CHAPTER-3 CLASSIFICATION OF ELEMENTS
... Ans- The 1st ionisation enthalpy of magnesium is higher than that of Na due to higher nuclear charge and slightly smaller atomic radius of Mg than Na. After the loss of first electron, Na+ formed has the electronic configuration of neon (2,8). The higher stability of the completely filled noble gas ...
... Ans- The 1st ionisation enthalpy of magnesium is higher than that of Na due to higher nuclear charge and slightly smaller atomic radius of Mg than Na. After the loss of first electron, Na+ formed has the electronic configuration of neon (2,8). The higher stability of the completely filled noble gas ...
Document
... elements. Scientists during Dmitri’s time were trying to figure out an easy way in which they could organize the elements of matter so that it would be easy for them to communicate about their properties (i.e. scientists, even back then, were lazy and they didn’t want to have to memorize all the ele ...
... elements. Scientists during Dmitri’s time were trying to figure out an easy way in which they could organize the elements of matter so that it would be easy for them to communicate about their properties (i.e. scientists, even back then, were lazy and they didn’t want to have to memorize all the ele ...
Inorganometallic Chemistry
... atoms of an organic group or molecule and the atom from the main group, transition, lanthanide or actinide metals. According to the IUPAC rules, organometallic compounds are those in which the carbon atoms are bonded to any other element with exception of H, C, N, O, F, Cl, Br, I and At. Some diffic ...
... atoms of an organic group or molecule and the atom from the main group, transition, lanthanide or actinide metals. According to the IUPAC rules, organometallic compounds are those in which the carbon atoms are bonded to any other element with exception of H, C, N, O, F, Cl, Br, I and At. Some diffic ...
d) Ramsay. The idea of arranging the elements in the periodic table
... b) table of metric equivalents. ...
... b) table of metric equivalents. ...
Discovering Elements
... The elements are arranged in order of their atomic number (the number of protons in the nucleus) 1H, 2He, 3Li, etc. Each element has a unique atomic number, which in turn determines the unique properties of that atom. For example, all fluorine atoms have 9 protons and all sodium atoms have 11 protons ...
... The elements are arranged in order of their atomic number (the number of protons in the nucleus) 1H, 2He, 3Li, etc. Each element has a unique atomic number, which in turn determines the unique properties of that atom. For example, all fluorine atoms have 9 protons and all sodium atoms have 11 protons ...
periodic table
... How are the elements arranged on the periodic table? • Each vertical column of elements on the periodic table is called a group, or family. There are 18 groups. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. • Valence electrons are the electrons foun ...
... How are the elements arranged on the periodic table? • Each vertical column of elements on the periodic table is called a group, or family. There are 18 groups. • Elements in a group are similar because their atoms have the same number of valence electrons. • Valence electrons are the electrons foun ...
Reactions of Main Group ...ith Nitrogen - Chemwiki
... General characteristics of the alkali metals include: relatively abundant high chemical reactivity (the most active metals) low melting and boiling points largest atomic and ionic radii highly metallic character low first ionization energy (they lose their valence electrons easily creating a strong ...
... General characteristics of the alkali metals include: relatively abundant high chemical reactivity (the most active metals) low melting and boiling points largest atomic and ionic radii highly metallic character low first ionization energy (they lose their valence electrons easily creating a strong ...
Nomenclature Powerpoint
... He actually arranged them such that elements with similar properties were located in the table underneath each other; thus, making it easier to observe the “periodicity.” ...
... He actually arranged them such that elements with similar properties were located in the table underneath each other; thus, making it easier to observe the “periodicity.” ...
What is the PERIODIC TABLE?
... linear accelerator at the GSI Helmholtz Center for Heavy Ion Research in Germany. It created the calcium-ions used in new tests that produced element 117. For now, number 117 is the most massive element confirmed to exist! Success Criteria: Can I recognize that all matter consists of atoms? (SPI0807 ...
... linear accelerator at the GSI Helmholtz Center for Heavy Ion Research in Germany. It created the calcium-ions used in new tests that produced element 117. For now, number 117 is the most massive element confirmed to exist! Success Criteria: Can I recognize that all matter consists of atoms? (SPI0807 ...
IX Chemistry Chapter 04
... valence shell and end up with zero group element with valence shell having 8 electrons, except He which has only 2 electrons. The First Period: It contains only two elements i.e. H and He. This period signifies the competition of K-shell or first orbit. It is the shortest period with two elements. T ...
... valence shell and end up with zero group element with valence shell having 8 electrons, except He which has only 2 electrons. The First Period: It contains only two elements i.e. H and He. This period signifies the competition of K-shell or first orbit. It is the shortest period with two elements. T ...
Chem Ch 5 Release Test
... c. periodic table. b. table of metric equivalents. d. table of isotopes. The periodic table a. permits the properties of an element to be predicted before the element is discovered. b. will be completed with element 118. c. has been of little use to chemists since the early 1900s. d. was completed w ...
... c. periodic table. b. table of metric equivalents. d. table of isotopes. The periodic table a. permits the properties of an element to be predicted before the element is discovered. b. will be completed with element 118. c. has been of little use to chemists since the early 1900s. d. was completed w ...
D. - Taylor County Schools
... • The two rows under the periodic table are called the inner transition metals. ...
... • The two rows under the periodic table are called the inner transition metals. ...
