grazing can be sustained in grasslands (with the loss of a few grazing-intolerant plant species), because most species are tolerant of being grazed. ...
Chapter 6. Ecology, Advanced 6.3. Biomes
... savanna – Central America, southern México These community types are called Biomes [a term frequently used in textbooks and supplemental materials for this age group]. This general pattern repeats in other parts of the World [South America, Europe & Scandinavia, Asia, Africa, Australia & New Zealand ...
... savanna – Central America, southern México These community types are called Biomes [a term frequently used in textbooks and supplemental materials for this age group]. This general pattern repeats in other parts of the World [South America, Europe & Scandinavia, Asia, Africa, Australia & New Zealand ...
Forest Resources
... • Timber from tree plantations in temperate and tropical countries is decreasing the need for timber production in the U.S. – This could help preserve the biodiversity in the U.S. by decreasing pressure to clear-cut old-growth and second-growth forests – This may lead to private land owners to sell ...
... • Timber from tree plantations in temperate and tropical countries is decreasing the need for timber production in the U.S. – This could help preserve the biodiversity in the U.S. by decreasing pressure to clear-cut old-growth and second-growth forests – This may lead to private land owners to sell ...
Rain Forest Products
... More than half (some say up to 90%) of all plant and animal species on Earth are found in rain forests. One-fourth of all medicine in use today is derived from plants. 70% of the plants containing compounds useful in cancer treatment are found only in rainforests, yet less than 1% of tropical ...
... More than half (some say up to 90%) of all plant and animal species on Earth are found in rain forests. One-fourth of all medicine in use today is derived from plants. 70% of the plants containing compounds useful in cancer treatment are found only in rainforests, yet less than 1% of tropical ...
6 - Class Index
... •Extends north from treeline along a line from Northern Alaska to northern Quebec and southern Baffin Island (10 degree C isotherm) •Cold, with low precipitation •Nearly the entire area is underlain with permafrost •Almost complete vegetation coverage (except unfavourable areas) •Dominated by dwarf ...
... •Extends north from treeline along a line from Northern Alaska to northern Quebec and southern Baffin Island (10 degree C isotherm) •Cold, with low precipitation •Nearly the entire area is underlain with permafrost •Almost complete vegetation coverage (except unfavourable areas) •Dominated by dwarf ...
populations
... 31. What is an increase in the average temperature on Earth? 32. What is the trapping of heat in the atmosphere? What are 2 implications? 33. Label the water cycle: ...
... 31. What is an increase in the average temperature on Earth? 32. What is the trapping of heat in the atmosphere? What are 2 implications? 33. Label the water cycle: ...
Forest - Materiell
... – Boreal forest = in Canada, Scandinavia, and Russia – Tropical rainforest = South and Central America, Africa, Indonesia, and southeast Asia – Temperate deciduous forests, temperate rainforests, and tropical dry forests also exist – Woodlands = ecosystems with lower density of trees ...
... – Boreal forest = in Canada, Scandinavia, and Russia – Tropical rainforest = South and Central America, Africa, Indonesia, and southeast Asia – Temperate deciduous forests, temperate rainforests, and tropical dry forests also exist – Woodlands = ecosystems with lower density of trees ...
BIOGEOGRAPHIC PROCESSES
... Ecosystem: an organized system made up of plants, animals, and inorganic components which are linked together by flows of energy and materials. examples… ...
... Ecosystem: an organized system made up of plants, animals, and inorganic components which are linked together by flows of energy and materials. examples… ...
HMS slide show for ecology 1 2015
... In your science folder create a page called ecology notes. Answer the questions on this slide show on that page. Do it by yourself first, when your group is finished talk in your groups to see if you agree. Then as a class we will discuss the answers. ...
... In your science folder create a page called ecology notes. Answer the questions on this slide show on that page. Do it by yourself first, when your group is finished talk in your groups to see if you agree. Then as a class we will discuss the answers. ...
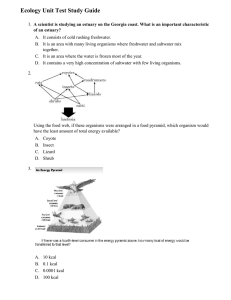
ecology unit study guide
... B. The dominant trees found in a deciduous forest lose their leaves in the winter whereas the dominant trees in the taiga retain their leaves year round. C. The dominant trees found in a taiga lose their leaves in the winter whereas the dominant trees in the deciduous forest retain their leaves year ...
... B. The dominant trees found in a deciduous forest lose their leaves in the winter whereas the dominant trees in the taiga retain their leaves year round. C. The dominant trees found in a taiga lose their leaves in the winter whereas the dominant trees in the deciduous forest retain their leaves year ...
Biomes of North America
... Belize, Guatemala, Nicaragua, Costa Rica and Panama. Rainfall 200-400 cm. Species diversity is very high (# species/area). Temperatures range 25-32°C and humidity seldom below 80%. No seasons based on temperature. Broadleaf evergreen trees dominate with canopy contiguous. Soils not very fertile, all ...
... Belize, Guatemala, Nicaragua, Costa Rica and Panama. Rainfall 200-400 cm. Species diversity is very high (# species/area). Temperatures range 25-32°C and humidity seldom below 80%. No seasons based on temperature. Broadleaf evergreen trees dominate with canopy contiguous. Soils not very fertile, all ...
Ecosystems
... • Brightly colored plants called lichens grow on rocks. • Plants have to adapt to cold temperature and little sunlight • Can have many brightly colored plants, mosses and lichens • Some plants have developed large leaves to absorb as much sun as possible. • Any animals that live her have thick fur a ...
