chapter 02a
... Section 5: The Roots of Judaism Later the Egyptian Pharaoh made slaves of the Hebrews Moses helped the Hebrews escape For forty years they wandered in the desert – Finally they set up the kingdom of Israel, with Jerusalem as its capital – The Hebrews believed that God had promised them this land – ...
... Section 5: The Roots of Judaism Later the Egyptian Pharaoh made slaves of the Hebrews Moses helped the Hebrews escape For forty years they wandered in the desert – Finally they set up the kingdom of Israel, with Jerusalem as its capital – The Hebrews believed that God had promised them this land – ...
Ch. 2 First Civilizations
... Section 5: The Roots of Judaism Later the Egyptian Pharaoh made slaves of the Hebrews Moses helped the Hebrews escape For forty years they wandered in the desert – Finally they set up the kingdom of Israel, with Jerusalem as its capital – The Hebrews believed that God had promised them this land – ...
... Section 5: The Roots of Judaism Later the Egyptian Pharaoh made slaves of the Hebrews Moses helped the Hebrews escape For forty years they wandered in the desert – Finally they set up the kingdom of Israel, with Jerusalem as its capital – The Hebrews believed that God had promised them this land – ...
Chapter 5 Ancient Egypt - 6th Grade Social Studies
... but never a pharaoh! Your white mourning robe is spotless. You spent hours preparing the wreath of flowers to crown your head. No one remembers any other pharaoh. Ramses II ruled Egypt when your grandparents were children. Some people thought he would live forever. Now he’s dead and headed for his t ...
... but never a pharaoh! Your white mourning robe is spotless. You spent hours preparing the wreath of flowers to crown your head. No one remembers any other pharaoh. Ramses II ruled Egypt when your grandparents were children. Some people thought he would live forever. Now he’s dead and headed for his t ...
World History: Patterns of Interaction
... Two empires along the Nile, Egypt and Nubia, forge commercial, cultural, and political connections. ...
... Two empires along the Nile, Egypt and Nubia, forge commercial, cultural, and political connections. ...
Women`s Monumental Mark on Ancient Egypt
... more as orenhancement, correction, tombof Tiat Sakkara.DrawingbyLeonard be sitto appear side by side seated Lesko. H. available. become sourcematerials Because another. one behind ting agreefirm no is there Although the wife is most oftendepictedas onthecivil mentamongEgyptologists the survivorandmo ...
... more as orenhancement, correction, tombof Tiat Sakkara.DrawingbyLeonard be sitto appear side by side seated Lesko. H. available. become sourcematerials Because another. one behind ting agreefirm no is there Although the wife is most oftendepictedas onthecivil mentamongEgyptologists the survivorandmo ...
wwtbam - River Grove School
... Who was the female ruler who dressed as a man and called herself “king”? ...
... Who was the female ruler who dressed as a man and called herself “king”? ...
PowerPoint
... 1.) Old Kingdom (2700 B.C.-2200 B.C.) 2.) Middle Kingdom (2050 B.C.-1800 B.C.) 3.) New Kingdom (1550 B.C.-1100 B.C.) ...
... 1.) Old Kingdom (2700 B.C.-2200 B.C.) 2.) Middle Kingdom (2050 B.C.-1800 B.C.) 3.) New Kingdom (1550 B.C.-1100 B.C.) ...
Chapter 2: Western Asia and Egypt, 3500-500 BC
... while braving high winds and temperatures that reached 120 degrees Fahrenheit (48.9° C). The man, William Loftus, led a small expedition in search of the roots of civilization. As he said, “From our childhood we have been led to regard this place as the cradle of the human race.” Guided by native Ar ...
... while braving high winds and temperatures that reached 120 degrees Fahrenheit (48.9° C). The man, William Loftus, led a small expedition in search of the roots of civilization. As he said, “From our childhood we have been led to regard this place as the cradle of the human race.” Guided by native Ar ...
WESTERN CIVILIZATION: AN INTRODUCTION
... structures which they build themselves from wood or brick or stone. In addition to family homes, they also build monumental structures like temples, palaces, forts and walls, and sometimes great tombs. This stuff requires a lot of effort and the ability to mobilize and control large numbers of peopl ...
... structures which they build themselves from wood or brick or stone. In addition to family homes, they also build monumental structures like temples, palaces, forts and walls, and sometimes great tombs. This stuff requires a lot of effort and the ability to mobilize and control large numbers of peopl ...
ancient civilizations
... Egypt is a long, narrow, fertile country located in the northeast corner of Africa. To the north, the country widens into the area known as the Delta, or Lower Egypt, and covers almost 4,250 square miles (11,000 sq km). In the south is Upper Egypt, known as the Valley, which stretches for 660 miles ...
