TigerStack™ II 10/100
... SMC’s SMC6624M is a new generation of high performance switch that has a non-blocking switch fabric of 9.6Gbps. With 24 fixed auto-MDIX 10/100 ports and two slots in the front panel for optional modules, it can be expanded up to 26 ports per switch, with a mix and match of 100BASE-FX or 1000BASE-X m ...
... SMC’s SMC6624M is a new generation of high performance switch that has a non-blocking switch fabric of 9.6Gbps. With 24 fixed auto-MDIX 10/100 ports and two slots in the front panel for optional modules, it can be expanded up to 26 ports per switch, with a mix and match of 100BASE-FX or 1000BASE-X m ...
paper
... correction technique which may be used to hide packet losses between two hosts on a TCP network. This can mask tail drops at the satellite gateways, but an end-to-end TCP/NC solution requires both the sending and receiving host to “speak” TCP/NC. While this could conceivably be achieved for onisland ...
... correction technique which may be used to hide packet losses between two hosts on a TCP network. This can mask tail drops at the satellite gateways, but an end-to-end TCP/NC solution requires both the sending and receiving host to “speak” TCP/NC. While this could conceivably be achieved for onisland ...
Networks - PEGSnet
... designed to control data transfer over a communications channel Some common examples: TCP/IP: Two protocols that control communication across the Internet and These examples are some networks often referred to as the POP3, IMAP, SMTP: Protocols that can ‘Internet protocols’ be used to send and r ...
... designed to control data transfer over a communications channel Some common examples: TCP/IP: Two protocols that control communication across the Internet and These examples are some networks often referred to as the POP3, IMAP, SMTP: Protocols that can ‘Internet protocols’ be used to send and r ...
Practice Questions: Congestion Control and Queuing COS 461: Computer Networks
... Assume that the network has an MSS of 1000 bytes and the roundtrip-time between sender and receiver of 100 milliseconds. Assume at time 0 the sender attempts to open the connection. Also assume that the sender can “write” a full window’s worth of data instantaneously, so the only latency you need to ...
... Assume that the network has an MSS of 1000 bytes and the roundtrip-time between sender and receiver of 100 milliseconds. Assume at time 0 the sender attempts to open the connection. Also assume that the sender can “write” a full window’s worth of data instantaneously, so the only latency you need to ...
Chapter 1: PowerPoint slides - ECE
... procedures (Postal Service’s Mail Manual) Postal-vehicle service-transportation routes obey carrierroute maps and delivery timetables ...
... procedures (Postal Service’s Mail Manual) Postal-vehicle service-transportation routes obey carrierroute maps and delivery timetables ...
Computer networks and data communication
... !? Question !? Task !? Problem !? How long takes the transfer of the contents of a 10 page ASCII document, using data communication via the voice telecommunication network with a modern modem? ...
... !? Question !? Task !? Problem !? How long takes the transfer of the contents of a 10 page ASCII document, using data communication via the voice telecommunication network with a modern modem? ...
Internetworking I
... • Each network must stand on its own, with no internal changes allowed to connect to the internet. • Communications should be on a best-effort basis. • “black boxes” (later called routers) should be used to connect the networks. • No global control at the operations level. ...
... • Each network must stand on its own, with no internal changes allowed to connect to the internet. • Communications should be on a best-effort basis. • “black boxes” (later called routers) should be used to connect the networks. • No global control at the operations level. ...
Introduction
... • Local area networks (LANs) connect computers within a building or a enterprise network • Almost all LANs are broadcast networks • Typical topologies of LANs are bus or ring or star • We will work with Ethernet LANs. Ethernet has a bus or star topology. ...
... • Local area networks (LANs) connect computers within a building or a enterprise network • Almost all LANs are broadcast networks • Typical topologies of LANs are bus or ring or star • We will work with Ethernet LANs. Ethernet has a bus or star topology. ...
Wireless Communications: Networking and - Assets
... entities. Communication protocols are organized in multiple layered communication stacks where each layer provides services to the layer above. The information models are collections of abstracted managed object definitions and attributes for devices having common characteristics. Currently, there ar ...
... entities. Communication protocols are organized in multiple layered communication stacks where each layer provides services to the layer above. The information models are collections of abstracted managed object definitions and attributes for devices having common characteristics. Currently, there ar ...
Wireless Communications: Networking and Management - Beck-Shop
... entities. Communication protocols are organized in multiple layered communication stacks where each layer provides services to the layer above. The information models are collections of abstracted managed object definitions and attributes for devices having common characteristics. Currently, there ar ...
... entities. Communication protocols are organized in multiple layered communication stacks where each layer provides services to the layer above. The information models are collections of abstracted managed object definitions and attributes for devices having common characteristics. Currently, there ar ...
Binti Sepaha - SOA and Web
... does not depend on the context or state of other services. Services are long running executables. ...
... does not depend on the context or state of other services. Services are long running executables. ...