... • Brightly colored plants called lichens grow on rocks. • Plants have to adapt to cold temperature and little sunlight • Can have many brightly colored plants, mosses and lichens • Some plants have developed large leaves to absorb as much sun as possible. • Any animals that live her have thick fur a ...
Bio07_TR__U02_CH4.QXD
... trees form a covering, called the canopy. Shorter trees and vines form another layer, called the understory In other forests, trees may be deciduous, meaning they shed their leaves during a particular season each year. Coniferous forests have trees called conifers that produce seed cones. Temperate ...
... trees form a covering, called the canopy. Shorter trees and vines form another layer, called the understory In other forests, trees may be deciduous, meaning they shed their leaves during a particular season each year. Coniferous forests have trees called conifers that produce seed cones. Temperate ...
climate - Science A 2 Z
... layer of snow are many different low laying plant species and mosses. ...
... layer of snow are many different low laying plant species and mosses. ...
APES review guide for Exam II (chapters 4 and 5) Name: Exam date
... 8. Relate the primary productivity of an ecosystem to its diversity. 9. Summarize ecological succession. Differentiate between primary and secondary succession. 10. Describe the potential damage to an ecosystem and indigenous species when an invasive species is introduced. (Provide examples) 11. Out ...
... 8. Relate the primary productivity of an ecosystem to its diversity. 9. Summarize ecological succession. Differentiate between primary and secondary succession. 10. Describe the potential damage to an ecosystem and indigenous species when an invasive species is introduced. (Provide examples) 11. Out ...
Levels of Organization
... • Group of organisms of one species living in the same place at the same time • Species= organisms with similar characteristics that are able to breed and produce fertile offspring • Compete for food water, mates, resources • Adaptations may lead to no competition • Ex) School of Tangs ...
... • Group of organisms of one species living in the same place at the same time • Species= organisms with similar characteristics that are able to breed and produce fertile offspring • Compete for food water, mates, resources • Adaptations may lead to no competition • Ex) School of Tangs ...
Week 5a - Evergreen State College Archives
... structure than other types of habitats. The idea here is that habitats with complex physical structures have more niches than habitats with a simple physical structure. Because more niches can be filled with more different types of species, diversity is higher here. Although this hypothesis explains ...
... structure than other types of habitats. The idea here is that habitats with complex physical structures have more niches than habitats with a simple physical structure. Because more niches can be filled with more different types of species, diversity is higher here. Although this hypothesis explains ...
Chapter 4 Ecosystems and Communities
... Niche Niche: Describes not only what an organism does, but also how it interacts with biotic and abiotic factors in the environment. It’s an organisms job. Resources: Any necessity of life, such as water, nutrients, light, food, or space. ...
... Niche Niche: Describes not only what an organism does, but also how it interacts with biotic and abiotic factors in the environment. It’s an organisms job. Resources: Any necessity of life, such as water, nutrients, light, food, or space. ...
Morphology 4 - University of Georgia
... We have seen that there are many different ways plant leaves can adapt to the relative lack of light under the forest canopy, or to the hot, intense tropical sunlight at the canopy. Leaf staggering, or light-sharing is a common approach to forest floor plants and vines that must collect every scrap ...
... We have seen that there are many different ways plant leaves can adapt to the relative lack of light under the forest canopy, or to the hot, intense tropical sunlight at the canopy. Leaf staggering, or light-sharing is a common approach to forest floor plants and vines that must collect every scrap ...
Lecture 4-Biomes and the Physical Environment
... Plant geographers noticed areas with similar climates had similar looking plants, though often from unrelated families ...
... Plant geographers noticed areas with similar climates had similar looking plants, though often from unrelated families ...
habitats outreach
... differences in habitats (a region where a plant or animal naturally occurs). Learn how animals are adapted for life in their particular habitats. Describe the relationship between various plants and animals within a habitat. Key Terms: Habitat, Food Chain, Habitat Destruction, Ecosystem, Adaptation ...
... differences in habitats (a region where a plant or animal naturally occurs). Learn how animals are adapted for life in their particular habitats. Describe the relationship between various plants and animals within a habitat. Key Terms: Habitat, Food Chain, Habitat Destruction, Ecosystem, Adaptation ...
Gondwana Rainforests - Department of the Environment
... in the Earth’s evolutionary history: the era of ferns, the era of conifers and the era of flowering plants. • It helps us understand how the earth and living things continue to develop over time The Gondwana Rainforests’ spectacular landforms are outstanding examples of ongoing geological process ...
... in the Earth’s evolutionary history: the era of ferns, the era of conifers and the era of flowering plants. • It helps us understand how the earth and living things continue to develop over time The Gondwana Rainforests’ spectacular landforms are outstanding examples of ongoing geological process ...
Tropical rainforest

A tropical rainforest is a biome type that occurs roughly within the latitudes 28 degrees north or south of the equator (in the equatorial zone between the Tropic of Cancer and Tropic of Capricorn). This ecosystem experiences high average temperatures and a significant amount of rainfall. These rainforests can be found in Asia; Australia; Africa; South America; Central America; the U.S. of Florida and Hawaii; as well as Mexico and on many of the Pacific, Caribbean, and Indian Ocean islands. Within the World Wildlife Fund's biome classification, tropical rainforests are a type of tropical wet forest (or tropical moist broadleaf forest) and may also be referred to as lowland equatorial evergreen rainforest.