1 Foundations of Syntax Spr14 Handout One [CGEL: Quirk, R
... coordinating conjunction (and, or, but) ÷ multiple, complex (alárendelés) 1: Although I admire her reasoning, I reject her conclusions >> although etc. subordinating conjunction >> optional, adverbial/adjunct ÷ multiple, complex (alárendelés) 2: He predicted [that he would dicover the tiny particle ...
... coordinating conjunction (and, or, but) ÷ multiple, complex (alárendelés) 1: Although I admire her reasoning, I reject her conclusions >> although etc. subordinating conjunction >> optional, adverbial/adjunct ÷ multiple, complex (alárendelés) 2: He predicted [that he would dicover the tiny particle ...
Example of Dice Steps
... The gazelle was killed by the lion; The children have been left at home alone; A new cancer drug has been discovered by scientists Use of the passive voice makes the written language sound more formal. It also changes the focus of the sentence from who is doing the verb to the thing that receives th ...
... The gazelle was killed by the lion; The children have been left at home alone; A new cancer drug has been discovered by scientists Use of the passive voice makes the written language sound more formal. It also changes the focus of the sentence from who is doing the verb to the thing that receives th ...
My favourite leisure activity
... Whether you would recommend it to other young people, with reasons Whether you expect to continue the activity in the future – why, why not? ...
... Whether you would recommend it to other young people, with reasons Whether you expect to continue the activity in the future – why, why not? ...
Past Participles
... • Format for Perfekt: • Helping verb: haben or sein • haben: most verbs take haben as a helping verb • sein: verbs that show motion or a change in condition • Whether you use haben or sein, the helping verb is conjugated and in the second position • Past participle (ge-verb) • This goes at the end o ...
... • Format for Perfekt: • Helping verb: haben or sein • haben: most verbs take haben as a helping verb • sein: verbs that show motion or a change in condition • Whether you use haben or sein, the helping verb is conjugated and in the second position • Past participle (ge-verb) • This goes at the end o ...
Sentence Patterns #1-17
... wonderfully active imagination.” One of Canada’s greatest prime ministers, Mackenzie King, summed up the dilemma when he said, “If other countries have too much history, we have too much geography.” ...
... wonderfully active imagination.” One of Canada’s greatest prime ministers, Mackenzie King, summed up the dilemma when he said, “If other countries have too much history, we have too much geography.” ...
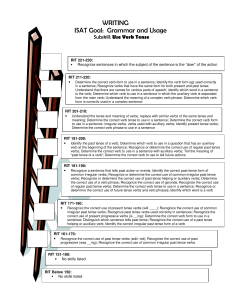
WRITING ISA T Goal: Gram m ar and U sage
... RIT 171-180: • Recognize the correct use of present tense verbs (will ____); Recognize the correct use of common irregular past tense verbs; Recognize past tense verbs used correctly in sentences; Recognize the correct use of present progressive verbs (is __ing); Determine the correct verb form to u ...
... RIT 171-180: • Recognize the correct use of present tense verbs (will ____); Recognize the correct use of common irregular past tense verbs; Recognize past tense verbs used correctly in sentences; Recognize the correct use of present progressive verbs (is __ing); Determine the correct verb form to u ...
Active and Passive
... Because the subject is being "acted upon" (or is passive), such sentences are said to be in the passive voice. NOTE: Colorful parrots live in the rainforests cannot be changed to passive voice because the sentence does not have a direct object. To change a sentence from active to passive voice, do ...
... Because the subject is being "acted upon" (or is passive), such sentences are said to be in the passive voice. NOTE: Colorful parrots live in the rainforests cannot be changed to passive voice because the sentence does not have a direct object. To change a sentence from active to passive voice, do ...
Verbal Phrases Notes
... Be sure not to confuse an infinitive with a prepositional phrase beginning with “to.” An infinitive must contain a ___________ and a prepositional phrase must contain a _____________ or ...
