Geo Fun - Latitude Festival
... 1. Name some other stratovolcanoes and their locations around the world. 2. On the paper model, a small town has been built at the foot of the volcano. This is a common situation around the world. What are some of the problems or hazards the townspeople might have to face living so close to a volcan ...
... 1. Name some other stratovolcanoes and their locations around the world. 2. On the paper model, a small town has been built at the foot of the volcano. This is a common situation around the world. What are some of the problems or hazards the townspeople might have to face living so close to a volcan ...
Scientists are monitoring volcanic activity at Yellowstone and if it
... the “volcanic winters” lasted from the past three Yellowstone super eruptions, but they likely had a significant impact on life on Earth at that time. Although it is possible, scientists are not convinced that there will ever be another catastrophic eruption at Yellowstone. Given Yellowstone's past ...
... the “volcanic winters” lasted from the past three Yellowstone super eruptions, but they likely had a significant impact on life on Earth at that time. Although it is possible, scientists are not convinced that there will ever be another catastrophic eruption at Yellowstone. Given Yellowstone's past ...
Volcano Project
... There are 3 basic types of volcanoes, some are explosive and some erupt quietly. Some are active for millions of years and others for only a few years. The type of volcanic structure and its location on Earth’s surface is determined by the type of magma it erupts. The type of magma is determined by ...
... There are 3 basic types of volcanoes, some are explosive and some erupt quietly. Some are active for millions of years and others for only a few years. The type of volcanic structure and its location on Earth’s surface is determined by the type of magma it erupts. The type of magma is determined by ...
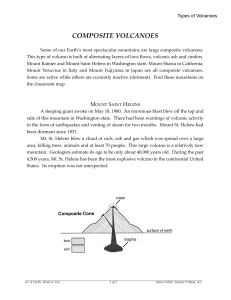
composite volcanoes - Mesa Public Schools
... A sleeping giant awoke on May 18, 1980. An enormous blast blew off the top and side of this mountain in Washington state. There had been warnings of volcanic activity in the form of earthquakes and venting of steam for two months. Mount St. Helens had been dormant since 1831. Mt. St. Helens blew a c ...
... A sleeping giant awoke on May 18, 1980. An enormous blast blew off the top and side of this mountain in Washington state. There had been warnings of volcanic activity in the form of earthquakes and venting of steam for two months. Mount St. Helens had been dormant since 1831. Mt. St. Helens blew a c ...
Volcano Glossary III
... Pumice from basaltic magma, where the walls surrounding the gas bubbles have burst leaving only the stems between each three former bubble walls, and junctions at the intersection of four bubbles. This gives a rock a honeycomb structure. Though it seems light enough to float on water, reticulite doe ...
... Pumice from basaltic magma, where the walls surrounding the gas bubbles have burst leaving only the stems between each three former bubble walls, and junctions at the intersection of four bubbles. This gives a rock a honeycomb structure. Though it seems light enough to float on water, reticulite doe ...
lesson 24 effects of ash fall
... Magma is buoyont, and lighter than the solid rock that surrounds it, which is why it rises. ...
... Magma is buoyont, and lighter than the solid rock that surrounds it, which is why it rises. ...
GAPS Guidelines
... the atmosphere before they settle to earth. Depth and particle size diminish away from the volcano. The ash becomes widely dispersed, covering extensive areas, moving downwind with the heavier particles falling out of the lower atmosphere within hours or days after the eruption. Finer particles reac ...
... the atmosphere before they settle to earth. Depth and particle size diminish away from the volcano. The ash becomes widely dispersed, covering extensive areas, moving downwind with the heavier particles falling out of the lower atmosphere within hours or days after the eruption. Finer particles reac ...
6.15 Eruptions and Volcano Types
... the main cracks and weaknesses in the lithosphere? These are found at the boundaries between the tectonic plates. And there is where we find the main zones or section of volcanic activity. Magma is a liquid. When it reaches the earth’s surface, it may erupt In the form of solids, liquids, and gases. ...
