Учитель: Размахнина О
... A 1____________ is an opening in the Earth's surface where molten rock can escape from underneath. About 30 km beneath your feet is the Earth's 2_______________. It's a region of superhot rock that extends down to the Earth's 3_____________. This region is so hot that molten rock can squeeze out and ...
... A 1____________ is an opening in the Earth's surface where molten rock can escape from underneath. About 30 km beneath your feet is the Earth's 2_______________. It's a region of superhot rock that extends down to the Earth's 3_____________. This region is so hot that molten rock can squeeze out and ...
Eruption
... Bomb – a lump of rock thrown out in an eruption Crater – a deep hollow at the top of a volcano Crust – The top layer of the Earth Eruption – the release of gases, magma and rock from a volcano Lava – melted rock that flows down the volcano Magma – melted rock inside the Earth Molten – melted, liquid ...
... Bomb – a lump of rock thrown out in an eruption Crater – a deep hollow at the top of a volcano Crust – The top layer of the Earth Eruption – the release of gases, magma and rock from a volcano Lava – melted rock that flows down the volcano Magma – melted rock inside the Earth Molten – melted, liquid ...
volcanoes stations
... 13. After looking at the samples, sketch the crystal sizes of each in the boxes below. Based on the picture of where each of these formed, fill in the blanks below for each sample with (cooled) quickly or slowly or quickly and slowly, large or small or large and small (crystals). Texture information ...
... 13. After looking at the samples, sketch the crystal sizes of each in the boxes below. Based on the picture of where each of these formed, fill in the blanks below for each sample with (cooled) quickly or slowly or quickly and slowly, large or small or large and small (crystals). Texture information ...
Volcano tourism
... Every year millions of tourists visit active and dormant volcanoes. They want to see the fantastic scenery. They enjoy beautiful sunsets and take spectacular photographs of eruptions. Some even do more extreme activities like climbing volcanic mountains or taking a hot air balloon trip over the volc ...
... Every year millions of tourists visit active and dormant volcanoes. They want to see the fantastic scenery. They enjoy beautiful sunsets and take spectacular photographs of eruptions. Some even do more extreme activities like climbing volcanic mountains or taking a hot air balloon trip over the volc ...
Build a Volcano
... Earth. The term volcano also refers to the opening or vent through which the molten rock and associated gases are expelled. Driven by buoyancy and gas pressure, the molten rock, which is lighter than the surrounding solid rock, forces its way upward and may ultimately break though zones of weaknesse ...
... Earth. The term volcano also refers to the opening or vent through which the molten rock and associated gases are expelled. Driven by buoyancy and gas pressure, the molten rock, which is lighter than the surrounding solid rock, forces its way upward and may ultimately break though zones of weaknesse ...
Volcanoes by Marida Torosyan and Ani Tashyan
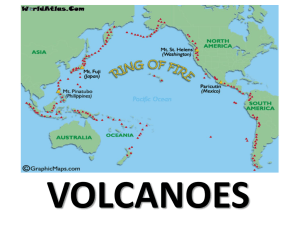
... One important volcanic belt is the Ring of Fire. Plates are immense pieces of crust that cause volcanic eruptions. Volcanoes are made on plate boundaries that also cause volcanic eruptions. ...
... One important volcanic belt is the Ring of Fire. Plates are immense pieces of crust that cause volcanic eruptions. Volcanoes are made on plate boundaries that also cause volcanic eruptions. ...
Objective: Identify and describe the three kinds of volcanic cones
... Objective: Identify and describe the three kinds of volcanic cones Both active and inactive volcanoes can be found in many places around the world. They are also found in space. Jupiter’s moon Io is the first moon or body other than Earth on which scientists have seen active volcanoes. The volcanoes ...
... Objective: Identify and describe the three kinds of volcanic cones Both active and inactive volcanoes can be found in many places around the world. They are also found in space. Jupiter’s moon Io is the first moon or body other than Earth on which scientists have seen active volcanoes. The volcanoes ...
Volcanoes form as molten rock erupts.
... escapes to the surface through volcanoes. A volcano is an opening in Earth’s crust through which molten rock, rock fragments, and hot gases erupt. A mountain built up from erupted material is also called a volcano. A volcano may erupt violently or gently. A violent eruption can cause tremendous dest ...
... escapes to the surface through volcanoes. A volcano is an opening in Earth’s crust through which molten rock, rock fragments, and hot gases erupt. A mountain built up from erupted material is also called a volcano. A volcano may erupt violently or gently. A violent eruption can cause tremendous dest ...