... Egypt is a long, narrow, fertile country located in the northeast corner of Africa. To the north, the country widens into the area known as the Delta, or Lower Egypt, and covers almost 4,250 square miles (11,000 sq km). In the south is Upper Egypt, known as the Valley, which stretches for 660 miles ...
context - Homework Market
... Scholars divide Egyptian history into three main periods of achievement. Almost all of the conventions of Egyptian art were established during the first period, the Old ...
... Scholars divide Egyptian history into three main periods of achievement. Almost all of the conventions of Egyptian art were established during the first period, the Old ...
File
... After the flooding of the Nile, there is some work to be done. Since there’s a lot of water that flooded, it turns the soil into mud. Although you can’t use mud to grow crops, Egyptians decided to apply a lot of water into the mud so they can reuse the mud. It was a very conservative and useful way ...
... After the flooding of the Nile, there is some work to be done. Since there’s a lot of water that flooded, it turns the soil into mud. Although you can’t use mud to grow crops, Egyptians decided to apply a lot of water into the mud so they can reuse the mud. It was a very conservative and useful way ...
The Kingdom of Kush - Hale Charter Academy
... attributes of Osiris and AmenRe. Unfortunately, it has no associated inscription to identify the intended god, or the name of the ruler whose features it might bear. Stylistically, however, it is generally believed to represent the Pharaoh Taharqa, who ruled over the area of present day Egypt and Su ...
... attributes of Osiris and AmenRe. Unfortunately, it has no associated inscription to identify the intended god, or the name of the ruler whose features it might bear. Stylistically, however, it is generally believed to represent the Pharaoh Taharqa, who ruled over the area of present day Egypt and Su ...
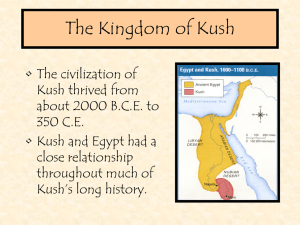
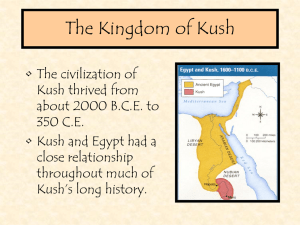
The Kingdom of Kush
... attributes of Osiris and AmenRe. Unfortunately, it has no associated inscription to identify the intended god, or the name of the ruler whose features it might bear. Stylistically, however, it is generally believed to represent the Pharaoh Taharqa, who ruled over the area of present day Egypt and Su ...
... attributes of Osiris and AmenRe. Unfortunately, it has no associated inscription to identify the intended god, or the name of the ruler whose features it might bear. Stylistically, however, it is generally believed to represent the Pharaoh Taharqa, who ruled over the area of present day Egypt and Su ...
Egyptian Civilization
... Evidence Found in the Tomb of Tutankhamen During the New Kingdom, many pharaohs were buried in a desolate valley known as the Valley of the Kings. Their tombs, known to be filled with fantastic riches, were a temptation to robbers in ancient times. As a result, most royal tombs were stripped of thei ...
... Evidence Found in the Tomb of Tutankhamen During the New Kingdom, many pharaohs were buried in a desolate valley known as the Valley of the Kings. Their tombs, known to be filled with fantastic riches, were a temptation to robbers in ancient times. As a result, most royal tombs were stripped of thei ...
Welcome to AP World History
... Step 4. Write the first Body or Supporting Paragraph A. Make sure the reader can tell where your paragraphs begin and end by indenting the first sentence of each new paragraph. B. Begin with a topic sentence!!! The topic sentence must be connected to the thesis (it is usually a restatement of part o ...
... Step 4. Write the first Body or Supporting Paragraph A. Make sure the reader can tell where your paragraphs begin and end by indenting the first sentence of each new paragraph. B. Begin with a topic sentence!!! The topic sentence must be connected to the thesis (it is usually a restatement of part o ...
Jeopardy Review - Schoolwires.net
... The Kingdom of Kush is ____________ in relation to the Empire of Egypt North South East West ...
... The Kingdom of Kush is ____________ in relation to the Empire of Egypt North South East West ...
6th Grade Social Studies Curriculum Guide
... 2. delta - a fan-shaped area of marshy land near where a river flows into the sea 3. shadoof - a bucket attached to a long pole, used to move water for irrigation 4. papyrus - a reed plant that grows along the Nile River 5. hieroglyphics - a writing system made up of picture and sound symbols 6. dyn ...
... 2. delta - a fan-shaped area of marshy land near where a river flows into the sea 3. shadoof - a bucket attached to a long pole, used to move water for irrigation 4. papyrus - a reed plant that grows along the Nile River 5. hieroglyphics - a writing system made up of picture and sound symbols 6. dyn ...
Who Were the First Surveyors? - International Federation of Surveyors
... families from their biographical tomb paintings and inscriptions, as well as finding out some more information regarding the most colourful and legendary times in which they lived, where they were interred and under whose Pharaohnic rule they worked and were buried. 1. INTRODUCTION A five year recor ...
