Dave Hollinger`s TCP/IP slides from RPI
... Address Resolution Protocol is used by a sending host when it knows the IP address of the destination but needs the Ethernet address. ARP is a broadcast protocol - every host on the network receives the request. Each host checks the request against it’s IP address - the right one responds. ...
... Address Resolution Protocol is used by a sending host when it knows the IP address of the destination but needs the Ethernet address. ARP is a broadcast protocol - every host on the network receives the request. Each host checks the request against it’s IP address - the right one responds. ...
Slide 1
... When a computer wants to send data, how does the sending computer know if the Destination computer is on the same network? ...
... When a computer wants to send data, how does the sending computer know if the Destination computer is on the same network? ...
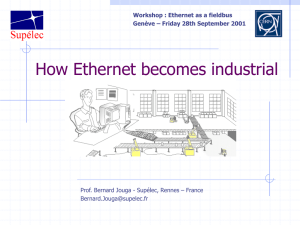
How Ethernet becomes industrial
... One standard solution for determinism and QoS issues (not yet ?) One standard solution for connecting in industrial environment (not yet ?) One standard solution for redundancy management A satisfying solution for accurate stations synchronization ...
... One standard solution for determinism and QoS issues (not yet ?) One standard solution for connecting in industrial environment (not yet ?) One standard solution for redundancy management A satisfying solution for accurate stations synchronization ...
answers - Cs.princeton.edu
... Because all packets are lost, we only detect loss through a timeout. This causes the sender's window to be reduced to a single MSS (1000 bytes / RTT), at which time it enters "slow-start restart". Namely, it will perform slowstart until half of its prior cwnd (16,000 bytes/second), then do additive- ...
... Because all packets are lost, we only detect loss through a timeout. This causes the sender's window to be reduced to a single MSS (1000 bytes / RTT), at which time it enters "slow-start restart". Namely, it will perform slowstart until half of its prior cwnd (16,000 bytes/second), then do additive- ...
solution
... reuses the same port numbers on the port and the destination, Otherwise, the FIN message will not be associated with the TCP for the new connection and will not be processed as part of the new connection. The host waits two maximum segment lifetimes before reusing the port from the old connection. T ...
... reuses the same port numbers on the port and the destination, Otherwise, the FIN message will not be associated with the TCP for the new connection and will not be processed as part of the new connection. The host waits two maximum segment lifetimes before reusing the port from the old connection. T ...
NAME: Computer Science 461 Midterm Exam March 30, 2009
... Because all packets are lost, we only detect loss through a timeout. This causes the sender's window to be reduced to a single MSS (1000 bytes / RTT), at which time it enters "slow-start restart". Namely, it will perform slowstart until half of its prior cwnd (16,000 bytes/second), then do additive- ...
... Because all packets are lost, we only detect loss through a timeout. This causes the sender's window to be reduced to a single MSS (1000 bytes / RTT), at which time it enters "slow-start restart". Namely, it will perform slowstart until half of its prior cwnd (16,000 bytes/second), then do additive- ...
WaveReady® System Controller with Built-in OSC
... The USB craft port can be used to directly connect to the COM-300 module for initial configuration and to locally manage other modules. The two small form factor pluggable (SFP) interfaces can be used to directly connect to remote nodes using an Ethernet-based OSC. The OSC SFPs support extended reac ...
... The USB craft port can be used to directly connect to the COM-300 module for initial configuration and to locally manage other modules. The two small form factor pluggable (SFP) interfaces can be used to directly connect to remote nodes using an Ethernet-based OSC. The OSC SFPs support extended reac ...
Link Layer
... with start transmitting as soon as they find the channel empty after the 3rd stations transmission is over. p- persistent: when a station is has data to send, it senses the channel. If it is idle, it transmits with probability p. otherwise it defers to the next slot with probability q = 1-p. the p ...
... with start transmitting as soon as they find the channel empty after the 3rd stations transmission is over. p- persistent: when a station is has data to send, it senses the channel. If it is idle, it transmits with probability p. otherwise it defers to the next slot with probability q = 1-p. the p ...
Introduction to networking
... monetary expense, or other measurement, that is assigned by an administrator ...
... monetary expense, or other measurement, that is assigned by an administrator ...
IP packet filtering Packet filtering
... Stateful/dynamic filtering • Routers must keep state information – For how long? ...
... Stateful/dynamic filtering • Routers must keep state information – For how long? ...