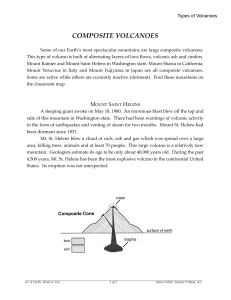
composite volcanoes - Mesa Public Schools
... A sleeping giant awoke on May 18, 1980. An enormous blast blew off the top and side of this mountain in Washington state. There had been warnings of volcanic activity in the form of earthquakes and venting of steam for two months. Mount St. Helens had been dormant since 1831. Mt. St. Helens blew a c ...
... A sleeping giant awoke on May 18, 1980. An enormous blast blew off the top and side of this mountain in Washington state. There had been warnings of volcanic activity in the form of earthquakes and venting of steam for two months. Mount St. Helens had been dormant since 1831. Mt. St. Helens blew a c ...
Warm up question
... producing steep slopes and the other kind with voluminous lava flows producing gentle slopes. * Students know the explanation for the location and properties of volcanoes that are due to hot spots and the explanation for those that are due to subduction. ...
... producing steep slopes and the other kind with voluminous lava flows producing gentle slopes. * Students know the explanation for the location and properties of volcanoes that are due to hot spots and the explanation for those that are due to subduction. ...
Types of Volcanoes Article File
... geologists can interpret of its past, a high volcano--called Mount Mazama- probably similar in appearance to present-day Mount Rainier was once located at this spot. Following a series of tremendous explosions about 6,800 years ago, the volcano lost its top. Enormous volumes of volcanic ash and dust ...
... geologists can interpret of its past, a high volcano--called Mount Mazama- probably similar in appearance to present-day Mount Rainier was once located at this spot. Following a series of tremendous explosions about 6,800 years ago, the volcano lost its top. Enormous volumes of volcanic ash and dust ...
Principal Types of Volcanoes
... From what geologists can interpret of its past, a high volcano--called Mount Mazamaprobably similar in appearance to present-day Mount Rainier was once located at this spot. Following a series of tremendous explosions about 6,800 years ago, the volcano lost its top. Enormous volumes of volcanic ash ...
... From what geologists can interpret of its past, a high volcano--called Mount Mazamaprobably similar in appearance to present-day Mount Rainier was once located at this spot. Following a series of tremendous explosions about 6,800 years ago, the volcano lost its top. Enormous volumes of volcanic ash ...
Volcanic Eruptions
... • Cool stiff lava that does not travel far from the erupting vent. • It cools and form sharp edged chunks. ...
... • Cool stiff lava that does not travel far from the erupting vent. • It cools and form sharp edged chunks. ...
Volcanoes - Ms. Inden's Geography 12 Website | When one
... • The rock expands as the temperature rises, and also gas is produced • This causes pressure underground • The magma will erupt (now lava), along with gasses, steam, ash, volcanic bombs and rock fragments • The eruption, and the violence involved depends on the sort of volcano the type of rock invol ...
... • The rock expands as the temperature rises, and also gas is produced • This causes pressure underground • The magma will erupt (now lava), along with gasses, steam, ash, volcanic bombs and rock fragments • The eruption, and the violence involved depends on the sort of volcano the type of rock invol ...
What are Volcanoes?
... Often people think of a river of red-hot lava when they think of a volcanic eruption. Lava flow is a river of hot lava. Lava flows are common in nonexplosive eruptions where the lava flows continually. Sometimes they will spray, they are not explosive. ...
... Often people think of a river of red-hot lava when they think of a volcanic eruption. Lava flow is a river of hot lava. Lava flows are common in nonexplosive eruptions where the lava flows continually. Sometimes they will spray, they are not explosive. ...
Volcanoes lesson 2
... collapse of an ancient volcano, posthumously named Mount Mazama. This volcano violently erupted approximately 7700 years ago. The basin was formed after the top 5000 feet of the volcano collapsed. Subsequent lava flows sealed the bottom, allowing the caldera to fill with approximately 4.6 trillion g ...
... collapse of an ancient volcano, posthumously named Mount Mazama. This volcano violently erupted approximately 7700 years ago. The basin was formed after the top 5000 feet of the volcano collapsed. Subsequent lava flows sealed the bottom, allowing the caldera to fill with approximately 4.6 trillion g ...
3 TYPES OF FAULTS (MOTIONS) 3 TYPES OF VOLCANOES
... 9. geyeser A type of hot spring that shoots water into the air. This forms where water collects in an underground chamber then erupts through a narrow channel. 10. Tsunami: A water wave triggered by an earthquake, volcanic eruption, or landslide. 11. Pyroclastic flow: A dense cloud of super-hot gase ...
... 9. geyeser A type of hot spring that shoots water into the air. This forms where water collects in an underground chamber then erupts through a narrow channel. 10. Tsunami: A water wave triggered by an earthquake, volcanic eruption, or landslide. 11. Pyroclastic flow: A dense cloud of super-hot gase ...
