Chapter 4 - Egypt - Blanchard Middle School
... 2) What mathematical contributions did the Egyptians make to civilization ? ________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 3) What medical contributions did the Egyptians make to other civilizations ? _____ ...
... 2) What mathematical contributions did the Egyptians make to civilization ? ________ _________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________ 3) What medical contributions did the Egyptians make to other civilizations ? _____ ...
Section Summary Key Terms and People Academic Vocabulary
... classes developed, with the pharaoh at the top and nobles from rich and powerful families making up the upper class. The middle class included some government officials, the scribes, and rich craftspeople. Most people, including farmers, belonged to the lower class. The pharaoh often used people fro ...
... classes developed, with the pharaoh at the top and nobles from rich and powerful families making up the upper class. The middle class included some government officials, the scribes, and rich craftspeople. Most people, including farmers, belonged to the lower class. The pharaoh often used people fro ...
Study Guide The Geography of the
... • The dates of the kingdoms are not important. • The intermediate periods were the times between the kingdoms. These were unstable times for Egypt. ...
... • The dates of the kingdoms are not important. • The intermediate periods were the times between the kingdoms. These were unstable times for Egypt. ...
Ancient Egypt: The Rule of The God King
... Hieroglyphs or “scared words” were called so because it was believed that the symbols represented a real or mythical power Hieroglyphs had three meanings ...
... Hieroglyphs or “scared words” were called so because it was believed that the symbols represented a real or mythical power Hieroglyphs had three meanings ...
Blank Jeopardy
... The “Gift of the Nile” means if it was not for the longest river in the world the Ancient Egyptians would not have any means of work and travel. The Nile’s floods gave water to the crops so Egypt could flourish. ...
... The “Gift of the Nile” means if it was not for the longest river in the world the Ancient Egyptians would not have any means of work and travel. The Nile’s floods gave water to the crops so Egypt could flourish. ...
Chapter 2: Ancient Egypt and Kush
... When their king died, the Kushites asked the god Amon-Re to appoint a new leader. “[The Kushite officials said] ‘We have come to you, O Amon-Re . . . that you might give to us a lord. . . . That beneficent office [helpful task] is in your hands—may you give it to your son whom you love!’ Then they o ...
... When their king died, the Kushites asked the god Amon-Re to appoint a new leader. “[The Kushite officials said] ‘We have come to you, O Amon-Re . . . that you might give to us a lord. . . . That beneficent office [helpful task] is in your hands—may you give it to your son whom you love!’ Then they o ...
Ancient Egypt
... c) Drought – March – June. There is very little rain. Crops are harvested during this period. ...
... c) Drought – March – June. There is very little rain. Crops are harvested during this period. ...
HW/ Social Studies Chapter Four/ Section One – Egypt Under the
... 5. Where is the Egypt’s cropland located? Use relative and absolute ( approx.) locations. Specify which is a relative location and which is an absolute location. ...
... 5. Where is the Egypt’s cropland located? Use relative and absolute ( approx.) locations. Specify which is a relative location and which is an absolute location. ...
The Rise of Civilization
... ● The Nile river, which is the longest river in the world, was mainly used for exports, and transporting goods. This was actually a huge advantage for Egypt, because it took them less time to transport goods across the middle east, which is one of the reasons why they used to be one of the richest l ...
... ● The Nile river, which is the longest river in the world, was mainly used for exports, and transporting goods. This was actually a huge advantage for Egypt, because it took them less time to transport goods across the middle east, which is one of the reasons why they used to be one of the richest l ...
Ancient Egypt sec 3,4, and 5
... destroyed by grave robbers and was in the exact condition it had been left in at the time of Tut’s death. There were four chambers in the tomb and more than 5,000 artifacts were discovered. It took the team more than 10 years to record all of the artifacts found. Archaeologists today are still study ...
... destroyed by grave robbers and was in the exact condition it had been left in at the time of Tut’s death. There were four chambers in the tomb and more than 5,000 artifacts were discovered. It took the team more than 10 years to record all of the artifacts found. Archaeologists today are still study ...
