Lucas on the Relationship between Theory and Ideology
... “Methods and Problems in Business Cycle Theory” ([1980a] 1981a) comes closest to such an enterprise — it should be noted that about half the essays in his book, Studies in Business Cycle Theory, are of a methodological nature. The above account is drawn mainly from them. Note also that, with a few e ...
... “Methods and Problems in Business Cycle Theory” ([1980a] 1981a) comes closest to such an enterprise — it should be noted that about half the essays in his book, Studies in Business Cycle Theory, are of a methodological nature. The above account is drawn mainly from them. Note also that, with a few e ...
The Case for a Long-Run Inflation Target of Four Percent
... A central bank does not perfectly control the short-run behavior of inflation, but it does control inflation in the long run, or steady state. Policymakers can choose a target for the inflation rate and keep inflation close to this level on average. What is the optimal inflation target? This is a c ...
... A central bank does not perfectly control the short-run behavior of inflation, but it does control inflation in the long run, or steady state. Policymakers can choose a target for the inflation rate and keep inflation close to this level on average. What is the optimal inflation target? This is a c ...
6The Short-run Model for the Closed Economy
... gone through recurrent periods of boom and bust. This is the fascinating phenomenon of business cycles described in Chapter 14. Although long periods of high economic growth have sometimes led people to believe that the business cycle was dead, Figs 19.1 and 19.2 show that it is still alive and well ...
... gone through recurrent periods of boom and bust. This is the fascinating phenomenon of business cycles described in Chapter 14. Although long periods of high economic growth have sometimes led people to believe that the business cycle was dead, Figs 19.1 and 19.2 show that it is still alive and well ...
THE MULTIPLIER EFFECT A FORMULA FOR THE SPENDING
... vices supplied. For instance, consider the effects of tax changes on aggregate supply. One of the Ten Principles of Economics in Chapter 1 is that people respond to incentives. When government policymakers cut tax rates, workers get to keep more of each dollar they earn, so they have a greater incen ...
... vices supplied. For instance, consider the effects of tax changes on aggregate supply. One of the Ten Principles of Economics in Chapter 1 is that people respond to incentives. When government policymakers cut tax rates, workers get to keep more of each dollar they earn, so they have a greater incen ...
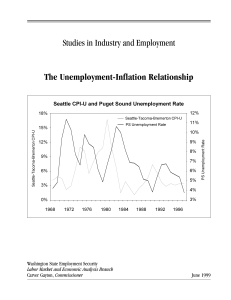
Unemployment-Inflation Relationship
... and regional (e.g., western region) levels, though that is a minor shortcoming. The ECI will establish a solid historical series over time, which will enable researchers to determine if it is a more effective alternative than the CPI in tracking the NAIRU. For the time being, however, it might be be ...
... and regional (e.g., western region) levels, though that is a minor shortcoming. The ECI will establish a solid historical series over time, which will enable researchers to determine if it is a more effective alternative than the CPI in tracking the NAIRU. For the time being, however, it might be be ...
Chapter 21 Stabilization Policy with Backward
... gain from stabilisation policy. Some economists like Robert Lucas have argued that the quantitative gains from consumption smoothing are very small for realistic values of the intertemporal elasticity of substitution in consumption1 . Others have argued that Lucas underestimates the degree of consum ...
... gain from stabilisation policy. Some economists like Robert Lucas have argued that the quantitative gains from consumption smoothing are very small for realistic values of the intertemporal elasticity of substitution in consumption1 . Others have argued that Lucas underestimates the degree of consum ...
the evolution of economic understanding
... output and a model of the economy in which inflation certainly did not lower long-run unemployment and quite possibly raised it. As a result, they believed that the most aggregate demand policy could do was keep output close to potential and inflation low. In the early 1960s, policymakers adopted th ...
... output and a model of the economy in which inflation certainly did not lower long-run unemployment and quite possibly raised it. As a result, they believed that the most aggregate demand policy could do was keep output close to potential and inflation low. In the early 1960s, policymakers adopted th ...
REAL WAGES AND UNEMPLOYMENT WITH EFFECTIVE AND
... This seems to be true irrespective of the exact neoclassical model of employment, be they New Keynesian models of efficiency wages or price-setting/wage setting models (PS-WS) of the Layard et al. variety (1991). In the so-called Post-Walrasian models, as presented by Colander (1996), unemployment i ...
... This seems to be true irrespective of the exact neoclassical model of employment, be they New Keynesian models of efficiency wages or price-setting/wage setting models (PS-WS) of the Layard et al. variety (1991). In the so-called Post-Walrasian models, as presented by Colander (1996), unemployment i ...
Modules 12 and 13 ~ Unemployment.notebook
... 4 reasons why structural unemployment always exists, explaining why the natural rate of unemployment isn't zero. 1) Efficiency wages ~ firm's pay people a little more than equilibrium wage rate to get a more loyal and stable work force. Reason why Surplus of labor exists: Labor is more expensive f ...
... 4 reasons why structural unemployment always exists, explaining why the natural rate of unemployment isn't zero. 1) Efficiency wages ~ firm's pay people a little more than equilibrium wage rate to get a more loyal and stable work force. Reason why Surplus of labor exists: Labor is more expensive f ...
fiscal policy in an expectations driven liquidity trap
... be conditioned on the underlying reasons for the continued weak growth performance and on how policies affect consumer confidence. Because confidence shocks can create an environment that in the short run is hard to distinguish from one caused by fundamental shocks, the best fiscal policy response i ...
