Constellation Information
... The night skies of winter are famously bright with stars. People often think this is because the air is especially clear at this time of year. Its true dry winter air is more transparent than the humid hazes of summer, but theres a more important reason why we see brighter stars now. They really a ...
... The night skies of winter are famously bright with stars. People often think this is because the air is especially clear at this time of year. Its true dry winter air is more transparent than the humid hazes of summer, but theres a more important reason why we see brighter stars now. They really a ...
Other Galaxies, their Distances, and the Expansion of the Universe
... n It can, if it has a companion (that is, it is in a binary star). n ...
... n It can, if it has a companion (that is, it is in a binary star). n ...
Name: Notes – #54 White Dwarf Supernovae
... 9. Radioactive nickel is created that then decays into _______________ and then into ________________. In the process _________________________ (very high energy light) is produced. 10. How much nickel is formed during a Type 1a supernova explosion? 11. What would we see if the radioactive nickel a ...
... 9. Radioactive nickel is created that then decays into _______________ and then into ________________. In the process _________________________ (very high energy light) is produced. 10. How much nickel is formed during a Type 1a supernova explosion? 11. What would we see if the radioactive nickel a ...
Astronomy
... • Galileo used his telescope to show that Venus went through a complete set of phases, just like the Moon. This was probably the most important observation that Galileo made, because this proved that Venus was revolving around the Sun. • In the old system of thinking, Venus should always be in cresc ...
... • Galileo used his telescope to show that Venus went through a complete set of phases, just like the Moon. This was probably the most important observation that Galileo made, because this proved that Venus was revolving around the Sun. • In the old system of thinking, Venus should always be in cresc ...
pps
... For massive stars, Thomson scattering dominates the opacity (Compton scattering on free electrons). The cross section for this process is a constant. For complete ionization it leads to a opacity of 0.4 cm2/g ...
... For massive stars, Thomson scattering dominates the opacity (Compton scattering on free electrons). The cross section for this process is a constant. For complete ionization it leads to a opacity of 0.4 cm2/g ...
your star chart here - Australasian Science Magazine
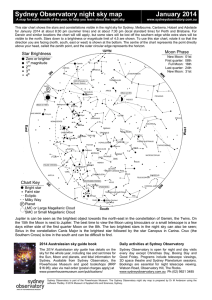
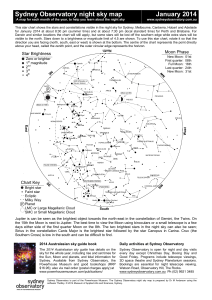
... This star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for January 2014 at about 8:30 pm (summer time) and at about 7:30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still ap ...
... This star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for January 2014 at about 8:30 pm (summer time) and at about 7:30 pm (local standard time) for Perth and Brisbane. For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still ap ...
Student 4
... Please note – This is an extract from one student’s response Red Dwarfs and Barnard’s star. Their origin and significance to astronomy. What is a Red Dwarf? A red dwarf is a small and relatively cool star on the main sequence, being a M spectral type. Red dwarfs range in mass from a low of 0.075 sol ...
... Please note – This is an extract from one student’s response Red Dwarfs and Barnard’s star. Their origin and significance to astronomy. What is a Red Dwarf? A red dwarf is a small and relatively cool star on the main sequence, being a M spectral type. Red dwarfs range in mass from a low of 0.075 sol ...
Volume 20 Number 4 March 2012 - Forsyth Astronomical Society
... Peering deep inside the hub of the Andromeda galaxy, the Hubble Space Telescope has uncovered a large, rare population of hot, bright stars. Blue is typically an indicator of hot, young stars but these stellar oddities are aging, Sun-like stars that have prematurely cast off their outer layers of ma ...
... Peering deep inside the hub of the Andromeda galaxy, the Hubble Space Telescope has uncovered a large, rare population of hot, bright stars. Blue is typically an indicator of hot, young stars but these stellar oddities are aging, Sun-like stars that have prematurely cast off their outer layers of ma ...
OUSNMAR05 - The Open University
... pair provide a good test for reasonable eyesight. The pair form a optical double ie. they are not physically associated. Through large binoculars or small telescopes Mizar itself is shown to have a fourth magnitude companion forming a true binary system. NGC3031 (M81) (6.9) sg. One of the more beaut ...