Ancient Egypt - WordPress.com
... The Suez Canal has enjoyed increased traffic in recent years, with roughly 50 ships passing through its waters every day. Shipping tolls allow Egypt to rake in around $5 billion annually, but the canal is still hampered by its narrow width and shallow depth, which are insufficient to accommodate two ...
... The Suez Canal has enjoyed increased traffic in recent years, with roughly 50 ships passing through its waters every day. Shipping tolls allow Egypt to rake in around $5 billion annually, but the canal is still hampered by its narrow width and shallow depth, which are insufficient to accommodate two ...
Mr. Hessel: Global History I: Ancient Egypt
... "Protected by nature from enemies and blessed with natural resources, the Ancient Egyptians were more self-contained than most have been, but the need for the cedars of Lebanon brought them into the stream of influences emanating from Mesopotamia." Charles Alexander Robinson Jr. Ancient History ...
... "Protected by nature from enemies and blessed with natural resources, the Ancient Egyptians were more self-contained than most have been, but the need for the cedars of Lebanon brought them into the stream of influences emanating from Mesopotamia." Charles Alexander Robinson Jr. Ancient History ...
3.1 Notes
... that was left behind when the river flooded. The best soil was found in the delta, the area at the mouth of the river that is made up of silt deposits. The Nile also protected the Egyptians from invasion. Its cataracts, or rocky stretches marked by rapid currents and waterfalls, kept invaders’ boats ...
... that was left behind when the river flooded. The best soil was found in the delta, the area at the mouth of the river that is made up of silt deposits. The Nile also protected the Egyptians from invasion. Its cataracts, or rocky stretches marked by rapid currents and waterfalls, kept invaders’ boats ...
Ancient Egypt - World History
... o Both the Egyptian and ___________ kingdoms fell to these mysterious enemies. o In 671 B.C. ___________ took over Egypt. A century and a half later it was the ___________ turn to conquer Egypt. ...
... o Both the Egyptian and ___________ kingdoms fell to these mysterious enemies. o In 671 B.C. ___________ took over Egypt. A century and a half later it was the ___________ turn to conquer Egypt. ...
Class Lesson Plan
... Ancient History 7/8 Usborne Encyclopedia of World History 21. With what did the Egyptians link most of their gods and goddesses? ______________________________________________________________ 22. Where did the Egyptians believe their gods and goddesses lived? _______________________________________ ...
... Ancient History 7/8 Usborne Encyclopedia of World History 21. With what did the Egyptians link most of their gods and goddesses? ______________________________________________________________ 22. Where did the Egyptians believe their gods and goddesses lived? _______________________________________ ...
The Middle and New Kingdoms
... • At the end of the Old Kingdom, the wealth and power of the pharaoh's declined. Building and maintaining pyramids cost lots of money. • By about 2200 BC the Old Kingdom had fallen. • For the next 160 years, local nobles ruled much of Egypt. • Finally, around 2050 BC, a powerful pharaoh defeated hi ...
... • At the end of the Old Kingdom, the wealth and power of the pharaoh's declined. Building and maintaining pyramids cost lots of money. • By about 2200 BC the Old Kingdom had fallen. • For the next 160 years, local nobles ruled much of Egypt. • Finally, around 2050 BC, a powerful pharaoh defeated hi ...
Chapter Summary - White Plains Public Schools
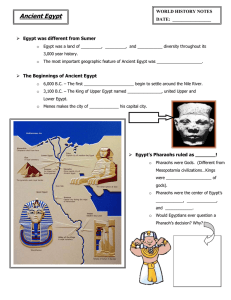
... Egypt lived. Egypt became the largest empire of its time. Menes made ___________________ his capital. Local leaders performed their regular duties such as collecting ___________________ and serving as judges, but they also had to report to the new government. Egypt’s pharaoh’s had religious duties, ...
... Egypt lived. Egypt became the largest empire of its time. Menes made ___________________ his capital. Local leaders performed their regular duties such as collecting ___________________ and serving as judges, but they also had to report to the new government. Egypt’s pharaoh’s had religious duties, ...