... the main cracks and weaknesses in the lithosphere? These are found at the boundaries between the tectonic plates. And there is where we find the main zones or section of volcanic activity. Magma is a liquid. When it reaches the earth’s surface, it may erupt In the form of solids, liquids, and gases. ...
Why Do Volcanoes Erupt? A Step by Step Guide
... molten rock, called magma, rises up into the mountain and the mountain is ready to erupt. When the volcanoes in Hawaii, like this one, erupt, the magna, the molten rock, flows out like lava, but when the scientists studied Mt. St. Helens, they found that the magma was very thick and gooey. It could ...
... molten rock, called magma, rises up into the mountain and the mountain is ready to erupt. When the volcanoes in Hawaii, like this one, erupt, the magna, the molten rock, flows out like lava, but when the scientists studied Mt. St. Helens, they found that the magma was very thick and gooey. It could ...
What mainly controls eruptive style? Viscosity in magma 2. Eruptive
... Flood Basalts (aka Plateau Basalts) Fissure eruptions of basalt—Earth’s largest lava flows ...
... Flood Basalts (aka Plateau Basalts) Fissure eruptions of basalt—Earth’s largest lava flows ...
Volcanoes Booklet Info Basic Info
... Make a list of things you think might happen and what might be damaged by them ...
... Make a list of things you think might happen and what might be damaged by them ...
Debris Flows and Avalanches
... • Large scale landslide associated with volcanic activity- moves under gravity • Term avalanche used to emphasize the fact that material has little or no water in it when emplaced- may have steam, gas, ice, snow but not liquid water • Debris Flows or lahars are rapid, watersaturated flows. • Many de ...
... • Large scale landslide associated with volcanic activity- moves under gravity • Term avalanche used to emphasize the fact that material has little or no water in it when emplaced- may have steam, gas, ice, snow but not liquid water • Debris Flows or lahars are rapid, watersaturated flows. • Many de ...
Volcanoes - SchoolRack
... flows easily • -oozes out quietly and flows for many km • -sets fire to and buries everything in path • -produces both pahoehoe & aa • -ex. Hawaiian islands ...
... flows easily • -oozes out quietly and flows for many km • -sets fire to and buries everything in path • -produces both pahoehoe & aa • -ex. Hawaiian islands ...
Volcanoes!
... • Dissolves in the magma (turns into gas because of high temps.) • Gases need more room • Pressure builds up • (like shaking a can of pop) ...
... • Dissolves in the magma (turns into gas because of high temps.) • Gases need more room • Pressure builds up • (like shaking a can of pop) ...
Earthquakes originate at a point
... Rock fragments thrown into the air during a volcanic eruption ...
... Rock fragments thrown into the air during a volcanic eruption ...
the webquest worksheet
... _____________ erupt high into the air, but no __________ flows. 16. In the next stage, a superhot cloud of ____________ and _____________ flowed down the side of Vesuvius covering the town of __________________________. ...
... _____________ erupt high into the air, but no __________ flows. 16. In the next stage, a superhot cloud of ____________ and _____________ flowed down the side of Vesuvius covering the town of __________________________. ...
Volcanoes Day 1 - NVHSEarthScienceOlsen
... Viscocity - _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ ______. – This means that something that has a high viscosity does not flow easily. A substance with a high viscosity would be honey. A substance with a low viscosity would be water. – If the lava of a volcano has _______ __ ...
... Viscocity - _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ _______ ______. – This means that something that has a high viscosity does not flow easily. A substance with a high viscosity would be honey. A substance with a low viscosity would be water. – If the lava of a volcano has _______ __ ...
What can low frequency seismicity tell us about eruption processes
... assessing the reliability of eruption forecasting protocols, and for testing any underlying physical models for the origin of the signals and eruption mechanisms. Frequently-active subduction zone volcanoes of intermediate composition (andesite to dacite) exhibit a range of different eruption mechan ...
... assessing the reliability of eruption forecasting protocols, and for testing any underlying physical models for the origin of the signals and eruption mechanisms. Frequently-active subduction zone volcanoes of intermediate composition (andesite to dacite) exhibit a range of different eruption mechan ...