3. classification of elements and periodicity in properties
... fundamental property than atomic mass. Based on this observation, he modified the Mendeleev’s periodic law as “the physical and chemical properties of elements are the periodic functions of their atomic numbers”. This is known as Modern Periodic law. Based on modern periodic law, numerous forms of p ...
... fundamental property than atomic mass. Based on this observation, he modified the Mendeleev’s periodic law as “the physical and chemical properties of elements are the periodic functions of their atomic numbers”. This is known as Modern Periodic law. Based on modern periodic law, numerous forms of p ...
10C The Periodic Table
... Review: Atomic number, Symbol, and Atomic Mass Use the periodic table to find the answers to the following questions. As you become more familiar with the layout of the periodic table, you’ll be able to find this information quickly. Atomic Number: Write the name of the element that corresponds to e ...
... Review: Atomic number, Symbol, and Atomic Mass Use the periodic table to find the answers to the following questions. As you become more familiar with the layout of the periodic table, you’ll be able to find this information quickly. Atomic Number: Write the name of the element that corresponds to e ...
Activity 2 Elements and Their Properties
... bodies different in form.” The first modern definition of element, which is not much different, is from Robert Boyle: “Bodies, which not being made of any other bodies, or of one another, are the ingredients of which all those . . . mixed bodies are . . . compounded.” Scientists now state that an el ...
... bodies different in form.” The first modern definition of element, which is not much different, is from Robert Boyle: “Bodies, which not being made of any other bodies, or of one another, are the ingredients of which all those . . . mixed bodies are . . . compounded.” Scientists now state that an el ...
Unit Expectations – Periodic Table
... Law States: In the periodic table, elements are arranged in order of increasing number of protons (called the atomic number). Vertical groups in the periodic table (families) have similar physical and chemical properties due to the same outer electron structures, 9. C4.9A Introduced: _______ Basic: ...
... Law States: In the periodic table, elements are arranged in order of increasing number of protons (called the atomic number). Vertical groups in the periodic table (families) have similar physical and chemical properties due to the same outer electron structures, 9. C4.9A Introduced: _______ Basic: ...
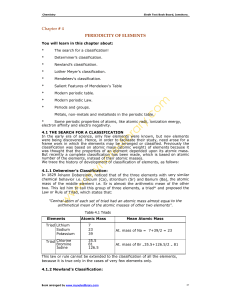
Question (1): Explain `Dobereiner`s Triads and its drawback. Answer
... 2) It was also observed that dissimilar elements were being grouped into triads. Question (2): State Newland's 'Law of Octaves'. Answer: When elements are arranged in ascending order of their atomic weights, every eighth element had similar physical and chemical properties and resembled the first el ...
... 2) It was also observed that dissimilar elements were being grouped into triads. Question (2): State Newland's 'Law of Octaves'. Answer: When elements are arranged in ascending order of their atomic weights, every eighth element had similar physical and chemical properties and resembled the first el ...
Section 1 How Are Elements Organized
... • As the number of electrons in each element increases, stronger bonds between atoms can form. • As a result, more energy is needed for melting and boiling to occur. Near the middle of the d-block, the melting and boiling points reach a peak. As more electrons are added, they begin to form pairs wit ...
... • As the number of electrons in each element increases, stronger bonds between atoms can form. • As a result, more energy is needed for melting and boiling to occur. Near the middle of the d-block, the melting and boiling points reach a peak. As more electrons are added, they begin to form pairs wit ...
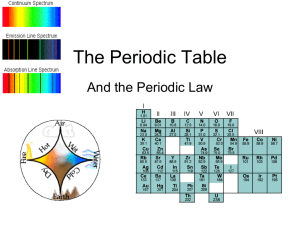
The Periodic Table
... lower boiling and melting points than metals (except carbon) • usually have lower densities than metals ...
... lower boiling and melting points than metals (except carbon) • usually have lower densities than metals ...
Periodic Table Packet
... 19, 37,55, and 87 red, because they are wildly reactive. Color lightest at the top through darkest at the bottom to indicate the increasing reactivity of the group members. 2. Color a box around each of the alkaline earth metals, atomic, numbers 4, 12, 20, 38, 56, and 88 orange, because they are mil ...
... 19, 37,55, and 87 red, because they are wildly reactive. Color lightest at the top through darkest at the bottom to indicate the increasing reactivity of the group members. 2. Color a box around each of the alkaline earth metals, atomic, numbers 4, 12, 20, 38, 56, and 88 orange, because they are mil ...
Chp4Sec1and2
... An atom is composed of positively charged protons, neutral neutrons, and negatively charged electrons. Protons and neutrons are about equal in mass. An electron has about 1/2,000 the mass of a proton or neutron. ...
... An atom is composed of positively charged protons, neutral neutrons, and negatively charged electrons. Protons and neutrons are about equal in mass. An electron has about 1/2,000 the mass of a proton or neutron. ...
The periodic table and electron structure - Chemistry
... The actinoids go on the f block below the lanthanoids, outside the main body of the table. You will not find these elements in common household products such as oven cleaners or air fresheners as they are radioactive and artificially produced. Groups of Elements Each group has characteristic propert ...
... The actinoids go on the f block below the lanthanoids, outside the main body of the table. You will not find these elements in common household products such as oven cleaners or air fresheners as they are radioactive and artificially produced. Groups of Elements Each group has characteristic propert ...
PERIODIC TABLE
... properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers. (When elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, similar properties occur in elements at regular intervals) ...
... properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers. (When elements are arranged by increasing atomic number, similar properties occur in elements at regular intervals) ...