Ancient Egypt - Ms. Byrne's Social Studies Class Website
... • Believed the dead needed to take the things they would need with them • Believed the earthly body is needed as a home for the soul • Preserved the bodies of the dead through mummification – Originally reserved for rulers and nobles ...
... • Believed the dead needed to take the things they would need with them • Believed the earthly body is needed as a home for the soul • Preserved the bodies of the dead through mummification – Originally reserved for rulers and nobles ...
The Later Middle Ages
... triangle-shaped area of soil deposited by a river. (delta/cataract) 2. Egyptians believed that a person’s ________________________ left the body and became a spirit after death. (sarcophagus/ka) 3. A powerful pharaoh reunited the ________________________ around 2050 BC. (Middle Kingdom/New Kingdom) ...
... triangle-shaped area of soil deposited by a river. (delta/cataract) 2. Egyptians believed that a person’s ________________________ left the body and became a spirit after death. (sarcophagus/ka) 3. A powerful pharaoh reunited the ________________________ around 2050 BC. (Middle Kingdom/New Kingdom) ...
Describe how the Nile River influenced Egyptian
... To get the stones to proper location they used wooden sleds to move the stones to the Nile and floated them down the river. They then dragged or pushed the blocks up ramps to be set in place on the pyramid. ...
... To get the stones to proper location they used wooden sleds to move the stones to the Nile and floated them down the river. They then dragged or pushed the blocks up ramps to be set in place on the pyramid. ...
Pyramids on the Nile
... bowling ball pin. • Around 3100 B.C., an Upper Egypt king named Menes united all of Egypt. • As a symbol of this union he created a double crown that mixed the red and white crowns. ...
... bowling ball pin. • Around 3100 B.C., an Upper Egypt king named Menes united all of Egypt. • As a symbol of this union he created a double crown that mixed the red and white crowns. ...
Egypt
... • Pharaohs were thought to be almost splendid and powerful as the gods of the heavens. ...
... • Pharaohs were thought to be almost splendid and powerful as the gods of the heavens. ...
3-Ancient Hebrews-Judaism and Egypt PPt PowerNotes
... called “silt.” There’d have been NO civilization here without this! Egypt had many natural barriers (deserts, seas, and cataracts). The Nile had several cataracts (shallow, rocky river areas; often with waterfalls). Egypt’s natural barriers protected its civilization for thousands of years with few ...
... called “silt.” There’d have been NO civilization here without this! Egypt had many natural barriers (deserts, seas, and cataracts). The Nile had several cataracts (shallow, rocky river areas; often with waterfalls). Egypt’s natural barriers protected its civilization for thousands of years with few ...
Nubia

Nubia is a region along the Nile river located in what is today northern Sudan and southern Egypt. One of the earliest civilizations of ancient Northeastern Africa, with a history that can be traced from at least 2000 B.C. onward through Nubian monuments and artifacts as well as written records from Egypt and Rome, it was home to one of the African empires. There were a number of large Nubian kingdoms throughout the Postclassical Era, the last of which collapsed in 1504, when Nubia became divided between Egypt and the Sennar sultanate resulting in the Arabization of much of the Nubian population. Nubia was again united within Ottoman Egypt in the 19th century, and within Anglo-Egyptian Sudan from 1899 to 1956.The name Nubia is derived from that of the Noba people, nomads who settled the area in the 4th century, with the collapse of the kingdom of Meroë. The Noba spoke a Nilo-Saharan language, ancestral to Old Nubian. Old Nubian was mostly used in religious texts dating from the 8th and 15th centuries AD. Before the 4th century, and throughout classical antiquity, Nubia was known as Kush, or, in Classical Greek usage, included under the name Ethiopia (Aithiopia).Historically, the people of Nubia spoke at least two varieties of the Nubian language group, a subfamily which includes Nobiin (the descendant of Old Nubian), Kenuzi-Dongola, Midob and several related varieties in the northern part of the Nuba Mountains in South Kordofan. Until at least 1970, the Birgid language was spoken north of Nyala in Darfur but is now extinct.