Earth Science
... Directions: Select from the numbered definitions or descriptions the best answer for each of the given terms. Put the number in the proper space in the magic square box. The sum of the numbers will be the same horizontally, vertically, and diagonally. ...
... Directions: Select from the numbered definitions or descriptions the best answer for each of the given terms. Put the number in the proper space in the magic square box. The sum of the numbers will be the same horizontally, vertically, and diagonally. ...
2_2013_papervolcanoactivity
... 1. Name some other stratovolcanoes and their locations around the world. 2. On the paper model, a small town has been built at the foot of the volcano. This is a common situation around the world. What are some of the problems or hazards the townspeople might have to face living so close to a volcan ...
... 1. Name some other stratovolcanoes and their locations around the world. 2. On the paper model, a small town has been built at the foot of the volcano. This is a common situation around the world. What are some of the problems or hazards the townspeople might have to face living so close to a volcan ...
Preparing for Volcanoes
... global warming by giving off carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, which contributes to the greenhouse effect. Greenhouses (or, hot houses) are heated by the sun's rays that enter through glass or plastic, and the heat is retained inside like a parked car on a hot day with the windows rolled up. Carbo ...
... global warming by giving off carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, which contributes to the greenhouse effect. Greenhouses (or, hot houses) are heated by the sun's rays that enter through glass or plastic, and the heat is retained inside like a parked car on a hot day with the windows rolled up. Carbo ...
Volcanoes 11.4 - Ramsey Public School District
... Formation of Volcanoes 1. Magma forms: rock melts, forming liquid magma (melted rock + trapped gas) 2. Magma rises through the crust, erupting at the surface. Magma rises b/c it is less dense than rock (it’s hotter & has gas in it). 3. Magma collects & melts more rock …Pressure builds as more gas i ...
... Formation of Volcanoes 1. Magma forms: rock melts, forming liquid magma (melted rock + trapped gas) 2. Magma rises through the crust, erupting at the surface. Magma rises b/c it is less dense than rock (it’s hotter & has gas in it). 3. Magma collects & melts more rock …Pressure builds as more gas i ...
Mount Pinatubo

Mount Pinatubo (Filipino: Bundok Pinatubo) is an active stratovolcano in the Cabusilan Mountains on the island of Luzon, near the tripoint of the Philippine provinces of Zambales, Tarlac, and Pampanga. Before the volcanic activities of 1991, its eruptive history was unknown to most people. It was heavily eroded, inconspicuous and obscured from view. It was covered with dense forest which supported a population of several thousand indigenous people, the Aetas, who fled to the mountains during the Spanish conquest of the Philippines.The volcano's Plinian / Ultra-Plinian eruption on 15 June 1991 produced the second largest terrestrial eruption of the 20th century after the 1912 eruption of Novarupta in the Alaska Peninsula.Complicating the eruption was the arrival of Typhoon Yunya (Diding), bringing a lethal mix of ash and rain to areas surrounding the volcano. Successful predictions at the onset of the climactic eruption led to the evacuation of tens of thousands of people from the surrounding areas, saving many lives, but the surrounding areas were severely damaged by pyroclastic flows, ash deposits, and subsequently, by the lahars caused by rainwaters re-mobilizing earlier volcanic deposits causing extensive destruction to infrastructure and changing the river systems months to years after the eruption.The effects of the eruption were felt worldwide. It ejected roughly 10,000,000,000 tonnes (1.1×1010 short tons) or 10 km3 (2.4 cu mi) of magma, and 20,000,000 tonnes (22,000,000 short tons) SO2, bringing vast quantities of minerals and metals to the surface environment. It injected more particulate into the stratosphere than any eruption since Krakatoa in 1883. Over the following months, the aerosols formed a global layer of sulfuric acid haze. Global temperatures dropped by about 0.5 °C (0.9 °F) in the years 1991-93, and ozone depletion temporarily increased substantially.