Lim-TMC09-slide
... addresses and port numbers for a connection in MN and its CNs and uses this association to hide the changes in IP address when MN moves from one network to another. Owing to the manipulation of IP addresses in the IP header of each packet, TMSP ensures that packets are sent directly between CN and ...
... addresses and port numbers for a connection in MN and its CNs and uses this association to hide the changes in IP address when MN moves from one network to another. Owing to the manipulation of IP addresses in the IP header of each packet, TMSP ensures that packets are sent directly between CN and ...
Lecture 9 Analyzing Network Packets
... Apart from UDP’s capability to preserve message boundaries, it has another problem. Because UDP does not guarantee data delivery, your application must perform that function if it is concerned about the data getting to its destination. Just because a device sends a UDP data packet doesn’t necessari ...
... Apart from UDP’s capability to preserve message boundaries, it has another problem. Because UDP does not guarantee data delivery, your application must perform that function if it is concerned about the data getting to its destination. Just because a device sends a UDP data packet doesn’t necessari ...
ppt
... IP Header: Checksum on the Header • Checksum (16 bits) – Sum of all 16-bit words in the IP packet header – If any bits of the header are corrupted in transit – … the checksum won’t match at receiving host – Receiving host discards corrupted packets • Sending host will retransmit the packet, if need ...
... IP Header: Checksum on the Header • Checksum (16 bits) – Sum of all 16-bit words in the IP packet header – If any bits of the header are corrupted in transit – … the checksum won’t match at receiving host – Receiving host discards corrupted packets • Sending host will retransmit the packet, if need ...
Network Layer and IP
... separate (Class C) network ID for each link. And then every other router in the Internet had to know about every network ID in every organization, which led to large address tables. Small organizations wanted Class B in case they grew to more than 255 hosts. But there were only about 16,000 Class B ...
... separate (Class C) network ID for each link. And then every other router in the Internet had to know about every network ID in every organization, which led to large address tables. Small organizations wanted Class B in case they grew to more than 255 hosts. But there were only about 16,000 Class B ...
4th Edition: Chapter 1 - UF CISE
... interpret meaning of data, e.g., encryption, compression, machinespecific conventions session: synchronization, checkpointing, recovery of data exchange Internet stack “missing” these layers! these services, if needed, must be implemented in application needed? Other protocol stacks? ATM, ...
... interpret meaning of data, e.g., encryption, compression, machinespecific conventions session: synchronization, checkpointing, recovery of data exchange Internet stack “missing” these layers! these services, if needed, must be implemented in application needed? Other protocol stacks? ATM, ...
Quality of Service in Industrial Ethernet
... Transmission and queuing delay gives a lower bound ...
... Transmission and queuing delay gives a lower bound ...
TDC 463-98-501/502, Summer II 2002 2-1
... setup requests if busy) •Protocol Examples: X.25, Frame Relay, ATM TDC 463-98-501/502, Summer II 2002 ...
... setup requests if busy) •Protocol Examples: X.25, Frame Relay, ATM TDC 463-98-501/502, Summer II 2002 ...
Provisioning IP traffic across MAC based access networks of tree
... access systems with increased bandwidth and service offering are imminent. An important drive for high bandwidth is the need for full service access networks. Operators want to have one network that can serve voice, video and data services. Another trend is that the network traffic becomes more and ...
... access systems with increased bandwidth and service offering are imminent. An important drive for high bandwidth is the need for full service access networks. Operators want to have one network that can serve voice, video and data services. Another trend is that the network traffic becomes more and ...
MPLS
... … “invisible” at internetwork layer. Looks like a link layer technology to IP! 5: DataLink Layer ...
... … “invisible” at internetwork layer. Looks like a link layer technology to IP! 5: DataLink Layer ...
Lecture 1: Course Introduction and Overview
... switch in warning state sent back to the source via choke packet. Source reduces traffic to that destination by a fixed % (e.g., ATM) ...
... switch in warning state sent back to the source via choke packet. Source reduces traffic to that destination by a fixed % (e.g., ATM) ...
Note
... including 56K modems, DSL, cable modem, T-lines, and SONET. To briefly discuss the technology of switched WANs including X.25, Frame Relay, and ATM. ...
... including 56K modems, DSL, cable modem, T-lines, and SONET. To briefly discuss the technology of switched WANs including X.25, Frame Relay, and ATM. ...
5_Data Link Layer
... PPP for dial-up access. Point-to-point link between Ethernet switch and host. ...
... PPP for dial-up access. Point-to-point link between Ethernet switch and host. ...