... pair provide a good test for reasonable eyesight. The pair form a optical double ie. they are not physically associated. Through large binoculars or small telescopes Mizar itself is shown to have a fourth magnitude companion forming a true binary system. NGC3031 (M81) (6.9) sg. One of the more beaut ...
Big Bang Theory Scientific origin of the Universe
... approaching train and the sharp decrease in pitch as the train passes by and recedes. The effect arises because the sound waves arrive at the listener's ear closer together as the source approaches, and further apart as it recedes. ...
... approaching train and the sharp decrease in pitch as the train passes by and recedes. The effect arises because the sound waves arrive at the listener's ear closer together as the source approaches, and further apart as it recedes. ...
Red Shift, Blue Shift
... closer to Earth than the previous wave. To an observer on Earth, the distance between wave crests will be smaller than if the star were at rest relative to Earth. The observer would see light that has a shorter wavelength than it had when it was emitted. In this example, the light has shifted toward ...
... closer to Earth than the previous wave. To an observer on Earth, the distance between wave crests will be smaller than if the star were at rest relative to Earth. The observer would see light that has a shorter wavelength than it had when it was emitted. In this example, the light has shifted toward ...
Semester #1 – GeoScience Review Guide – Final Exam Scale
... 44. What is important about Hubble’s discovery that there is a red shift in the spectra of galaxies? 45. What object in space is so dense that even light can not escape? 46. Which type of spectrum is observed when studying the light radiation given off by most stars? 47. Where are the Blue stars loc ...
... 44. What is important about Hubble’s discovery that there is a red shift in the spectra of galaxies? 45. What object in space is so dense that even light can not escape? 46. Which type of spectrum is observed when studying the light radiation given off by most stars? 47. Where are the Blue stars loc ...
Answers - ddns.net
... (a) The sun is 330,000 times more massive than the earth (M/m = 330, 000). The earth orbits at a distance of 1.5 × 108 km about the center of mass. What is the distance of the sun to the center of mass? The radius of the sun is 7 × 105 km. Is this distance smaller or larger than the sun’s radius? No ...
... (a) The sun is 330,000 times more massive than the earth (M/m = 330, 000). The earth orbits at a distance of 1.5 × 108 km about the center of mass. What is the distance of the sun to the center of mass? The radius of the sun is 7 × 105 km. Is this distance smaller or larger than the sun’s radius? No ...
Name: Period : _____ Bulldog Review #9 1. The Milky Wa
... B. Gravity is a force that causes objects to move toward the center of the Earth. Gravity is caused by tectonic plate movement. C. Gravity is the force that is formed in the crust of the planet and it holds objects to the surface of the Earth. D. Gravity is the natural force that causes objects to m ...
... B. Gravity is a force that causes objects to move toward the center of the Earth. Gravity is caused by tectonic plate movement. C. Gravity is the force that is formed in the crust of the planet and it holds objects to the surface of the Earth. D. Gravity is the natural force that causes objects to m ...
deep space - altaastronomy
... • Regular black holes are thought to form from heavy stars. When these stars end their lives in a supernova explosion, their cores collapse and gravity wins out over any other force that might be able to hold the star up. • Eventually, the star collapses so much that it is contained within its Schwa ...
... • Regular black holes are thought to form from heavy stars. When these stars end their lives in a supernova explosion, their cores collapse and gravity wins out over any other force that might be able to hold the star up. • Eventually, the star collapses so much that it is contained within its Schwa ...
Merit - NZQA
... Red giants are bright starts (10-100 x brighter than our sun) that have used up all of their hydrogen fuel. To fuse He → C their core had to collapse and their outer layers expanded outwards. This means red giants have a large surface area but a low temperature range of ...
... Red giants are bright starts (10-100 x brighter than our sun) that have used up all of their hydrogen fuel. To fuse He → C their core had to collapse and their outer layers expanded outwards. This means red giants have a large surface area but a low temperature range of ...
R136a1

RMC 136a1 (usually abbreviated to R136a1) is a Wolf-Rayet star located at the center of R136, the central condensation of stars of the large NGC 2070 open cluster in the Tarantula Nebula. It lies at a distance of about 50 kiloparsecs (163,000 light-years) in the Large Magellanic Cloud. It has the highest mass and luminosity of any known star, at 265 M☉ and 8.7 million L☉, and also one of the hottest at over 50,000 K.