21. Application Layer
... TELNET (TELecommunication NETwork) was developed in 1969 beginning with RFC 15 and standardized as IETF STD 8, one of the first Internet standards. ...
... TELNET (TELecommunication NETwork) was developed in 1969 beginning with RFC 15 and standardized as IETF STD 8, one of the first Internet standards. ...
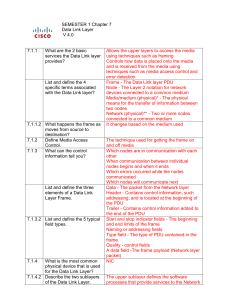
SEMESTER 1 Chapter 5
... The data Link layer provides addressing that is used in transporting the frame across the shared local media. Unlike Layer 3 logical addresses that are hierarchical, physical addresses do not indicate on what network the device is located. Device addresses at this layer are referred to as phys ...
... The data Link layer provides addressing that is used in transporting the frame across the shared local media. Unlike Layer 3 logical addresses that are hierarchical, physical addresses do not indicate on what network the device is located. Device addresses at this layer are referred to as phys ...
IPSec VPN`s
... – Implemented as a User Software – No need to modify operating system or underlying network structure – Each application and system requires its own security mechanisms ...
... – Implemented as a User Software – No need to modify operating system or underlying network structure – Each application and system requires its own security mechanisms ...
Communications in Distributed Autonomous Vehicles
... Channel Capacity • Capacity constraint for the control traffic. • Channel capacity in terms of received and transmitted power, jamming power, spread factor, bit rate. • Goal is to know the reliable transmitting distance between the nodes at 2Mbps for the given parameters. ...
... Channel Capacity • Capacity constraint for the control traffic. • Channel capacity in terms of received and transmitted power, jamming power, spread factor, bit rate. • Goal is to know the reliable transmitting distance between the nodes at 2Mbps for the given parameters. ...
Simple Network Management Protocol(SNMP) is simply define as
... organizations. Different entities such as, vendors can define private branches that include managed objects for their own products; MIBs that have not been standardized typically are positioned in the experimental branch. The SNMP and data representation must account for an adjustment in incompatibi ...
... organizations. Different entities such as, vendors can define private branches that include managed objects for their own products; MIBs that have not been standardized typically are positioned in the experimental branch. The SNMP and data representation must account for an adjustment in incompatibi ...
lecture 1 – Internet Layer IP, ARP,ICMP and IGMP
... Airport analogy - > direct or indirect flight ...
... Airport analogy - > direct or indirect flight ...
Ch. 11
... • Alternatively, assume that X wants to transmit to W or Z—then the local switch routes the frame accordingly—unicast addressing. ...
... • Alternatively, assume that X wants to transmit to W or Z—then the local switch routes the frame accordingly—unicast addressing. ...
Network Routing - Yale University
... devices in local network can change addresses of devices in local network without notifying outside world ...
... devices in local network can change addresses of devices in local network without notifying outside world ...
networking-1234619450976217-2
... Lan card is used for both transmission and receiving of data MAC address is physical or hardware address. Size of MAC address is 48 bit ...
... Lan card is used for both transmission and receiving of data MAC address is physical or hardware address. Size of MAC address is 48 bit ...
TCP/IP - Austin Community College
... Core Layer • Responsible for switching large amounts of data quickly and efficiently • To prevent slowing down the switching process: – This layer should not be burdened with security or traffic control measures or any unnecessary additional equipment ...
... Core Layer • Responsible for switching large amounts of data quickly and efficiently • To prevent slowing down the switching process: – This layer should not be burdened with security or traffic control measures or any unnecessary additional equipment ...
Content-aware Switch - University of California, Riverside
... An Alternative Implementation SRAM: control blocks, hash tables, locks Can become a bottleneck when thousands of connections are processed simultaneously; Not possible to maintain a large number due to its size ...
... An Alternative Implementation SRAM: control blocks, hash tables, locks Can become a bottleneck when thousands of connections are processed simultaneously; Not possible to maintain a large number due to its size ...
Internet protocol suite

The Internet protocol suite is the computer networking model and set of communications protocols used on the Internet and similar computer networks. It is commonly known as TCP/IP, because among many protocols, the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP) is the accepted and most widely used protocol in Internet. Often also called the Internet model, it was originally also known as the DoD model, because the development of the networking model was funded by DARPA, an agency of the United States Department of Defense.TCP/IP provides end-to-end connectivity specifying how data should be packetized, addressed, transmitted, routed and received at the destination. This functionality is organized into four abstraction layers which are used to sort all related protocols according to the scope of networking involved. From lowest to highest, the layers are the link layer, containing communication technologies for a single network segment (link); the internet layer, connecting hosts across independent networks, thus establishing internetworking; the transport layer handling host-to-host communication; and the application layer, which provides process-to-process application data exchange.The TCP/IP model and related protocol models are maintained by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).