LaBrake, Fundamentals Diagnostic Questions
... 45. How many moles of glucose are there in 2.4088 × 1024 molecules of glucose? a) 4 moles b) 2 moles c) 6.0221 × 1023 moles d) 1.4506 × 1048 moles e) insufficient information to answer 46. Calculate the molar mass of copper (II) nitrate, Cu(NO3)2. a) 187.57 g·mol-1 b) 93.56 g·mol-1 c) 125.56 g·mol- ...
... 45. How many moles of glucose are there in 2.4088 × 1024 molecules of glucose? a) 4 moles b) 2 moles c) 6.0221 × 1023 moles d) 1.4506 × 1048 moles e) insufficient information to answer 46. Calculate the molar mass of copper (II) nitrate, Cu(NO3)2. a) 187.57 g·mol-1 b) 93.56 g·mol-1 c) 125.56 g·mol- ...
unit 7a homework packet - District 196 e
... There are __________ of anything in a dozen of that thing. There are ____________________ of anything in a mole of that thing. Avogadro’s number is _______________________. A mole of any gas at STP (standard temperature pressure) has a volume of __________ liters. 8. The abbreviation for “mole” is _ ...
... There are __________ of anything in a dozen of that thing. There are ____________________ of anything in a mole of that thing. Avogadro’s number is _______________________. A mole of any gas at STP (standard temperature pressure) has a volume of __________ liters. 8. The abbreviation for “mole” is _ ...
CLASSES AND NOMENCLATURE OF INORGANIC COMPOUNDS
... Specify the factor which does not shift the 2 times: equilibrium to the right: A 8 times A increase the temperature of the system B 2 times B increase the concentration of H2S. C 4 times C decrease the concentration of SO2. D 16 times D increase of the pressure E 6 times E decrease of the temperatur ...
... Specify the factor which does not shift the 2 times: equilibrium to the right: A 8 times A increase the temperature of the system B 2 times B increase the concentration of H2S. C 4 times C decrease the concentration of SO2. D 16 times D increase of the pressure E 6 times E decrease of the temperatur ...
Chemistry - Resonance
... The organic compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons. These are the simplest organic compounds and are regarded as parent organic compounds. All other compounds are considered to be derived from them by the replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms by other atoms or grou ...
... The organic compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen are called hydrocarbons. These are the simplest organic compounds and are regarded as parent organic compounds. All other compounds are considered to be derived from them by the replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms by other atoms or grou ...
Chemistry Transition Information
... Calcium atoms each lose two electrons to form calcium ions. Chlorine atoms each gain one electron to form chloride ions. This means that calcium atoms react with chlorine atoms in the ratio of one calcium atom for every two chlorine atoms. Complete the following diagram to show the electronic struct ...
... Calcium atoms each lose two electrons to form calcium ions. Chlorine atoms each gain one electron to form chloride ions. This means that calcium atoms react with chlorine atoms in the ratio of one calcium atom for every two chlorine atoms. Complete the following diagram to show the electronic struct ...
AQA GCSE Chemistry My Revision Notes
... In 1869 Dimitri Mendeleev arranged the elements by putting them in order of their atomic weights. When he put them into a table he ensured that elements with similar properties were in columns. (b) What two things did Mendeleev do to ensure that elements in the same column had similar properties? (2 ...
... In 1869 Dimitri Mendeleev arranged the elements by putting them in order of their atomic weights. When he put them into a table he ensured that elements with similar properties were in columns. (b) What two things did Mendeleev do to ensure that elements in the same column had similar properties? (2 ...
Chemistry Unit Outcomes
... List the names of the first persons to recognize that it would be convenient to represent chemical substances using symbols? 2. Outline what John Dalton, an English chemist, did in 1808. 3. Explain how Dalton represented element and why there was a problem with Dalton’s system. 4. Define the term ch ...
... List the names of the first persons to recognize that it would be convenient to represent chemical substances using symbols? 2. Outline what John Dalton, an English chemist, did in 1808. 3. Explain how Dalton represented element and why there was a problem with Dalton’s system. 4. Define the term ch ...
