science project 2012
... Type of Materials Ejected Plug Dome volcanoes spill loose fragments, (parts of the volcano) down its sides. Some domes form craggy knobs or spines over the volcanic vent, while others form short steep-sided lava flows known as “coulees.” ...
... Type of Materials Ejected Plug Dome volcanoes spill loose fragments, (parts of the volcano) down its sides. Some domes form craggy knobs or spines over the volcanic vent, while others form short steep-sided lava flows known as “coulees.” ...
Cornell Notes Template
... All lava is not the same; the viscosity of lava varies Viscosity- the inability for a liquid to flow ↑ viscosity=↓ ability to flow/move Lava that has more silica is more viscous, lava that has less silica is less viscous The ingredients (composition) of the lava determines if a volcano will have a v ...
... All lava is not the same; the viscosity of lava varies Viscosity- the inability for a liquid to flow ↑ viscosity=↓ ability to flow/move Lava that has more silica is more viscous, lava that has less silica is less viscous The ingredients (composition) of the lava determines if a volcano will have a v ...
Ch 8 Volcanoes Test – Study Guide
... Know your vocabulary!!! Be ready to look at past chapter vocabulary too! a. b. c. d. e. f. ...
... Know your vocabulary!!! Be ready to look at past chapter vocabulary too! a. b. c. d. e. f. ...
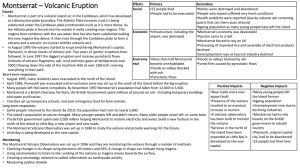
Montserrat * Volcanic Eruption
... (mixture of volcanic fragments, ash, mud and toxic gases at temperature over become uninhabitable. ntal •Forest fires caused by pyroclastic flows 500C) flowing down the side of the Soufriere Hills at over 130km/h covering •Floods as valleys blocked everything in their path. with ash. Short term resp ...
... (mixture of volcanic fragments, ash, mud and toxic gases at temperature over become uninhabitable. ntal •Forest fires caused by pyroclastic flows 500C) flowing down the side of the Soufriere Hills at over 130km/h covering •Floods as valleys blocked everything in their path. with ash. Short term resp ...
Volcanoes
... Volcanoes can be active dormant or extinct. Slieve Gullion is an extinct volcano! The erupsion in Pompeii in 79AD saw plumbs of gas and pumice spew from the volcano – knot lava. The ash and pumice fell up to 25 metres deep covering the town and preserving everything in perfect condition for 2000 yea ...
... Volcanoes can be active dormant or extinct. Slieve Gullion is an extinct volcano! The erupsion in Pompeii in 79AD saw plumbs of gas and pumice spew from the volcano – knot lava. The ash and pumice fell up to 25 metres deep covering the town and preserving everything in perfect condition for 2000 yea ...
Volcano-Glacier Interactions during Historical Eruptions of Aleutian
... open melt pits with ephemeral lakes. Although catastrophic release of water and flooding did not occur, larger eruptions that produce more extensive lava flows could lead to outburst floods from the caldera ice field. This eruption highlights lava-flow interaction with glacier ice. Augustine Volcano ...
... open melt pits with ephemeral lakes. Although catastrophic release of water and flooding did not occur, larger eruptions that produce more extensive lava flows could lead to outburst floods from the caldera ice field. This eruption highlights lava-flow interaction with glacier ice. Augustine Volcano ...
Volcanoes - SD43 Teacher Sites
... • Last eruption was in the 1800’s, but eruption of hot fluids and gas in the late 1970’s show the volcano is still active • Glaciers cover Mt. Baker – an eruption would not only produce large quantities of ash, but create volcanic debris flow, floods, and landslides that would cause extensive damage ...
... • Last eruption was in the 1800’s, but eruption of hot fluids and gas in the late 1970’s show the volcano is still active • Glaciers cover Mt. Baker – an eruption would not only produce large quantities of ash, but create volcanic debris flow, floods, and landslides that would cause extensive damage ...
In the 1960s, while studying the volcanic history of Yellowstone
... eruption was, since humans were still hunter-gatherers back then, but there is evidence to show it was a whopper. (12) Ice cores taken from the very old Greenland ice sheet show that the Toba eruption was followed by at least 6 years of “volcanic winter”. There is evidence to suggest this super erup ...
