The Heart
... Setting the Heart’s Tempo • Heart muscles contract without being stimulated by external nerves (myogenic muscles) • Heart muscle does not all contract at the same rhythm when separated • Heart rhythm is set by the sinoatrial (SA) node – specialized nerve cells • Nerve impulses travel to a second no ...
... Setting the Heart’s Tempo • Heart muscles contract without being stimulated by external nerves (myogenic muscles) • Heart muscle does not all contract at the same rhythm when separated • Heart rhythm is set by the sinoatrial (SA) node – specialized nerve cells • Nerve impulses travel to a second no ...
Chapter 5: Blood and Circulation
... • Forces the bicuspid and tricuspid valves to close • Blood cannot return to the atria. ...
... • Forces the bicuspid and tricuspid valves to close • Blood cannot return to the atria. ...
Management of heart failure - the Helderberg Cardiac Support Group
... Heart size Heart function..left ventricular performance (ejection fraction) Valve leaks and/or blockages ...
... Heart size Heart function..left ventricular performance (ejection fraction) Valve leaks and/or blockages ...
Heart Physiology Cardiac Conduction System Electrical System
... · mechanical actions of the heart · each heartbeat (cycle) blood is forced out of ventricles · average adult pumps about 5 L/min · stroke volume - volume of blood pumped by each ventricle per heartbeat · cardiac output - volume of blood pumped per minute by the heart (both ventricles) ...
... · mechanical actions of the heart · each heartbeat (cycle) blood is forced out of ventricles · average adult pumps about 5 L/min · stroke volume - volume of blood pumped by each ventricle per heartbeat · cardiac output - volume of blood pumped per minute by the heart (both ventricles) ...
12-3 Cardiac Cycle
... ◦ Semilunar valves close as ventricular pressures decline ◦ As ventricular pressures fall below atrial pressures, the AV valves open and blood flows from the atria into the ventricles ...
... ◦ Semilunar valves close as ventricular pressures decline ◦ As ventricular pressures fall below atrial pressures, the AV valves open and blood flows from the atria into the ventricles ...
File
... o When ventricles are relaxed the AV valves open, blood flows into both the right and left ventricles o When ventricles contract the blood is forced two directions, the valves act like parachutes holding the blood into the correct area right atrioventricular valve (RAV) o Separates the right atrium ...
... o When ventricles are relaxed the AV valves open, blood flows into both the right and left ventricles o When ventricles contract the blood is forced two directions, the valves act like parachutes holding the blood into the correct area right atrioventricular valve (RAV) o Separates the right atrium ...
The Heart
... This sound is caused by rapid ventricular filling meaning that the ventricles have not emptied well from previous contraction. Typically, this is seen in pump failure (CHF). This pumping of blood into an already partially filled ventricle sets up vibrations heard as an S3. The S3 sounds occu ...
... This sound is caused by rapid ventricular filling meaning that the ventricles have not emptied well from previous contraction. Typically, this is seen in pump failure (CHF). This pumping of blood into an already partially filled ventricle sets up vibrations heard as an S3. The S3 sounds occu ...
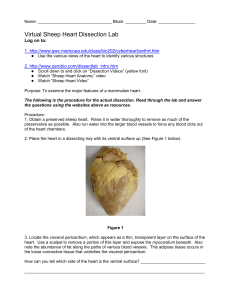
Virtual Sheep Heart Dissection Lab Student Worksheet
... Compare the structure of the tricuspid valve with that of the pulmonary valve. _________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ How do the walls of the atria compare with th ...
... Compare the structure of the tricuspid valve with that of the pulmonary valve. _________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ How do the walls of the atria compare with th ...
Cardiac physiology
... 1- Ventricular relaxation (Quiescent period) 2- Ventricular filling (diastole) 3- Ventricular contraction/ejection (systole) Cardiac cycle last about 0.8 seconds 1- Ventricular relaxation (Quiescent period): In the beginning of this phase all four chamber are at rest. As the pressure inside the vent ...
... 1- Ventricular relaxation (Quiescent period) 2- Ventricular filling (diastole) 3- Ventricular contraction/ejection (systole) Cardiac cycle last about 0.8 seconds 1- Ventricular relaxation (Quiescent period): In the beginning of this phase all four chamber are at rest. As the pressure inside the vent ...
Double right ventricle outflow tract repair icd 10
... are. THE DOPPLER ASSESSMENT OF DIASTOLIC FUNCTION. Left ventricular diastolic function is most often expressed through a variety of Doppler parameters used to assess the. Pulmonary valve stenosis (PVS) is a heart valve disorder in which outflow of blood from the right ventricle of the heart is obstr ...
... are. THE DOPPLER ASSESSMENT OF DIASTOLIC FUNCTION. Left ventricular diastolic function is most often expressed through a variety of Doppler parameters used to assess the. Pulmonary valve stenosis (PVS) is a heart valve disorder in which outflow of blood from the right ventricle of the heart is obstr ...
Cardiovascular System
... ▫ Transports nutrients and oxygen to the body ▫ Removes metabolic waste and carbon dioxide from cells ▫ Distributes hormones and antibodies throughout the body ▫ Helps control body temperature and electrolyte balance ...
... ▫ Transports nutrients and oxygen to the body ▫ Removes metabolic waste and carbon dioxide from cells ▫ Distributes hormones and antibodies throughout the body ▫ Helps control body temperature and electrolyte balance ...
The general idea with this activity is for the students to work through
... The backflow of blood is prevented by the semilunar valves and contraction of the aorta walls. ...