... Be sure not to confuse an infinitive with a prepositional phrase beginning with “to.” An infinitive must contain a ___________ and a prepositional phrase must contain a _____________ or ...
will and would
... Need expresses necessity. When reference is made to the present or future it is followed by the simple infinitive. It is used in negative and interrogative sentences. In interrogative sentences need usually implies that there is no necessity of performing the action. e.g. You needn't be afraid of me ...
... Need expresses necessity. When reference is made to the present or future it is followed by the simple infinitive. It is used in negative and interrogative sentences. In interrogative sentences need usually implies that there is no necessity of performing the action. e.g. You needn't be afraid of me ...
Parts of the Sentence - Thought - full English
... • That part of the sentence which says something about the subject, “what about it?” • The action of the sentence • Simple predicate: the principal verb • Complete predicate: a group of words that includes the verb but also the words that follow it (the entire back half of the sentence!) • Dolphins ...
... • That part of the sentence which says something about the subject, “what about it?” • The action of the sentence • Simple predicate: the principal verb • Complete predicate: a group of words that includes the verb but also the words that follow it (the entire back half of the sentence!) • Dolphins ...
All About Gerunds, Participles, and Infinitives
... • The old flag, battered by wind and weather, was finally replaced. • Exhausted, Victor fell to the ground after his long run. • The skaters, moving effortlessly, danced across the ice. ...
... • The old flag, battered by wind and weather, was finally replaced. • Exhausted, Victor fell to the ground after his long run. • The skaters, moving effortlessly, danced across the ice. ...
(2)
... when they is a group of boys or boys and girls, and ellas for ‘they’ Usted- Use when speaking when its only girls. to a person you don’t know Ustedes- Use ustedes formally when in Spain; use it in L.A. somone older, or someone with any group of people to whom you want to show ...
... when they is a group of boys or boys and girls, and ellas for ‘they’ Usted- Use when speaking when its only girls. to a person you don’t know Ustedes- Use ustedes formally when in Spain; use it in L.A. somone older, or someone with any group of people to whom you want to show ...
Writing Clinic – Session 1
... or more subordinate clauses. Subordinate clauses – has a subject and a verb but doesn’t express a complete thought and can’t stand alone. The subordinate clauses in the examples below are underlined. If you study the American Revolution, be sure you also read historians who present the British p ...
... or more subordinate clauses. Subordinate clauses – has a subject and a verb but doesn’t express a complete thought and can’t stand alone. The subordinate clauses in the examples below are underlined. If you study the American Revolution, be sure you also read historians who present the British p ...
the passive voice - Aula Virtual Maristas Mediterránea
... ACTIVE: SUBJECT + VERB+ OBJECT. The object of the verb in the active sentence becomes the subject in the passive sentence. The subject of the active sentence becomes the agent in the passive sentence. PASSIVE : OBJECT + VERB + SUBJECT: by agent when necessary) ...
... ACTIVE: SUBJECT + VERB+ OBJECT. The object of the verb in the active sentence becomes the subject in the passive sentence. The subject of the active sentence becomes the agent in the passive sentence. PASSIVE : OBJECT + VERB + SUBJECT: by agent when necessary) ...
Only transitive verbs can be made passive
... The Passive: How it is formed • To understand the passive, we must first understand that there are three important types of verbs in English: transitive, intransitive, and linking. ...
... The Passive: How it is formed • To understand the passive, we must first understand that there are three important types of verbs in English: transitive, intransitive, and linking. ...
Aspect cross-categorially: states in nominalizations DATA. In
... 2001), a great deal of attention has been devoted to event nouns, (1), or to object nouns, (2), which express non-aspectual notions corresponding to some participants in the event. In this paper we focus on a third class of nominalizations, much less studied, (3), which, we argue, denote states. ...
... 2001), a great deal of attention has been devoted to event nouns, (1), or to object nouns, (2), which express non-aspectual notions corresponding to some participants in the event. In this paper we focus on a third class of nominalizations, much less studied, (3), which, we argue, denote states. ...
correction codes for compositions
... This symbol will be written among symbols when a word has more than one error. Ej: s/e + o Missing or misplaced accent mark: dia (día). Personal “a” is/is not required. Missing, misplaced or Incorrect use of possessive adjectives: nos historia (nuestra historia). An indefinte article is used instead ...