... eruption was, since humans were still hunter-gatherers back then, but there is evidence to show it was a whopper. (12) Ice cores taken from the very old Greenland ice sheet show that the Toba eruption was followed by at least 6 years of “volcanic winter”. There is evidence to suggest this super erup ...
volcano
... thinning of the crust. For example the Hawaii was created from magma 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Erupting volcanoes have many dangers not only near the eruption. One such danger is that volcanic ash can be a threat to aircraft. Also, large eruptions can affect temperature and cool the Earth's atmosp ...
... thinning of the crust. For example the Hawaii was created from magma 3,000 km deep in the Earth. Erupting volcanoes have many dangers not only near the eruption. One such danger is that volcanic ash can be a threat to aircraft. Also, large eruptions can affect temperature and cool the Earth's atmosp ...
What is Lava?
... •magma explodes from volcano and solidifies in the air •existing rock is shattered by powerful eruptions ...
... •magma explodes from volcano and solidifies in the air •existing rock is shattered by powerful eruptions ...
Typical shield volcano Mauna Loa, Hawaii
... Diagram of the eruption of Mt. St.Helens St. Pierre as it appeared shortly after the eruption of Mt. Pelee, Pelee, Martinique ...
... Diagram of the eruption of Mt. St.Helens St. Pierre as it appeared shortly after the eruption of Mt. Pelee, Pelee, Martinique ...
Unit 4 Chapter
... form steep sided volcanoes with a lot of activity Most famous volcanoes Mt St Helen's & Mt Vesuvius The Aleutian Islands, island arcs, by the North Pacific Ocean, ...
... form steep sided volcanoes with a lot of activity Most famous volcanoes Mt St Helen's & Mt Vesuvius The Aleutian Islands, island arcs, by the North Pacific Ocean, ...
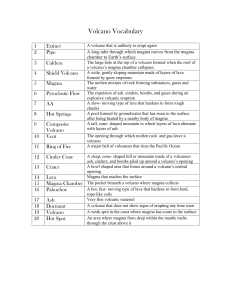
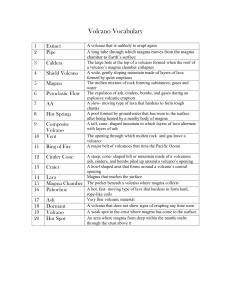
Volcano Vocabulary
... The expulsion of ash, cinders, bombs, and gases during an explosive volcanic eruption A slow- moving type of lava that hardens to form rough chunks A pool formed by groundwater that has risen to the surface after being heated by a nearby body of magma A tall, cone- shaped mountain in which layers of ...
... The expulsion of ash, cinders, bombs, and gases during an explosive volcanic eruption A slow- moving type of lava that hardens to form rough chunks A pool formed by groundwater that has risen to the surface after being heated by a nearby body of magma A tall, cone- shaped mountain in which layers of ...
Volcano Vocabulary
... The expulsion of ash, cinders, bombs, and gases during an explosive volcanic eruption A slow- moving type of lava that hardens to form rough chunks A pool formed by groundwater that has risen to the surface after being heated by a nearby body of magma A tall, cone- shaped mountain in which layers of ...
... The expulsion of ash, cinders, bombs, and gases during an explosive volcanic eruption A slow- moving type of lava that hardens to form rough chunks A pool formed by groundwater that has risen to the surface after being heated by a nearby body of magma A tall, cone- shaped mountain in which layers of ...
Lab 5 Lecture
... The magma chamber below is (partially or completely) emptied after an eruption The emptied magma chamber can no longer support the weight of the overlying rock The overlying rock collapses into itself, forming a circular basin ...
... The magma chamber below is (partially or completely) emptied after an eruption The emptied magma chamber can no longer support the weight of the overlying rock The overlying rock collapses into itself, forming a circular basin ...
What is Lava? - Princeton ISD
... Craters, Calderas, and Lava Plateau Crater • From explosions of material out of the vent and the collapse of material back into vent ...
... Craters, Calderas, and Lava Plateau Crater • From explosions of material out of the vent and the collapse of material back into vent ...
Analysis of Distribution of Volcanoes around the Korean Peninsula
... Taiwan, and the Kamchatka area in Russia, and then identified a high-risk group of 29 volcanoes that are highly likely to affect the region, based on conditions such as volcanic activity, types of rock at risk of eruption, distance from Seoul, and volcanoes having Plinian eruption history with volca ...