"Part 1" Resource
... Harry D. Hubbard, of the United States National Bureau of Standards, modernized Mendeleev's periodic table, and his first work was published in 1924. This was known as the "Periodic Chart of the Atoms". Into the 1930s the heaviest elements were being put up in the body of the periodic table, and Gle ...
... Harry D. Hubbard, of the United States National Bureau of Standards, modernized Mendeleev's periodic table, and his first work was published in 1924. This was known as the "Periodic Chart of the Atoms". Into the 1930s the heaviest elements were being put up in the body of the periodic table, and Gle ...
Record: 1 THE EVOLUTION OF THE PERIODIC SYSTEM Page 1 of
... The name "noble" derives from the fact that all these gases seem to stand apart from the other elements, rarely interacting with them to form compounds. As a result, some chemists suggested that the noble gases did not even belong in the periodic table. These elements had not been predicted by Mende ...
... The name "noble" derives from the fact that all these gases seem to stand apart from the other elements, rarely interacting with them to form compounds. As a result, some chemists suggested that the noble gases did not even belong in the periodic table. These elements had not been predicted by Mende ...
Practice Packet Unit: 5 Periodic Table
... The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. The elements in each vertical column or group have similar properties. There are a number of major groups with similar properties. They are as follows: ...
... The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. The elements in each vertical column or group have similar properties. There are a number of major groups with similar properties. They are as follows: ...
CBSE Living Science Chemistry Class X
... of a Bunsen burner. Magnesium ribbon burns with a dazzling flame and white powder is collected on a watch glass kept below the flame. The white powder is ...
... of a Bunsen burner. Magnesium ribbon burns with a dazzling flame and white powder is collected on a watch glass kept below the flame. The white powder is ...
File
... The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. The elements in each vertical column or group have similar properties. There are a number of major groups with similar properties. They are as follows: ...
... The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. The elements in each vertical column or group have similar properties. There are a number of major groups with similar properties. They are as follows: ...
ХИМИЯ НА АНГЛИЙСКОМ ЯЗЫКЕ
... c) Find the mass of O in the compound. d) Find the total number of atoms in the compound. 2.39. 0.02 mol of unknown compound Y2O5 weighs 2.16 g. Calculate: a) the molar mass of the compound; b) the atomic mass of the element, Y; c) the mass of a single Y atom. 2.40. 0.05 mol of an unknown compound ...
... c) Find the mass of O in the compound. d) Find the total number of atoms in the compound. 2.39. 0.02 mol of unknown compound Y2O5 weighs 2.16 g. Calculate: a) the molar mass of the compound; b) the atomic mass of the element, Y; c) the mass of a single Y atom. 2.40. 0.05 mol of an unknown compound ...
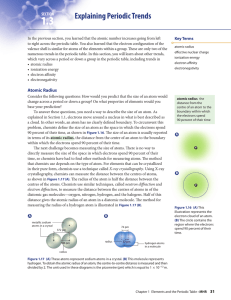
1.3 Explaining Periodic Trends
... previous electron because there are fewer negative charges repelling each subsequent electron but the same number of positive charges attracting it. A graph of first ionization energy versus atomic number is shown in Figure 1.19. Notice that the elements at all of the peaks in the graph are noble ga ...
... previous electron because there are fewer negative charges repelling each subsequent electron but the same number of positive charges attracting it. A graph of first ionization energy versus atomic number is shown in Figure 1.19. Notice that the elements at all of the peaks in the graph are noble ga ...
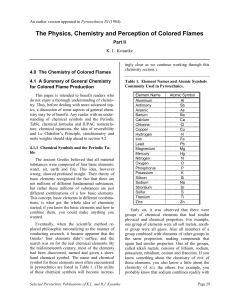
The Physics, Chemistry and Perception of Colored Flames
... well as “chemical” properties such as tendency to combine with other elements, the relative proportions in which they combine, etc. (B) Molecules formed by combining different elements of the same two groups will generally have similar physical properties. Thus, sodium chloride, lithium bromide and ...
