Latin II notebook Ch 27 packet Reflexive pronoun: “reflects”/ refers to
... * Participle: adjective form of a verb * 4th principle part of most verbs *not –urus [like futurus] this is an FAP (later) *3rd pr. pt of deponent verbs (later) * a verb cannot become passive unless it has a PPP * has us, a, um [1st/2nd decl adj] endings * translate: literal- “[having been] _____ed” ...
... * Participle: adjective form of a verb * 4th principle part of most verbs *not –urus [like futurus] this is an FAP (later) *3rd pr. pt of deponent verbs (later) * a verb cannot become passive unless it has a PPP * has us, a, um [1st/2nd decl adj] endings * translate: literal- “[having been] _____ed” ...
6 - Fountainhead Press
... Cultures all over the world have signs and symbols for good luck. Many people are familiar with four leaf clovers, but there are many more good luck charms than that! Crickets are considered lucky by European, Middle Eastern, Far Eastern, and Native American cultures. Ladybugs are similarly consider ...
... Cultures all over the world have signs and symbols for good luck. Many people are familiar with four leaf clovers, but there are many more good luck charms than that! Crickets are considered lucky by European, Middle Eastern, Far Eastern, and Native American cultures. Ladybugs are similarly consider ...
VERBS
... Verbs with Indirect Objects An indirect object answers the question to whom? or for whom? an action is done ...
... Verbs with Indirect Objects An indirect object answers the question to whom? or for whom? an action is done ...
Verbs
... As we have all probably heard, it is a good rule to keep your sentence constructions active unless you have a good reason to move into the passive voice. KEEP IT ACTIVE is an age-old rule that can be reasonably explained. The active voice usually makes your prose less wordy and more easily understoo ...
... As we have all probably heard, it is a good rule to keep your sentence constructions active unless you have a good reason to move into the passive voice. KEEP IT ACTIVE is an age-old rule that can be reasonably explained. The active voice usually makes your prose less wordy and more easily understoo ...
Verbals - Mater Academy Lakes High School
... 1. At the outdoor market, my grandmother likes to bargain. 2. Would you try to explain? 3. Give an explanation to Glen. 4. To believe took considerable faith. 5. Lindsey wrote letters to friends. ...
... 1. At the outdoor market, my grandmother likes to bargain. 2. Would you try to explain? 3. Give an explanation to Glen. 4. To believe took considerable faith. 5. Lindsey wrote letters to friends. ...
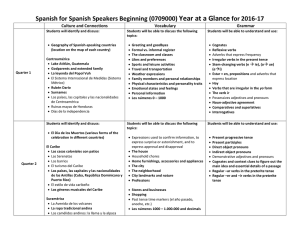
Spanish for Spanish Speakers Beginning (0709000) Year at a
... Irregular verbs in the preterite tense Stem-changing –ir verbs in the preterite tense Time expressions with hace Words to express quantity: indefinites Singular affirmative commands, regular and irregular Regular and irregular verbs in the imperfect tense. ...
... Irregular verbs in the preterite tense Stem-changing –ir verbs in the preterite tense Time expressions with hace Words to express quantity: indefinites Singular affirmative commands, regular and irregular Regular and irregular verbs in the imperfect tense. ...
Latin III: Translation – Dei Deaeque: Iuppiter Part I
... flying kite, the swimming fish, the rolling ball. In each case we have taken a verb (to run, to fly, to swim, to roll) and used it to describe, or modify, a noun. There are several different participles in English, just like Latin has several participles. We’ll learn all of them in time, but for now ...
... flying kite, the swimming fish, the rolling ball. In each case we have taken a verb (to run, to fly, to swim, to roll) and used it to describe, or modify, a noun. There are several different participles in English, just like Latin has several participles. We’ll learn all of them in time, but for now ...
Baker affirms that, in a bottom-up approach to translation
... between masculine feminine and neuter (inanimate) using three different pronouns (he/she/it). This distinction, though, does not apply to the third-person plural like in Italian and French. In Spanish, this difference is applied also to the first and second-person plural. Other languages, such as Ch ...
... between masculine feminine and neuter (inanimate) using three different pronouns (he/she/it). This distinction, though, does not apply to the third-person plural like in Italian and French. In Spanish, this difference is applied also to the first and second-person plural. Other languages, such as Ch ...
PAST PARTICIPIAL PHRASES
... PAST PARTICIPLES are just like PRESENT PARTICIPLES except that they look like verbs in the past tense (85% of the time!) ...
... PAST PARTICIPLES are just like PRESENT PARTICIPLES except that they look like verbs in the past tense (85% of the time!) ...
Perfect Tense with Modal Verbs
... Present Perfect Tense with Modal Verbs Introduction to the double infintive construction ...
... Present Perfect Tense with Modal Verbs Introduction to the double infintive construction ...
Auxiliary verb
... There are nine modal verbs: can, could, may, might, shall, should, will, would, and must. They differ from the other auxiliaries both in that they are defective verbs, and in that they can never function as main verbs. (There do exist main verbs can and will, but these are distinct.) They express th ...
... There are nine modal verbs: can, could, may, might, shall, should, will, would, and must. They differ from the other auxiliaries both in that they are defective verbs, and in that they can never function as main verbs. (There do exist main verbs can and will, but these are distinct.) They express th ...
rules-grammar-3-t2
... We use commas to separate a series of names, actions, and to separate two simple sentences joined together with the joining word “and-or- but” - My friend is nice. - My friends are Hani, Yassin, and Mohamed. - I must eat, study, and sleep early. - We can go to the movies, or to the theatre. Titles o ...