... be conditioned on the underlying reasons for the continued weak growth performance and on how policies affect consumer confidence. Because confidence shocks can create an environment that in the short run is hard to distinguish from one caused by fundamental shocks, the best fiscal policy response i ...
Aggregate Supply
... data for the U.S. economy from 1960 to 2000. If Keynes’s prediction were correct, the dots in this figure would show a downward-sloping pattern, indicating a negative relationship.Yet the figure shows only a weak correlation between the real wage and output, and it is the opposite of what Keynes pre ...
... data for the U.S. economy from 1960 to 2000. If Keynes’s prediction were correct, the dots in this figure would show a downward-sloping pattern, indicating a negative relationship.Yet the figure shows only a weak correlation between the real wage and output, and it is the opposite of what Keynes pre ...
chapter 6 - McGraw
... In this chapter we further develop the aggregate supply side of the economy. The aggregate supply curve describes the price adjustment mechanism of the economy. In the very short run, we know the aggregate supply curve is horizontal; and in the long run, we know the aggregate supply curve is vertica ...
... In this chapter we further develop the aggregate supply side of the economy. The aggregate supply curve describes the price adjustment mechanism of the economy. In the very short run, we know the aggregate supply curve is horizontal; and in the long run, we know the aggregate supply curve is vertica ...
Targeting Nominal GDP or Prices: Expectation Dynamics and the Interest Rate
... nominal GDP targeting can potentially be more appropriate frameworks for the conduct of monetary policy. History-dependence is a key feature of nominal income and price-level targeting as it can provide more guidance to the economy than inflation targeting.2 This guidance can be helpful and is argua ...
... nominal GDP targeting can potentially be more appropriate frameworks for the conduct of monetary policy. History-dependence is a key feature of nominal income and price-level targeting as it can provide more guidance to the economy than inflation targeting.2 This guidance can be helpful and is argua ...
PDF
... and 1975-90, _respectively, are normalized by the nominal gross state product of the previous year and aggregated into the 8 standard regions used by the Bureau of Economic Analysis. The results (Table 3) indicate that state rather than local governments stabilize over the cycle. When the equations ...
... and 1975-90, _respectively, are normalized by the nominal gross state product of the previous year and aggregated into the 8 standard regions used by the Bureau of Economic Analysis. The results (Table 3) indicate that state rather than local governments stabilize over the cycle. When the equations ...
1 - Hans-Böckler
... and if households behave in the manner claimed, it will also hold in Keynesian macro models. Moreover, even if the full set of necessary assumptions is not met, bond financed tax cuts and government purchases will tend to have significantly diminished AD effects to the extent households engage in o ...
... and if households behave in the manner claimed, it will also hold in Keynesian macro models. Moreover, even if the full set of necessary assumptions is not met, bond financed tax cuts and government purchases will tend to have significantly diminished AD effects to the extent households engage in o ...
The relevance of Keynes
... that causes the economy to collapse would not happen, interest rates would automatically rebalance any discrepancy between ex ante saving and investment, and the classical theory of the optimally self-regulating market would be the relevant one in all circumstances. Many commentators have presumed t ...
... that causes the economy to collapse would not happen, interest rates would automatically rebalance any discrepancy between ex ante saving and investment, and the classical theory of the optimally self-regulating market would be the relevant one in all circumstances. Many commentators have presumed t ...
DP2010/14 Monetary Policy, In‡ation and Unemployment Nicolas Groshenny December 2010
... as q is not identi…ed. The steady-state government spending/output ratio G=Y is set equal to 0:20. Finally, the steady-state values of the unemployment rate U; the rate of in‡ation ; the nominal interest rate r; and the growth rate of output z; are set equal to their respective sample averages over ...
... as q is not identi…ed. The steady-state government spending/output ratio G=Y is set equal to 0:20. Finally, the steady-state values of the unemployment rate U; the rate of in‡ation ; the nominal interest rate r; and the growth rate of output z; are set equal to their respective sample averages over ...
The Evolution of Economic Understanding and Postwar Stabilization Policy Christina D. Romer
... controls and incomes policies, because they were so pessimistic about the effectiveness of slack in reducing inflation. In contrast, after 1979 policymakers pursued very tight policy because they were convinced that the natural rate of unemployment was relatively high, that slack was necessary to re ...
... controls and incomes policies, because they were so pessimistic about the effectiveness of slack in reducing inflation. In contrast, after 1979 policymakers pursued very tight policy because they were convinced that the natural rate of unemployment was relatively high, that slack was necessary to re ...
Edmund Phelps

Edmund Strother Phelps, Jr. (born July 26, 1933) is an American economist and the winner of the 2006 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences. Early in his career he became renowned for his research at Yale's Cowles Foundation in the first half of the 1960s on the sources of economic growth. His demonstration of the Golden Rule savings rate, a concept first devised by John von Neumann and Maurice Allais, started a wave of research on how much a nation ought to spend on present consumption rather than save and invest for future generations. His most seminal work inserted a microfoundation—one featuring imperfect information, incomplete knowledge and expectations about wages and prices—to support a macroeconomic theory of employment determination and price-wage dynamics. This led to his development of the natural rate of unemployment—its existence and the mechanism governing its size.Phelps has been McVickar Professor of Political Economy at Columbia University since 1982. He is also the director of Columbia's Center on Capitalism and Society.