Relativistic Third Kepler Law for Circular Orbits
... The orbital time differences from the Newton orbit time are plotted in Fig.1. It is interesting to note that both formulas converge to the gravitational red shift formula for large distances, but for the Schwarzschild metric there is a zero shift at the three halves of the Schwarzschild radius. This ...
... The orbital time differences from the Newton orbit time are plotted in Fig.1. It is interesting to note that both formulas converge to the gravitational red shift formula for large distances, but for the Schwarzschild metric there is a zero shift at the three halves of the Schwarzschild radius. This ...
Energy and Mass - Cornell Astronomy
... Cygnus X-1 emits X-rays and γ-ray bursts, like an X-ray binary neutron star, but the companion is too massive to be a neutron star ⇒ BLACK HOLE? ...
... Cygnus X-1 emits X-rays and γ-ray bursts, like an X-ray binary neutron star, but the companion is too massive to be a neutron star ⇒ BLACK HOLE? ...
Neutron Stars and Pulsars
... • Tidal forces squeeze, stretch, tear apart, and ionize material before it reaches the event horizon. ...
... • Tidal forces squeeze, stretch, tear apart, and ionize material before it reaches the event horizon. ...
Chapter 2 Cosmic tombstones
... must be a mass large enough to make escape from its gravity impossible (escape velocity would have to be greater than the speed of light) ...
... must be a mass large enough to make escape from its gravity impossible (escape velocity would have to be greater than the speed of light) ...
Approaching a black hole
... • Advance of Mercury’s perihelion • Bending of light by the Sun’s gravity General Relativity predicts new effects, completely absent in the Newton’s theory: black holes, event horizons, gravitational waves. ...
... • Advance of Mercury’s perihelion • Bending of light by the Sun’s gravity General Relativity predicts new effects, completely absent in the Newton’s theory: black holes, event horizons, gravitational waves. ...
Name________________________ Student I.D.___________________ Math 2250−1 Quiz 7
... 1) Consider the differential equation for y x y 5 y 6 y=0 . 1a) Find the general solution to this differential equation. rx ...
... 1) Consider the differential equation for y x y 5 y 6 y=0 . 1a) Find the general solution to this differential equation. rx ...
Do flares in Saggitarius A* reflect the last stage of tidal capture
... most transparent material available – hydrogen at a high enough temperature -, so that its opacity is due only to Thomson scattering (k = 0.4cm2/g), and assume that photons are loosing no energy when diffusively scattering to the surface. Then: tg = (1/c) (k M/R), or ...
... most transparent material available – hydrogen at a high enough temperature -, so that its opacity is due only to Thomson scattering (k = 0.4cm2/g), and assume that photons are loosing no energy when diffusively scattering to the surface. Then: tg = (1/c) (k M/R), or ...
Astronomy 100 Tuesday, Thursday 2:30
... Pulsars • Pulsars were interpreted as rotating neutron stars • Only neutron stars could rotate that fast • Strong magnetic fields can beam radiation out ...
... Pulsars • Pulsars were interpreted as rotating neutron stars • Only neutron stars could rotate that fast • Strong magnetic fields can beam radiation out ...
A-105 Homework 1
... 8. (2 pts.) Pulsars radiate their energy into space as their magnetic fields interact with the accreting matter. Where does this energy ultimately come from? What happens to the pulsar as it loses its energy? ...
... 8. (2 pts.) Pulsars radiate their energy into space as their magnetic fields interact with the accreting matter. Where does this energy ultimately come from? What happens to the pulsar as it loses its energy? ...
Black Hole
... Photon energies decrease due to a gravitational redshift Luminosity decreases due to light bending The star becomes dark within a free-fall time of order R/c However, from our point of view the collapse slows down to a complete freeze as the star surface approaches the event horizon – time dilation! ...
... Photon energies decrease due to a gravitational redshift Luminosity decreases due to light bending The star becomes dark within a free-fall time of order R/c However, from our point of view the collapse slows down to a complete freeze as the star surface approaches the event horizon – time dilation! ...
A Plunge Into a Black Hole
... Photon energies decrease due to a gravitational redshift Luminosity decreases due to light bending The star becomes dark within a free-fall time of order R/c However, from our point of view the collapse slows down to a complete freeze as the star surface approaches the event horizon – time dilation! ...