Directions: Read the information below. Use this information and
... approach their maximum size. They rarely exceed 250m in height and 500m in diameter. Shield volcanoes are huge in size. They are built by many layers of runny lava flows. Lava spills out of a central vent or group of vents. A broad shaped, gently sloping cone is formed. This is caused by the very fl ...
... approach their maximum size. They rarely exceed 250m in height and 500m in diameter. Shield volcanoes are huge in size. They are built by many layers of runny lava flows. Lava spills out of a central vent or group of vents. A broad shaped, gently sloping cone is formed. This is caused by the very fl ...
Volcanoes - Mrs. Pechan`s Class!
... A volcano is an opening exposed on the earth’s surface where volcanic material (or magma—molten rock) is emitted. The volcanoe’s coneshaped structure is build by the accumulation of lava around it’s summit. There are many types of volcanoes. Here are some examples below that demonstrate the variou ...
... A volcano is an opening exposed on the earth’s surface where volcanic material (or magma—molten rock) is emitted. The volcanoe’s coneshaped structure is build by the accumulation of lava around it’s summit. There are many types of volcanoes. Here are some examples below that demonstrate the variou ...
File
... How are volcanoes formed? Volcanoes are formed when magma from within the Earth's upper mantle works its way to the surface. At the surface, it erupts to form lava flows and ash deposits. Over time as the volcano continues to erupt, it will get bigger and bigger. What are the different stages of vol ...
... How are volcanoes formed? Volcanoes are formed when magma from within the Earth's upper mantle works its way to the surface. At the surface, it erupts to form lava flows and ash deposits. Over time as the volcano continues to erupt, it will get bigger and bigger. What are the different stages of vol ...
Composite volcanoes
... viscous (thick) magma. • When very viscous magma rises to the surface, it usually clogs the craterpipe, and gas in the craterpipe gets locked up. • Therefore, the pressure will increase resulting in an explosive eruption. ...
... viscous (thick) magma. • When very viscous magma rises to the surface, it usually clogs the craterpipe, and gas in the craterpipe gets locked up. • Therefore, the pressure will increase resulting in an explosive eruption. ...
Volcanoes PPT - Van Buren Public Schools
... – Activity that occurs within a tectonic plate away from plate boundaries. • Most intraplate volcanism occurs where a mass of hotter than normal mantle material called a mantle plume rises toward the surface. • The activity forms localized volcanic regions called hot spots. • An example is the Hawai ...
... – Activity that occurs within a tectonic plate away from plate boundaries. • Most intraplate volcanism occurs where a mass of hotter than normal mantle material called a mantle plume rises toward the surface. • The activity forms localized volcanic regions called hot spots. • An example is the Hawai ...
The Rock cycle: Initially proposed by James Hutton
... The Rock cycle was initially proposed by James Hutton Rocks are grouped into three main families based on their origin 1. Igneous 2. Sedimentary 3. Metamorphic. 1. IGNEOUS ROCKS: ...
... The Rock cycle was initially proposed by James Hutton Rocks are grouped into three main families based on their origin 1. Igneous 2. Sedimentary 3. Metamorphic. 1. IGNEOUS ROCKS: ...
Lassen Volcanic National Park
... theory of plate tectonics says the expanding oceanic crust is thrust beneath the continental plate margins. It penetrates deep into the Earth to be partly remelted. The result is magma (molten rock). These became the feeding chambers for volcanoes in Lassen Volcanic National Park. Lassen Volcanic Na ...
... theory of plate tectonics says the expanding oceanic crust is thrust beneath the continental plate margins. It penetrates deep into the Earth to be partly remelted. The result is magma (molten rock). These became the feeding chambers for volcanoes in Lassen Volcanic National Park. Lassen Volcanic Na ...
Volcanic Eruptions
... How It All Starts • Magma from the mantle rises up through the crust because it is less dense. • Magma becomes trapped beneath layers of rock. • Weak spots in the crust allow trapped magma to reach the surface, forming a volcano. ...
... How It All Starts • Magma from the mantle rises up through the crust because it is less dense. • Magma becomes trapped beneath layers of rock. • Weak spots in the crust allow trapped magma to reach the surface, forming a volcano. ...
Lastarria

Lastarria, also known as Azufre, is a stratovolcano along the border of Argentina (border of the Catamarca and Salta provinces) and Chile (Antofagasta region). The volcano is part of the Lazufre volcanic system and is noted for the presence of molten sulfur lava flows as well as a debris avalanche. There is no recorded activity in historical times, but ground inflation has been observed.