Data Structure and Algorithms
... algorithm design must go hand in hand with appropriate data structures for efficient program design to solve a problem irrespective of the discipline or application. This material is designed to give an overview of the fundamentals of data structures, their complexities and importance in solving pro ...
... algorithm design must go hand in hand with appropriate data structures for efficient program design to solve a problem irrespective of the discipline or application. This material is designed to give an overview of the fundamentals of data structures, their complexities and importance in solving pro ...
Chapter 24
... The array is dynamically created. If the capacity of the array is exceeded, create a new larger array and copy all the elements from the current array to the new array. Using linked list. The other approach is to use a linked structure. A linked structure consists of nodes. Each node is dynamically ...
... The array is dynamically created. If the capacity of the array is exceeded, create a new larger array and copy all the elements from the current array to the new array. Using linked list. The other approach is to use a linked structure. A linked structure consists of nodes. Each node is dynamically ...
COSC 2006 Data Structures I
... The equals method compares only the title of the books. Here we try out the getClass() method which returns the class name of the object instead of using instance of which cannot distinguish different classes in an inheritance hierarchy (returns true for all the subclasses) ...
... The equals method compares only the title of the books. Here we try out the getClass() method which returns the class name of the object instead of using instance of which cannot distinguish different classes in an inheritance hierarchy (returns true for all the subclasses) ...
Dynamic Data Structures: Orthogonal Range Queries and Update
... the x-coordinates of the points are drawn from a smooth probabilistic distribution, and the y-coordinates are drawn from a class of probabilistic distributions that exhibit unbounded density. In Section 2.4 we waive the assumption on the y-coordinates of the points. We present a dynamic data structu ...
... the x-coordinates of the points are drawn from a smooth probabilistic distribution, and the y-coordinates are drawn from a class of probabilistic distributions that exhibit unbounded density. In Section 2.4 we waive the assumption on the y-coordinates of the points. We present a dynamic data structu ...
E-Book Data Structures and Algorithm
... 3. Helps to reduce the number of things the programmer has to keep in mind at any time 4. Breaking down a complex task into a number of earlier subtasks also simplifies testing and debugging Algorithm: Definition: An algorithm is a finite set of instructions which, if followed, accomplish a particul ...
... 3. Helps to reduce the number of things the programmer has to keep in mind at any time 4. Breaking down a complex task into a number of earlier subtasks also simplifies testing and debugging Algorithm: Definition: An algorithm is a finite set of instructions which, if followed, accomplish a particul ...
Data structures
... A. Memory space and processor time B. Space complexity and time complexity C. Input and output properties D. None of the above 37. Space complexity of an algorithm is the maximum amount of _______ required by it during execution. A. Time B. Operations C. Memory space D. None of the above 38. Frequen ...
... A. Memory space and processor time B. Space complexity and time complexity C. Input and output properties D. None of the above 37. Space complexity of an algorithm is the maximum amount of _______ required by it during execution. A. Time B. Operations C. Memory space D. None of the above 38. Frequen ...
CS 46B: Introduction to Data Structures
... // This node is greater than the other node if and only if // this node's row is greater than the other node's row, // or, if the two rows are equal, this node's column is greater // than the other node's column. ...
... // This node is greater than the other node if and only if // this node's row is greater than the other node's row, // or, if the two rows are equal, this node's column is greater // than the other node's column. ...
Skip Ring/Circular Skip List: Circular Linked List Based
... ring data structure and encompasses all elements. Each ring from bottom to the top is lined as an index of previous ring. In addition, skip ring data structure is similar to skip list data structure. In contrast to skip list data structure, head and tail is not required together and only head is eno ...
... ring data structure and encompasses all elements. Each ring from bottom to the top is lined as an index of previous ring. In addition, skip ring data structure is similar to skip list data structure. In contrast to skip list data structure, head and tail is not required together and only head is eno ...
Making Data Structures Confluently Persistent
... Much work has been done on making specific data structures such as catenable deques and catenable finger search trees confluently persistent (see [3, 10, 14, 16, 18, 17, 13]). Despite these results no progress has been made on the problem of obtaining a general transformation that can make any point ...
... Much work has been done on making specific data structures such as catenable deques and catenable finger search trees confluently persistent (see [3, 10, 14, 16, 18, 17, 13]). Despite these results no progress has been made on the problem of obtaining a general transformation that can make any point ...
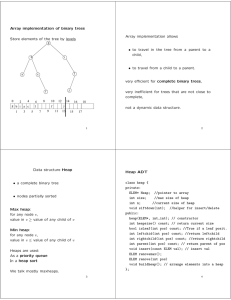
Array implementation of binary trees
... Move to front is better when some accesses are clustered together. It reacts very dynamically to changes of access patterns. Easy to implement for linked lists only. Transpose is easy to implement for both, arrays and linked lists. There are always some access patterns that make any of the above rat ...
... Move to front is better when some accesses are clustered together. It reacts very dynamically to changes of access patterns. Easy to implement for linked lists only. Transpose is easy to implement for both, arrays and linked lists. There are always some access patterns that make any of the above rat ...
Predecessor Data Structures - Algorithms for Massive Data Sets
... • Solution: Partition bitvector into u1/2 subvectors of length u1/2. • Maintain a summary bitvector of length u1/2 where index i is 1 iff subvector i contains a 1. • Example: S = {0,2,8,11,14}. ...
... • Solution: Partition bitvector into u1/2 subvectors of length u1/2. • Maintain a summary bitvector of length u1/2 where index i is 1 iff subvector i contains a 1. • Example: S = {0,2,8,11,14}. ...