peripheral artery disease (pad)
... Disease (PAD)? (PAD) is the narrowing or blockage of the arteries in the upper and lower extremities due to plaque build-up. The process that blocks these arteries (atherosclerosis) is basically the same as that which causes coronary artery disease and carotid artery disease. The slow build-up of pl ...
... Disease (PAD)? (PAD) is the narrowing or blockage of the arteries in the upper and lower extremities due to plaque build-up. The process that blocks these arteries (atherosclerosis) is basically the same as that which causes coronary artery disease and carotid artery disease. The slow build-up of pl ...
Heart Flashcards
... Pericarditis can be caused by damage to the blood vessels (from infection, wound, autoimmune disease, etc)--blood leaks into pericardial cavity Pericarditis can lead to pericardial friction rub, adhesions, additional excess fluid in the pericardial cavity, or cardiac tamponade (pressure from fluid ...
... Pericarditis can be caused by damage to the blood vessels (from infection, wound, autoimmune disease, etc)--blood leaks into pericardial cavity Pericarditis can lead to pericardial friction rub, adhesions, additional excess fluid in the pericardial cavity, or cardiac tamponade (pressure from fluid ...
Heart Flashcards
... Pericarditis can be caused by damage to the blood vessels (from infection, wound, autoimmune disease, etc)--blood leaks into pericardial cavity Pericarditis can lead to pericardial friction rub, adhesions, additional excess fluid in the pericardial cavity, or cardiac tamponade (pressure from fluid ...
... Pericarditis can be caused by damage to the blood vessels (from infection, wound, autoimmune disease, etc)--blood leaks into pericardial cavity Pericarditis can lead to pericardial friction rub, adhesions, additional excess fluid in the pericardial cavity, or cardiac tamponade (pressure from fluid ...
Cardiovasculat presentation from Kay Elliot
... Acute Heart Failure (CG187) October, 2014 Atrial Fibrillation (CG180) June 2014 Chest pain of recent onset (CG 95) March 2010 Chronic Heart Failure (CG 108) August 2010 Management of stable angina (CG 126) July 2011 Unstable angina and NSTEMI (CG 94) March 2010 MI with ST segment elevation (CG 167) ...
... Acute Heart Failure (CG187) October, 2014 Atrial Fibrillation (CG180) June 2014 Chest pain of recent onset (CG 95) March 2010 Chronic Heart Failure (CG 108) August 2010 Management of stable angina (CG 126) July 2011 Unstable angina and NSTEMI (CG 94) March 2010 MI with ST segment elevation (CG 167) ...
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
... What form of coronary abnormality may be observed in the background of stable (effort) angina pectoris? A minimum of 75 % stenosis, due to an atherosclerotic plaque What form of coronary abnormality may be observed in the background of unstable angina pectoris? Thrombus formation due to the rupture ...
... What form of coronary abnormality may be observed in the background of stable (effort) angina pectoris? A minimum of 75 % stenosis, due to an atherosclerotic plaque What form of coronary abnormality may be observed in the background of unstable angina pectoris? Thrombus formation due to the rupture ...
acute coronary syndrome
... Weight reduction Smoking Physical activity Avoid precipitating factors (walking into a wind or uphill, cold weather, large meals) ...
... Weight reduction Smoking Physical activity Avoid precipitating factors (walking into a wind or uphill, cold weather, large meals) ...
Human Body in health and Disease CV sys
... a. Explain the purpose of the four heart valves and describe their structure and location. b. What prevents the valves from opening backwards? 5. Which actions in the heart are happening simultaneously? 6. Trace a drop of blood from the superior vena cava to the lungs and from the lungs to the aorta ...
... a. Explain the purpose of the four heart valves and describe their structure and location. b. What prevents the valves from opening backwards? 5. Which actions in the heart are happening simultaneously? 6. Trace a drop of blood from the superior vena cava to the lungs and from the lungs to the aorta ...
HeartFlow Secures De Novo Clearance from the US Food and Drug
... Highly Accurate, Non-invasive Test Has the Potential to Change the Way Coronary Artery Disease is Managed REDWOOD CITY, Calif. – Dec. 1, 2014 – HeartFlow Inc., a pioneer in personalized medical technology for cardiovascular disease, today announced that it received de novo clearance from the U.S. Fo ...
... Highly Accurate, Non-invasive Test Has the Potential to Change the Way Coronary Artery Disease is Managed REDWOOD CITY, Calif. – Dec. 1, 2014 – HeartFlow Inc., a pioneer in personalized medical technology for cardiovascular disease, today announced that it received de novo clearance from the U.S. Fo ...
diseases of the cardiovascular system - Rachel`s E
... artery smooth and allows blood to easily flow through. When the endothelium is damaged that is when cholesterol starts to build up and when the body sends white blood cells to fix it they end up getting stuck and then the plaque is created. There are risk factors because it can cause many other seri ...