... Photon energies decrease due to a gravitational redshift Luminosity decreases due to light bending The star becomes dark within a free-fall time of order R/c However, from our point of view the collapse slows down to a complete freeze as the star surface approaches the event horizon – time dilation! ...
$doc.title
... • In order for it to be accreted over many orders of magnitude in radius, it has to release the amount of energy comparable to Eb namely G m M / Rmin = m c2 / 2, where Rmin ~ a few Rs Accretion to black holes can result in the energy release comparable to the rest mass energy! Usually a ~ 10% n ...
... • In order for it to be accreted over many orders of magnitude in radius, it has to release the amount of energy comparable to Eb namely G m M / Rmin = m c2 / 2, where Rmin ~ a few Rs Accretion to black holes can result in the energy release comparable to the rest mass energy! Usually a ~ 10% n ...
Black Holes
... event occurs within the boundary, information from that event cannot reach an outside observer, making it impossible to determine if such an event occurred. • To a distant observer, clocks near a black hole appear to tick more slowly than those further away from the black hole. Due to this effect, k ...
... event occurs within the boundary, information from that event cannot reach an outside observer, making it impossible to determine if such an event occurred. • To a distant observer, clocks near a black hole appear to tick more slowly than those further away from the black hole. Due to this effect, k ...
How to Detect Black Holes
... stated that a cluster of neutron stars would have similar effects on their neighbors (the accretion disk and resulting X-ray emission, for example). Another said that it was a cluster of smaller black holes as opposed to one large one. And a third stated that SgrA* is a large mass of heavy neutrinos ...
... stated that a cluster of neutron stars would have similar effects on their neighbors (the accretion disk and resulting X-ray emission, for example). Another said that it was a cluster of smaller black holes as opposed to one large one. And a third stated that SgrA* is a large mass of heavy neutrinos ...
Solution Set
... measured to be larger than 3 solar masses. To measure this, Alice would need to know the orbital velocity of the companion star and it’s mass. The velocity can be determined from spectra ...
... measured to be larger than 3 solar masses. To measure this, Alice would need to know the orbital velocity of the companion star and it’s mass. The velocity can be determined from spectra ...
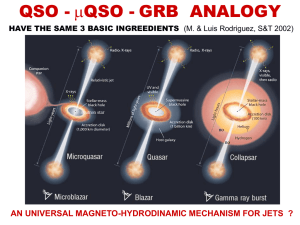
Relativistic jets in microquasars, AGN and GRBs
... Proper motion with HST + radial velocity from ground RUNAWAY VELOCITY ~120 km/s MOMENTUM = 550 M km/s as in runaway neutron stars ...
... Proper motion with HST + radial velocity from ground RUNAWAY VELOCITY ~120 km/s MOMENTUM = 550 M km/s as in runaway neutron stars ...
Black Holes!
... A Black Hole Scale Model: One of the first objects thought to be a stellar-mass black was Cygnus X-1, the first x-ray source discovered in the constellation Cygnus. Cygnus X-1 is a binary system which contains a supergiant O star and a compact object with a mass probably between 10 and 15 solar mas ...
... A Black Hole Scale Model: One of the first objects thought to be a stellar-mass black was Cygnus X-1, the first x-ray source discovered in the constellation Cygnus. Cygnus X-1 is a binary system which contains a supergiant O star and a compact object with a mass probably between 10 and 15 solar mas ...
Stellar Remnants White Dwarfs, Neutron Stars & Black Holes
... •Table II: the event horizon radius for the BH is 4.44 times the radius of its matter •The “event horizons” of the other objects are less than their actual sizes –14they effectively have no event horizon. ...
... •Table II: the event horizon radius for the BH is 4.44 times the radius of its matter •The “event horizons” of the other objects are less than their actual sizes –14they effectively have no event horizon. ...
WK7
... “Perhaps the greatest anomaly in this situation is the incredibly weak scientific case for the whole scenario of cosmic evolution. There can be no "experiments" or "observations" of stars evolving, in the very nature of the case, so it cannot be scientific, though it may be ...
... “Perhaps the greatest anomaly in this situation is the incredibly weak scientific case for the whole scenario of cosmic evolution. There can be no "experiments" or "observations" of stars evolving, in the very nature of the case, so it cannot be scientific, though it may be ...