... We use commas to separate a series of names, actions, and to separate two simple sentences joined together with the joining word “and-or- but” - My friend is nice. - My friends are Hani, Yassin, and Mohamed. - I must eat, study, and sleep early. - We can go to the movies, or to the theatre. Titles o ...
Participles
... “must be built, must be fortified” * again, remember that with 3rd-io and 4th conjugation verbs, you need to drop the entire infinitive ending, add -ie-, then add the adjective ending ...
... “must be built, must be fortified” * again, remember that with 3rd-io and 4th conjugation verbs, you need to drop the entire infinitive ending, add -ie-, then add the adjective ending ...
parts of speech - shoaib ahmed jatoi
... He had been eating all day long. He had been partying all night. He had been working in this factory for five years. He had been watching Television all night. 12. Future Perfect Continuous Tense. “This form of Future Tense is used to denote an action going on but not still completed in the future t ...
... He had been eating all day long. He had been partying all night. He had been working in this factory for five years. He had been watching Television all night. 12. Future Perfect Continuous Tense. “This form of Future Tense is used to denote an action going on but not still completed in the future t ...
arts language - Amazon Web Services
... You have already learned in Language Arts 701 and 705 that a pronoun is a word used to take the place of a noun. A pronoun is a noun substitute. The noun for which it substitutes is called its antecedent. Pronouns prevent the tiresome repetition of nouns. Example: Doug parked Doug’s car in the garag ...
... You have already learned in Language Arts 701 and 705 that a pronoun is a word used to take the place of a noun. A pronoun is a noun substitute. The noun for which it substitutes is called its antecedent. Pronouns prevent the tiresome repetition of nouns. Example: Doug parked Doug’s car in the garag ...
Unit 13: Adjectives and Adverbs
... My mother-in-law is afraid of taking an airplane. angry with: Don’t be angry with me for not having finished homework. annoyed with: His mother was annoyed with him for being so rude to his teacher. busy with: Sue is busy with her project. cruel to: The old man is cruel to animals. famous for: Chine ...
... My mother-in-law is afraid of taking an airplane. angry with: Don’t be angry with me for not having finished homework. annoyed with: His mother was annoyed with him for being so rude to his teacher. busy with: Sue is busy with her project. cruel to: The old man is cruel to animals. famous for: Chine ...
Mnemonics in the Latin Classroom
... This helps students remember the intermediate letters of each conjugation of the imperfect tense. The vowel(s) in front of the ba is/are also the same as those for present participles. Future Tense: -Bo, -Bi-, -Bu- for I and II (one and two) -A- and –E- for IV and III (four and three) In the future ...
... This helps students remember the intermediate letters of each conjugation of the imperfect tense. The vowel(s) in front of the ba is/are also the same as those for present participles. Future Tense: -Bo, -Bi-, -Bu- for I and II (one and two) -A- and –E- for IV and III (four and three) In the future ...
Verbs
... your sentence constructions active unless you have a good reason to move into the passive voice. KEEP IT ACTIVE is an age-old rule that can be reasonably explained. The active voice usually makes your prose less wordy and more easily understood. nevertheless. . . ...
... your sentence constructions active unless you have a good reason to move into the passive voice. KEEP IT ACTIVE is an age-old rule that can be reasonably explained. The active voice usually makes your prose less wordy and more easily understood. nevertheless. . . ...
English auxiliary verbs
... Auxiliary verbs serve grammatical functions, for this reason they are said to belong to the functional category of words. The main auxiliary verbs in English are DO, BE and HAVE. Others, which serve to mark ASPECT, MOOD and VOICE include, amongst others CAN, MAY, MIGHT, MUST, OUGHT TO, SHOULD, WILL ...
... Auxiliary verbs serve grammatical functions, for this reason they are said to belong to the functional category of words. The main auxiliary verbs in English are DO, BE and HAVE. Others, which serve to mark ASPECT, MOOD and VOICE include, amongst others CAN, MAY, MIGHT, MUST, OUGHT TO, SHOULD, WILL ...
Participles - Magister Jacobs
... Mr. Jacobs, what is a participle? • Participles are verbal adjectives • modify nouns in case, number, & gender • Participles retain verbal qualities • have tenses • can take objects • Latin has four participles ...
... Mr. Jacobs, what is a participle? • Participles are verbal adjectives • modify nouns in case, number, & gender • Participles retain verbal qualities • have tenses • can take objects • Latin has four participles ...
Using of past and present participle as an Adjective: 1
... 4- Electrons wander in the spaces between atoms. these electrons are weakly attracted to the nucleus . 5- Heat energy can be turned into mechanical energy. The heat is generated in an atomic reactor. 6- Substances change water properties. These substances are dissolved in water. 7- the mixture of ai ...
... 4- Electrons wander in the spaces between atoms. these electrons are weakly attracted to the nucleus . 5- Heat energy can be turned into mechanical energy. The heat is generated in an atomic reactor. 6- Substances change water properties. These substances are dissolved in water. 7- the mixture of ai ...
Formal Commands! - The Learning Hub
... In affirmative commands, all objects are attached to the end of the verb. ...
... In affirmative commands, all objects are attached to the end of the verb. ...