... artery smooth and allows blood to easily flow through. When the endothelium is damaged that is when cholesterol starts to build up and when the body sends white blood cells to fix it they end up getting stuck and then the plaque is created. There are risk factors because it can cause many other seri ...
Cardiovascular Disease
... Common Forms of Cardiovascular Diseases Angina Pectoris: (Ischemia) – chest pain • Blood flow not totally occluded • Insufficient to meet MVO2 (oxygen consumption of myocardial muscle) ...
... Common Forms of Cardiovascular Diseases Angina Pectoris: (Ischemia) – chest pain • Blood flow not totally occluded • Insufficient to meet MVO2 (oxygen consumption of myocardial muscle) ...
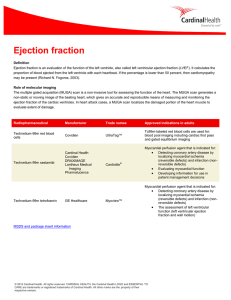
Nuclear Medicine: Ejection Fraction
... ejection fraction of the cardiac ventricles. In heart attack cases, a MUGA scan localizes the damaged portion of the heart muscle to evaluate extent of damage. ...
... ejection fraction of the cardiac ventricles. In heart attack cases, a MUGA scan localizes the damaged portion of the heart muscle to evaluate extent of damage. ...
Cardiac Disorders
... pressure, cigarette smoking (nicotine), diabetes mellitus with elevated blood glucose, obesity, sedentary lifestyle – Other factors • Stress, sex hormones, birth control pills, excessive alcohol intake, high homocysteine levels ...
... pressure, cigarette smoking (nicotine), diabetes mellitus with elevated blood glucose, obesity, sedentary lifestyle – Other factors • Stress, sex hormones, birth control pills, excessive alcohol intake, high homocysteine levels ...
coronary artery calcification and its relation to systolic function
... coronary artery calcification and its relation to LV function estimated by MsCT in chronic coronary artery disease. Patients and Methods: Out of 758 persons who were referred to 64 slices MSCT, the total of 156 (age 50 to 69 years, 64% males) in sinus rhythm with chronic coronary artery disease were ...
... coronary artery calcification and its relation to LV function estimated by MsCT in chronic coronary artery disease. Patients and Methods: Out of 758 persons who were referred to 64 slices MSCT, the total of 156 (age 50 to 69 years, 64% males) in sinus rhythm with chronic coronary artery disease were ...
Editor`s Perspective Editorials Original Articles
... Copyright © 2017 American Heart Association, Inc. All rights reserved. Print ISSN: 1941-7640. Online ISSN: 1941-7632 ...
... Copyright © 2017 American Heart Association, Inc. All rights reserved. Print ISSN: 1941-7640. Online ISSN: 1941-7632 ...
Current Perspective No
... No-Reflow Phenomenon By Rezkalla and Kloner Circulation 2002 February 5th ...
... No-Reflow Phenomenon By Rezkalla and Kloner Circulation 2002 February 5th ...
File
... Atheroma – fatty deposit in the inner lining of an artery (occurs in atherosclerosis) Atherosclerosis – refers to the build-up of fats, cholesterol, and other substances in artery walls (plaques) Cardiac arrest – sudden stop in blood circulation due to failure of the heart to contract Cardiac cachex ...
... Atheroma – fatty deposit in the inner lining of an artery (occurs in atherosclerosis) Atherosclerosis – refers to the build-up of fats, cholesterol, and other substances in artery walls (plaques) Cardiac arrest – sudden stop in blood circulation due to failure of the heart to contract Cardiac cachex ...
Myocardial infarction
... 1. Typical rise and gradual fall (troponin) or more rapid rise and fall (CK-MB) of biochemical markers of myocardial necrosis with at least one of the following: a. Ischemic symptoms b. Development of pathologic Q waves on the electrocardiogram c. Electrocardiographic changes indicative of ischemia ...
... 1. Typical rise and gradual fall (troponin) or more rapid rise and fall (CK-MB) of biochemical markers of myocardial necrosis with at least one of the following: a. Ischemic symptoms b. Development of pathologic Q waves on the electrocardiogram c. Electrocardiographic changes indicative of ischemia ...
Managing Chronic Heart Failure
... Class 1: Ordinary physical activity doesn’t cause undue fatigue, dyspnea, or anginal pain. Class II: Asymptomatic at rest, slight limitations of physical activity. Ordinary physical activity causes palpitations, dyspnea, & anginal pain. Class III: Marked limitations of physical activity, but asympto ...
... Class 1: Ordinary physical activity doesn’t cause undue fatigue, dyspnea, or anginal pain. Class II: Asymptomatic at rest, slight limitations of physical activity. Ordinary physical activity causes palpitations, dyspnea, & anginal pain. Class III: Marked limitations of physical activity, but asympto ...