... families from their biographical tomb paintings and inscriptions, as well as finding out some more information regarding the most colourful and legendary times in which they lived, where they were interred and under whose Pharaohnic rule they worked and were buried. 1. INTRODUCTION A five year recor ...
chapter-5-social-studies-curriculum
... 2. delta - a fan-shaped area of marshy land near where a river flows into the sea 3. shadoof - a bucket attached to a long pole, used to move water for irrigation 4. papyrus - a reed plant that grows along the Nile River 5. hieroglyphics - a writing system made up of picture and sound symbols 6. dyn ...
... 2. delta - a fan-shaped area of marshy land near where a river flows into the sea 3. shadoof - a bucket attached to a long pole, used to move water for irrigation 4. papyrus - a reed plant that grows along the Nile River 5. hieroglyphics - a writing system made up of picture and sound symbols 6. dyn ...
the DISCOVER ANCIENT EGYPT Educational Resource
... In the sands of the Sahara Desert in North East Africa, lie the archaeological remains of ancient Egypt—one of the world’s oldest and most fascinating civilizations. Protected from invading armies and foreign influences by the natural barriers of the desert to the west and the Red Sea to the east, a ...
... In the sands of the Sahara Desert in North East Africa, lie the archaeological remains of ancient Egypt—one of the world’s oldest and most fascinating civilizations. Protected from invading armies and foreign influences by the natural barriers of the desert to the west and the Red Sea to the east, a ...
Chapter 2: Ancient Egypt
... family is called a dynasty (DY • nuh • stee). When one dynasty died out, another took its place. Over time, ancient Egypt would be ruled by 31 dynasties, which together lasted about 2,800 years. Historians group Egypt’s dynasties into three main time periods called kingdoms. The earliest period, the ...
... family is called a dynasty (DY • nuh • stee). When one dynasty died out, another took its place. Over time, ancient Egypt would be ruled by 31 dynasties, which together lasted about 2,800 years. Historians group Egypt’s dynasties into three main time periods called kingdoms. The earliest period, the ...
Chapter 2: Ancient Egypt
... family is called a dynasty (DY • nuh • stee). When one dynasty died out, another took its place. Over time, ancient Egypt would be ruled by 31 dynasties, which together lasted about 2,800 years. Historians group Egypt’s dynasties into three main time periods called kingdoms. The earliest period, the ...
... family is called a dynasty (DY • nuh • stee). When one dynasty died out, another took its place. Over time, ancient Egypt would be ruled by 31 dynasties, which together lasted about 2,800 years. Historians group Egypt’s dynasties into three main time periods called kingdoms. The earliest period, the ...
Egyptian hierarchy and religion
... put by the Nile river. Since the Egyptians believed in the passage through to the After life, people were Buried as while as they could afford. ...
... put by the Nile river. Since the Egyptians believed in the passage through to the After life, people were Buried as while as they could afford. ...
Ancient Egypt: Early Egypt Visit resource for teachers Key Stage 2
... Discuss the decorated pots seen during the visit. Ask the students which images and patterns they recollect. Draw comparisons between the images and activities that took place in early Egypt. Reiterate the link between the images on the pots and the everyday life of the early Egyptians. Ask the ...
... Discuss the decorated pots seen during the visit. Ask the students which images and patterns they recollect. Draw comparisons between the images and activities that took place in early Egypt. Reiterate the link between the images on the pots and the everyday life of the early Egyptians. Ask the ...
Nubia

Nubia is a region along the Nile river located in what is today northern Sudan and southern Egypt. One of the earliest civilizations of ancient Northeastern Africa, with a history that can be traced from at least 2000 B.C. onward through Nubian monuments and artifacts as well as written records from Egypt and Rome, it was home to one of the African empires. There were a number of large Nubian kingdoms throughout the Postclassical Era, the last of which collapsed in 1504, when Nubia became divided between Egypt and the Sennar sultanate resulting in the Arabization of much of the Nubian population. Nubia was again united within Ottoman Egypt in the 19th century, and within Anglo-Egyptian Sudan from 1899 to 1956.The name Nubia is derived from that of the Noba people, nomads who settled the area in the 4th century, with the collapse of the kingdom of Meroë. The Noba spoke a Nilo-Saharan language, ancestral to Old Nubian. Old Nubian was mostly used in religious texts dating from the 8th and 15th centuries AD. Before the 4th century, and throughout classical antiquity, Nubia was known as Kush, or, in Classical Greek usage, included under the name Ethiopia (Aithiopia).Historically, the people of Nubia spoke at least two varieties of the Nubian language group, a subfamily which includes Nobiin (the descendant of Old Nubian), Kenuzi-Dongola, Midob and several related varieties in the northern part of the Nuba Mountains in South Kordofan. Until at least 1970, the Birgid language was spoken north of Nyala in Darfur but is now extinct.