... Taiwan, and the Kamchatka area in Russia, and then identified a high-risk group of 29 volcanoes that are highly likely to affect the region, based on conditions such as volcanic activity, types of rock at risk of eruption, distance from Seoul, and volcanoes having Plinian eruption history with volca ...
volcanism - Geophile.net
... – Caldera-forming eruption – Numerous pyroclastic flows • 10,000 deaths ...
... – Caldera-forming eruption – Numerous pyroclastic flows • 10,000 deaths ...
VOLCANOES form where molten rock is vented at Earth`s surface.
... • broad gentle slopes • formed from basalt lava of low viscosity • eruption is mostly lava rather than pyroclastic material • eruptions are not explosive (unless water gets into vents) • lava pours out of vents or as fountains ...
... • broad gentle slopes • formed from basalt lava of low viscosity • eruption is mostly lava rather than pyroclastic material • eruptions are not explosive (unless water gets into vents) • lava pours out of vents or as fountains ...
chapter 9 vocabulary terms
... Mantle Plume (p. 279) – A mass of hotter than normal mantle material that ascends toward the surface, where it may lead to igneous activity. These plumes of solid yet mobile material may originate as deep as the core-mantle boundary. ...
... Mantle Plume (p. 279) – A mass of hotter than normal mantle material that ascends toward the surface, where it may lead to igneous activity. These plumes of solid yet mobile material may originate as deep as the core-mantle boundary. ...
Volcano
... upper level winds as far away as New York City Volcanic dust lowered global temperatures for five years. ...
... upper level winds as far away as New York City Volcanic dust lowered global temperatures for five years. ...
volcanism - Edgartown School
... the brink of extinction (only a few thousand people on Earth believed to survived). Caused at least six years of “volcanic winter”. It was a whopper. A supervolcano is practically inconceivable. ...
... the brink of extinction (only a few thousand people on Earth believed to survived). Caused at least six years of “volcanic winter”. It was a whopper. A supervolcano is practically inconceivable. ...
Earthquake, Volcano and Mountain Review Sheet
... a. Earthquake: a shaking of the ground caused by the sudden movement of large blocks of rocks along a fault b. Fault: a fracture in Earth’s lithosphere along which blocks of rock move past each other i. In other words: an area between two tectonic plates that are moving past each other (transform bo ...
... a. Earthquake: a shaking of the ground caused by the sudden movement of large blocks of rocks along a fault b. Fault: a fracture in Earth’s lithosphere along which blocks of rock move past each other i. In other words: an area between two tectonic plates that are moving past each other (transform bo ...
Mount Pinatubo

Mount Pinatubo (Filipino: Bundok Pinatubo) is an active stratovolcano in the Cabusilan Mountains on the island of Luzon, near the tripoint of the Philippine provinces of Zambales, Tarlac, and Pampanga. Before the volcanic activities of 1991, its eruptive history was unknown to most people. It was heavily eroded, inconspicuous and obscured from view. It was covered with dense forest which supported a population of several thousand indigenous people, the Aetas, who fled to the mountains during the Spanish conquest of the Philippines.The volcano's Plinian / Ultra-Plinian eruption on 15 June 1991 produced the second largest terrestrial eruption of the 20th century after the 1912 eruption of Novarupta in the Alaska Peninsula.Complicating the eruption was the arrival of Typhoon Yunya (Diding), bringing a lethal mix of ash and rain to areas surrounding the volcano. Successful predictions at the onset of the climactic eruption led to the evacuation of tens of thousands of people from the surrounding areas, saving many lives, but the surrounding areas were severely damaged by pyroclastic flows, ash deposits, and subsequently, by the lahars caused by rainwaters re-mobilizing earlier volcanic deposits causing extensive destruction to infrastructure and changing the river systems months to years after the eruption.The effects of the eruption were felt worldwide. It ejected roughly 10,000,000,000 tonnes (1.1×1010 short tons) or 10 km3 (2.4 cu mi) of magma, and 20,000,000 tonnes (22,000,000 short tons) SO2, bringing vast quantities of minerals and metals to the surface environment. It injected more particulate into the stratosphere than any eruption since Krakatoa in 1883. Over the following months, the aerosols formed a global layer of sulfuric acid haze. Global temperatures dropped by about 0.5 °C (0.9 °F) in the years 1991-93, and ozone depletion temporarily increased substantially.