OSI Model Layers
... provides synchronization services by planning check points in the data stream => if session fails, only data after the most recent checkpoint need be transmitted manages who can transmit data at a certain time and for how long Examples are interactive login and file transfer connections, the session ...
... provides synchronization services by planning check points in the data stream => if session fails, only data after the most recent checkpoint need be transmitted manages who can transmit data at a certain time and for how long Examples are interactive login and file transfer connections, the session ...
Wireless Communications and Networks
... Uses internet protocol (IP) Provides routing functions to allow data to traverse multiple interconnected networks Implemented in end systems and routers ...
... Uses internet protocol (IP) Provides routing functions to allow data to traverse multiple interconnected networks Implemented in end systems and routers ...
Wireless Communications and Networks
... Uses internet protocol (IP) Provides routing functions to allow data to traverse multiple interconnected networks Implemented in end systems and routers ...
... Uses internet protocol (IP) Provides routing functions to allow data to traverse multiple interconnected networks Implemented in end systems and routers ...
Reference Models - UT School of Information
... TCP/IP 1. Physical layer – not really part of this model, since TCP and IP deal with software; usually thought to refer to all hardware beneath the network layer. 2. Network or data link layer – defined by whatever the Internet Protocol will run over, e.g., a token-ring network. 3. Internet or netw ...
... TCP/IP 1. Physical layer – not really part of this model, since TCP and IP deal with software; usually thought to refer to all hardware beneath the network layer. 2. Network or data link layer – defined by whatever the Internet Protocol will run over, e.g., a token-ring network. 3. Internet or netw ...
The OSI Networking Model - Oakton Community College
... The very first layer of the OSI model describes the transmission attributes of the cabling or wireless frequencies used at each "link" or step along the way. Layer 2 describes the error correction methodologies to be used on the link; layer 3 ensures that the data can hop from link to link on the wa ...
... The very first layer of the OSI model describes the transmission attributes of the cabling or wireless frequencies used at each "link" or step along the way. Layer 2 describes the error correction methodologies to be used on the link; layer 3 ensures that the data can hop from link to link on the wa ...
CCNA 1 v3.0 - chu.edu.tw
... It encapsulates frames into packets. It provides a service to the network layer. It encapsulates the network layer information into a frame. • Its header contains a physical address which is required to complete the data link ...
... It encapsulates frames into packets. It provides a service to the network layer. It encapsulates the network layer information into a frame. • Its header contains a physical address which is required to complete the data link ...
Document
... Additional problems: a) Two stations communicate via a 1Mb/s satellite link with a propagation delay of 270ms. The satellite serves merely to retransmit data received from one station to another, with neglidgible switching delay. Using HDLC frames of 1024 bits with 3bit sequence numbers, what is the ...
... Additional problems: a) Two stations communicate via a 1Mb/s satellite link with a propagation delay of 270ms. The satellite serves merely to retransmit data received from one station to another, with neglidgible switching delay. Using HDLC frames of 1024 bits with 3bit sequence numbers, what is the ...
1. Application layer, Transport layer, Internet layer, Link layer 2
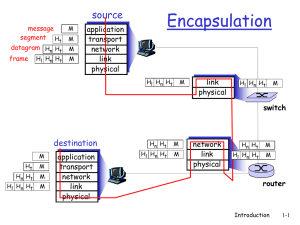
... PDU at the Layer 2 of the OSI model. A packet is encapsulated in one of more frames (depending on the size of the packet and maximum transmission unit of the frame) e.g. in Ethernet frames. 5. Connection-oriented protocols require that a logical connection be established between two device before tr ...
... PDU at the Layer 2 of the OSI model. A packet is encapsulated in one of more frames (depending on the size of the packet and maximum transmission unit of the frame) e.g. in Ethernet frames. 5. Connection-oriented protocols require that a logical connection be established between two device before tr ...
ch2
... if adapter receives frame with matching destination address, or with broadcast address (eg ARP packet), it passes data in frame to net-layer protocol otherwise, adapter discards frame ...
... if adapter receives frame with matching destination address, or with broadcast address (eg ARP packet), it passes data in frame to net-layer protocol otherwise, adapter discards frame ...