Economics
... Cardinal utility approach to demand theory: law of diminishing marginal utility, consumer equilibrium, Marshal's derivation of law of demand. Ordinal utility approach: indifference curve analysis; principle of diminishing marginal rate of substitution; consumer equilibrium, price consumption curve; ...
... Cardinal utility approach to demand theory: law of diminishing marginal utility, consumer equilibrium, Marshal's derivation of law of demand. Ordinal utility approach: indifference curve analysis; principle of diminishing marginal rate of substitution; consumer equilibrium, price consumption curve; ...
Test #3
... unemployment, other goals relating to the level and stability/volatility of interest rates, encouraging economic growth, and relating to the level and stability/volatility of exchange rates are common. If the economy does not allow monetary policy to affect output and unemployment even in the short ...
... unemployment, other goals relating to the level and stability/volatility of interest rates, encouraging economic growth, and relating to the level and stability/volatility of exchange rates are common. If the economy does not allow monetary policy to affect output and unemployment even in the short ...
What is a business cycle?
... Non-price rationing techniques redistribute income from consumers to producers; price rationing does not. The demand for goods will be more elastic if price rationing is used to allocate good When higher prices are used to resolve shortages, the higher prices will encourage suppliers to increase the ...
... Non-price rationing techniques redistribute income from consumers to producers; price rationing does not. The demand for goods will be more elastic if price rationing is used to allocate good When higher prices are used to resolve shortages, the higher prices will encourage suppliers to increase the ...
How the Intelligent Non-Economist can Refute Every Economist
... talking about when they use specific terms like income, profit, capital, market equilibrium, and so on. This is not the case. What, then, follows from the well-documented fact that the representative economist has no idea of what profit is? Quite simple: if the core concept profit is false then the ...
... talking about when they use specific terms like income, profit, capital, market equilibrium, and so on. This is not the case. What, then, follows from the well-documented fact that the representative economist has no idea of what profit is? Quite simple: if the core concept profit is false then the ...
Keynesian Theory and the AD-AS Framework: A
... analysis often relies on unstated or questionable assumptions concerning the process leading to a short-run Keynesian equilibrium. Our own presentation above is quite explicit in its assumptions (notes 2 and 4) but, perhaps unrealistically, it presumes that the adjustment to market-run equilibrium i ...
... analysis often relies on unstated or questionable assumptions concerning the process leading to a short-run Keynesian equilibrium. Our own presentation above is quite explicit in its assumptions (notes 2 and 4) but, perhaps unrealistically, it presumes that the adjustment to market-run equilibrium i ...
Chapter 17 Disputes Over Macro Theory and Policy
... 1. In supporting discretionary monetary policy, mainstream economists argue that the velocity of money is more variable and unpredictable, in short run monetary policy can help offset changes in AD than monetarists contend. 2. Mainstream economists oppose requirements to balance the budget annually ...
... 1. In supporting discretionary monetary policy, mainstream economists argue that the velocity of money is more variable and unpredictable, in short run monetary policy can help offset changes in AD than monetarists contend. 2. Mainstream economists oppose requirements to balance the budget annually ...
This PDF is a selection from an out-of-print volume from the... of Economic Research Volume Title: Rational Expectations and Economic Policy
... diagnosis and prescription process called for in the Employment Act cannot be made to work, given the level of scientific understanding of monetary dynamics at the time. The proposals are offered rather as a compromise, promising economic performance superior to that which had been observed historic ...
... diagnosis and prescription process called for in the Employment Act cannot be made to work, given the level of scientific understanding of monetary dynamics at the time. The proposals are offered rather as a compromise, promising economic performance superior to that which had been observed historic ...
The Relationship between Inflation and Unemployment: A
... “the salary - the prices” [8]. The result of these processes will be an accelerating of inflation. The essence of the Philips curve is visually represented through the analysis of the curves of aggregate supply and demand. The growth of aggregate demand in the economy creates new imbalances and psyc ...
... “the salary - the prices” [8]. The result of these processes will be an accelerating of inflation. The essence of the Philips curve is visually represented through the analysis of the curves of aggregate supply and demand. The growth of aggregate demand in the economy creates new imbalances and psyc ...
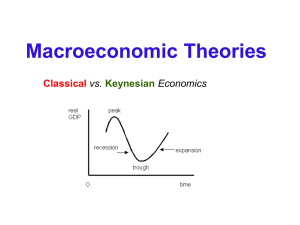
The Economic Cycle
... With falling levels of (C + I) it is likely that, even with the possibility of growth in government spending or the current account, this economy could move into severe slowdown or recession in the near future. Similarly, a jump in investment – as firms see greater business opportunities arise – wil ...
... With falling levels of (C + I) it is likely that, even with the possibility of growth in government spending or the current account, this economy could move into severe slowdown or recession in the near future. Similarly, a jump in investment – as firms see greater business opportunities arise – wil ...
Q 1
... When there is high unemployment, an increase in AD doesn’t lead to higher prices until you get close to full employment ...
... When there is high unemployment, an increase in AD doesn’t lead to higher prices until you get close to full employment ...
Department of Economics Working Papers
... which it was best of maintain the economy: high aggregate demand and some inflationary pressure or lower aggregate demand and a stable price level. It then covers the rise of the simple Phillips curve and its expectations-augmented version, which introduced into current macro theory a natural rate o ...
... which it was best of maintain the economy: high aggregate demand and some inflationary pressure or lower aggregate demand and a stable price level. It then covers the rise of the simple Phillips curve and its expectations-augmented version, which introduced into current macro theory a natural rate o ...
File - Mr. Trevino Economics
... expect some unemployment. An unemployment rate of 4 to 6 percent is considered full employment, the level of employment reached when there is no cyclical unemployment. However, some people with jobs are underemployed, meaning that they work part time when they want full-time jobs, or work at jobs th ...
... expect some unemployment. An unemployment rate of 4 to 6 percent is considered full employment, the level of employment reached when there is no cyclical unemployment. However, some people with jobs are underemployed, meaning that they work part time when they want full-time jobs, or work at jobs th ...
Working Paper No. 514 The Continuing Legacy of John Maynard
... workers. The sectoral balances approach implicitly adopted by Minsky (1963) in his earliest work, and developed in detail by Wynne Godley, carries the Kalecki analysis further by examining the implications for financial balances implied by spending growth. For example, an expansion led by private-s ...
... workers. The sectoral balances approach implicitly adopted by Minsky (1963) in his earliest work, and developed in detail by Wynne Godley, carries the Kalecki analysis further by examining the implications for financial balances implied by spending growth. For example, an expansion led by private-s ...
Edmund Phelps

Edmund Strother Phelps, Jr. (born July 26, 1933) is an American economist and the winner of the 2006 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences. Early in his career he became renowned for his research at Yale's Cowles Foundation in the first half of the 1960s on the sources of economic growth. His demonstration of the Golden Rule savings rate, a concept first devised by John von Neumann and Maurice Allais, started a wave of research on how much a nation ought to spend on present consumption rather than save and invest for future generations. His most seminal work inserted a microfoundation—one featuring imperfect information, incomplete knowledge and expectations about wages and prices—to support a macroeconomic theory of employment determination and price-wage dynamics. This led to his development of the natural rate of unemployment—its existence and the mechanism governing its size.Phelps has been McVickar Professor of Political Economy at Columbia University since 1982. He is also the director of Columbia's Center on Capitalism and Society.