... well as “chemical” properties such as tendency to combine with other elements, the relative proportions in which they combine, etc. (B) Molecules formed by combining different elements of the same two groups will generally have similar physical properties. Thus, sodium chloride, lithium bromide and ...
Periodic Table
... In many compounds, the negative charge of the valence electrons is concentrated closer to one atom than to another. Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons from another atom in the compound. ...
... In many compounds, the negative charge of the valence electrons is concentrated closer to one atom than to another. Electronegativity is a measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons from another atom in the compound. ...
Groundbreaking Measurement of Free Chlorine Disinfecting Power
... reagents to the water being tested that causes a color change representing the amount of FAC in water. In fact, they fundamentally change the chemistry of the water just to get an easy measurement. The most obvious change is related to pH. The typical reagent/dye used in the process forces the pH of ...
... reagents to the water being tested that causes a color change representing the amount of FAC in water. In fact, they fundamentally change the chemistry of the water just to get an easy measurement. The most obvious change is related to pH. The typical reagent/dye used in the process forces the pH of ...
The Periodic Table and Chemical Properties
... In this activity, you will use a simplified periodic table to discover the patterns of properties of elements. The table below shows the general shape of a simplified periodic table. Elements are represented with symbols and are arranged in order of their atomic number. Also shown are gases, liquids ...
... In this activity, you will use a simplified periodic table to discover the patterns of properties of elements. The table below shows the general shape of a simplified periodic table. Elements are represented with symbols and are arranged in order of their atomic number. Also shown are gases, liquids ...
KS4 The Periodic Table 3548KB
... element – A substance made up of only one type of atom. group – A column in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of outer shell electrons and similar chemical properties. period – A row in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of full electron shells. per ...
... element – A substance made up of only one type of atom. group – A column in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of outer shell electrons and similar chemical properties. period – A row in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of full electron shells. per ...
KS4 Chemistry The Periodic Table 1 of 47 © Boardworks Ltd 2005
... element – A substance made up of only one type of atom. group – A column in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of outer shell electrons and similar chemical properties. period – A row in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of full electron shells. per ...
... element – A substance made up of only one type of atom. group – A column in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of outer shell electrons and similar chemical properties. period – A row in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of full electron shells. per ...
The Periodic Table - Prairie Rose School Division No. 8
... element – A substance made up of only one type of atom. group – A column in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of outer shell electrons and similar chemical properties. period – A row in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of full electron shells. per ...
... element – A substance made up of only one type of atom. group – A column in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of outer shell electrons and similar chemical properties. period – A row in the periodic table containing elements with the same number of full electron shells. per ...
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE p
... Each Group of The p-Block The elements comprising s-block and p-block are called main groups or representative elements. Since the atomic radii decrease across a period, the p-block atoms are smaller than their nearest s or d block atoms; thus F atom has the smallest radius. Associated with small at ...
... Each Group of The p-Block The elements comprising s-block and p-block are called main groups or representative elements. Since the atomic radii decrease across a period, the p-block atoms are smaller than their nearest s or d block atoms; thus F atom has the smallest radius. Associated with small at ...
Organizing the periodic table
... but also have other important characteristics which are not found in metals. These elements can be used for many things. ...
... but also have other important characteristics which are not found in metals. These elements can be used for many things. ...
Last Name Professor BEAMER First Name
... Solution/Explanation: You are converting between particles (molecules) and mass (grams). Therefore, you need to use Avogadro’s Number. ...
... Solution/Explanation: You are converting between particles (molecules) and mass (grams). Therefore, you need to use Avogadro’s Number. ...
The Periodic Table
... elements had been identified. Included in this were the elements that had been known since ancient times like Cu and Au. In less than 100 years the number of elements had doubled, and scientists needed a better way of classifying them. ...
... elements had been identified. Included in this were the elements that had been known since ancient times like Cu and Au. In less than 100 years the number of elements had doubled, and scientists needed a better way of classifying them. ...