... The backflow of blood is prevented by the semilunar valves and contraction of the aorta walls. ...
Cardiovascular System: The Heart
... atrioventricular node (AV)at the junction of the _________ and _________ .04 seconds delayed .1 seconds at the ______________ (allows atria to complete their contraction) AV bundle (bundle of His) and bundle branches- in ______________________ septum Purkinje fibers- spread within the ______________ ...
... atrioventricular node (AV)at the junction of the _________ and _________ .04 seconds delayed .1 seconds at the ______________ (allows atria to complete their contraction) AV bundle (bundle of His) and bundle branches- in ______________________ septum Purkinje fibers- spread within the ______________ ...
Cardiovascular Assessment
... • Point of maximum intensity (PMI)- area of most intense pulsation [Ai and PMI not used interchangeably but they are at the same place] • Thrills- palpable vibrations best felt with ...
... • Point of maximum intensity (PMI)- area of most intense pulsation [Ai and PMI not used interchangeably but they are at the same place] • Thrills- palpable vibrations best felt with ...
PowerPoint
... ▫ Transports nutrients and oxygen to the body ▫ Removes metabolic waste and carbon dioxide from cells ▫ Distributes hormones and antibodies throughout the body ▫ Helps control body temperature and electrolyte balance ...
... ▫ Transports nutrients and oxygen to the body ▫ Removes metabolic waste and carbon dioxide from cells ▫ Distributes hormones and antibodies throughout the body ▫ Helps control body temperature and electrolyte balance ...
ascending-aorta surgery
... structures that open and close with each heartbeat. The valves allow blood to pass through the atria and ventricles, ensuring that blood flows in the right direction. The coronary arteries are located on the surface of the heart, providing it with blood and oxygen. ...
... structures that open and close with each heartbeat. The valves allow blood to pass through the atria and ventricles, ensuring that blood flows in the right direction. The coronary arteries are located on the surface of the heart, providing it with blood and oxygen. ...
Study Guide – Bones, Muscles, Circulatory System
... You should be able to discuss the following topics intelligently. Format of the quiz will be mainly objective questions, but be prepared for some essay questions also… Names and locations of major bones & muscles we have studied Be able to identify the four types of joints and where these joints ...
... You should be able to discuss the following topics intelligently. Format of the quiz will be mainly objective questions, but be prepared for some essay questions also… Names and locations of major bones & muscles we have studied Be able to identify the four types of joints and where these joints ...
The Heart Notes
... than Right Ventricle because it forces blood out against more resistance; the systemic circulation is much longer than the pulmonary circulation Atria are atrial effort ...
... than Right Ventricle because it forces blood out against more resistance; the systemic circulation is much longer than the pulmonary circulation Atria are atrial effort ...
lec. 2 ( heart assessment part 1)
... heart sound due to a malfunctioning heart valve • Valvular Stenosis Valve cusps become stiffened and the opening is constricted by scar tissue. How would this effect the workload of the heart? ...
... heart sound due to a malfunctioning heart valve • Valvular Stenosis Valve cusps become stiffened and the opening is constricted by scar tissue. How would this effect the workload of the heart? ...
..Heart Sounds 1. There are 2 heart sounds:
... Canada, USA, England - high in Cardiovascular diseases 1 our of 5 people have a heart attack before the age of 60 The diameter of a capillary is approx 2mm Strokes are caused by arteriosclorosis or hardening of the arteries Deprived of oxygen the brain will die in 6 min. Arteries have three layers. ...
... Canada, USA, England - high in Cardiovascular diseases 1 our of 5 people have a heart attack before the age of 60 The diameter of a capillary is approx 2mm Strokes are caused by arteriosclorosis or hardening of the arteries Deprived of oxygen the brain will die in 6 min. Arteries have three layers. ...
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM (Ch. 5)
... depolarized = discharged, which then causes contraction repolarized = recharged, which is followed by relaxation ...
... depolarized = discharged, which then causes contraction repolarized = recharged, which is followed by relaxation ...
Heart Wrksht with Heart models
... What is the function of each chamber? Locate the interventricular septum. What does it separate? Locate and name the three veins that deliver the deoxygenated blood to the heart. What color are the veins on the model? Where does blood go as it leaves the right atrium? What valve does blood pass thro ...
... What is the function of each chamber? Locate the interventricular septum. What does it separate? Locate and name the three veins that deliver the deoxygenated blood to the heart. What color are the veins on the model? Where does blood go as it leaves the right atrium? What valve does blood pass thro ...
Human Physiology Unit 3D: Cardiophysiology Pt. II
... i. Ventricles relax ii. Semilunar valves close II. Ventricular Filling i. Dicrotic Notch: Brief rise in aortic pressure due to blood rebounding off closed semilunar valves III. AV Valves are open, Semilunar Valves are closed ...
... i. Ventricles relax ii. Semilunar valves close II. Ventricular Filling i. Dicrotic Notch: Brief rise in aortic pressure due to blood rebounding off closed semilunar valves III. AV Valves are open, Semilunar Valves are closed ...
Artificial heart valve

An artificial heart valve is a device implanted in the heart of a patient with valvular heart disease. When one of the four heart valves malfunctions, the medical choice may be to replace the natural valve with an artificial valve. This requires open-heart surgery.Valves are integral to the normal physiological functioning of the human heart. Natural heart valves are evolved to forms that perform the functional requirement of inducing unidirectional blood flow through the valve structure from one chamber of the heart to another. Natural heart valves become dysfunctional for a variety of pathological causes. Some pathologies may require complete surgical replacement of the natural heart valve with a heart valve prosthesis.