... This symbol will be written among symbols when a word has more than one error. Ej: s/e + o Missing or misplaced accent mark: dia (día). Personal “a” is/is not required. Missing, misplaced or Incorrect use of possessive adjectives: nos historia (nuestra historia). An indefinte article is used instead ...
Complementary and Supplementary Infinitives
... You have seen this use with the verbs iubëre and vetäre. Such infinitives always have an expressed accusative ...
... You have seen this use with the verbs iubëre and vetäre. Such infinitives always have an expressed accusative ...
Nom - Mr. Brown`s French Classes
... o Le passé composé, or the ____________________, is a tense that is used to express action that happened, action that has happened, or action that did happen. For example, the French statement “J’ai regardé la télé” could mean _______________________, _________________________, or __________________ ...
... o Le passé composé, or the ____________________, is a tense that is used to express action that happened, action that has happened, or action that did happen. For example, the French statement “J’ai regardé la télé” could mean _______________________, _________________________, or __________________ ...
没有幻灯片标题
... Used he to go there? ( lexical verb ) Did he use to go there ? ( auxiliary ) He didn't use to go there. ( lexical verb ) In American English, "used to " is treated only as a lexical verb in these constructions, and this is also becoming increasingly the case in British English. ...
... Used he to go there? ( lexical verb ) Did he use to go there ? ( auxiliary ) He didn't use to go there. ( lexical verb ) In American English, "used to " is treated only as a lexical verb in these constructions, and this is also becoming increasingly the case in British English. ...
Defective verb - Basic Knowledge 101
... crucial distinction is that impersonal verbs are “missing” certain forms for semantic reasons — in other words, the forms themselves exist and the verb is capable of being fully conjugated with all its forms (and is therefore not defective) but some forms are unlikely to be found because they appear ...
... crucial distinction is that impersonal verbs are “missing” certain forms for semantic reasons — in other words, the forms themselves exist and the verb is capable of being fully conjugated with all its forms (and is therefore not defective) but some forms are unlikely to be found because they appear ...
3 kinds of verbs Linking verbs: A linking verb is a verb that does She
... Linking verbs: A linking verb is a verb that does not show actioÿ but connects the- subject to a noun or adjective in the predicate. Some verbs may be linking or action verbs, depending on how they are used. A way to determine whether a verb is linking or action is to replace the verb with a form of ...
... Linking verbs: A linking verb is a verb that does not show actioÿ but connects the- subject to a noun or adjective in the predicate. Some verbs may be linking or action verbs, depending on how they are used. A way to determine whether a verb is linking or action is to replace the verb with a form of ...
Verbs - Edmonds
... 4. Conjugate each verb listed in the vocabulary section of this lesson in Latin. In other words, put the personal endings on the different verb stems. 5. After you conjugate each verb in Latin, translate each verb form into English. Remember, the personal endings assign a subject to the action of th ...
... 4. Conjugate each verb listed in the vocabulary section of this lesson in Latin. In other words, put the personal endings on the different verb stems. 5. After you conjugate each verb in Latin, translate each verb form into English. Remember, the personal endings assign a subject to the action of th ...
Simple query language syntax
... VBG The -ing form of the verb BE: being VBI The infinitive form of the verb BE: be VBN The past participle form of the verb BE: been VBZ The -s form of the verb BE: is, 's VDB The finite base form of the verb DO: do VDD The past tense form of the verb DO: did VDG The -ing form of the verb DO: doing ...
... VBG The -ing form of the verb BE: being VBI The infinitive form of the verb BE: be VBN The past participle form of the verb BE: been VBZ The -s form of the verb BE: is, 's VDB The finite base form of the verb DO: do VDD The past tense form of the verb DO: did VDG The -ing form of the verb DO: doing ...