Kilauea: The World`s Most Livable Volcano
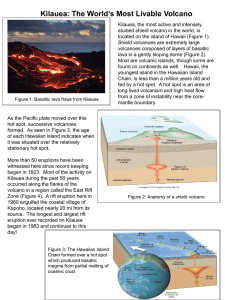
... As the Pacific plate moved over this hot spot, successive volcanoes formed. As seen in Figure 3, the age of each Hawaiian island indicates when it was situated over the relatively stationary hot spot. More than 50 eruptions have been witnessed here since record keeping began in 1823. Most of the act ...
... As the Pacific plate moved over this hot spot, successive volcanoes formed. As seen in Figure 3, the age of each Hawaiian island indicates when it was situated over the relatively stationary hot spot. More than 50 eruptions have been witnessed here since record keeping began in 1823. Most of the act ...
Chapter 8: Major Elements
... The Columbia River Basalts and Oregon High Lava Plateau are dominated by lava flows. During the peak of CRB activity (1618 million years ago) some massive individual flows may have exceeded 2000 km3 or even 3000 km3, which would qualify them as the largest known terrestrial lava flows ...
... The Columbia River Basalts and Oregon High Lava Plateau are dominated by lava flows. During the peak of CRB activity (1618 million years ago) some massive individual flows may have exceeded 2000 km3 or even 3000 km3, which would qualify them as the largest known terrestrial lava flows ...
new data on holocene monogenetic volcanism of the northern
... Geological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow. E-mail: suler@ginras.ru The recent volcanic activity in the Northern Kamchatka is particularly interesting, since it overlies the suggested northern rim of the subducting Pacific plate. We have found and documented a number of Holocene ...
... Geological Institute of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Moscow. E-mail: suler@ginras.ru The recent volcanic activity in the Northern Kamchatka is particularly interesting, since it overlies the suggested northern rim of the subducting Pacific plate. We have found and documented a number of Holocene ...
volcano
... The eruption happened on 17 January 2002. The volcano has a lava lake in its crater. Fissures opened up to the south side of the volcano and three streams of lava from the lake drained through the fissures. The lava reached speeds of 60 km/h. There was little warning as the lava reached the city of ...
... The eruption happened on 17 January 2002. The volcano has a lava lake in its crater. Fissures opened up to the south side of the volcano and three streams of lava from the lake drained through the fissures. The lava reached speeds of 60 km/h. There was little warning as the lava reached the city of ...
volcanic activity guided notes
... __________ content, how __________ or _________ the magma is, temperature and silica contents are important factors as to the __________ of a volcanic eruptions. The amount of ___________ in magma helps to determine how easily the magma flows. Silica is formed from the elements ___________ and ___ ...
... __________ content, how __________ or _________ the magma is, temperature and silica contents are important factors as to the __________ of a volcanic eruptions. The amount of ___________ in magma helps to determine how easily the magma flows. Silica is formed from the elements ___________ and ___ ...
• Once magma reaches the surface, it is called lava. • An example of
... A long tube that connects a magma chamber to the surface is called a pipe. A volcano that is no longer likely to erupt is said to be extinct. A huge hole left behind when a volcano collapses is a caldera. A volcano that erupts explosively produces ashes, cinders, and bombs. A sill forms when magma h ...
... A long tube that connects a magma chamber to the surface is called a pipe. A volcano that is no longer likely to erupt is said to be extinct. A huge hole left behind when a volcano collapses is a caldera. A volcano that erupts explosively produces ashes, cinders, and bombs. A sill forms when magma h ...
In the 1960s, while studying the volcanic history of Yellowstone
... but instead forms a caldera. A caldera volcano is so explosive that their single powerful eruption causes the crust to collapse into the partially emptied magma chamber, leaving a caldera, or very large, basin-shaped crater. Yellowstone was a caldera type volcano. (3) In the 1960s, NASA had taken hi ...
... but instead forms a caldera. A caldera volcano is so explosive that their single powerful eruption causes the crust to collapse into the partially emptied magma chamber, leaving a caldera, or very large, basin-shaped crater. Yellowstone was a caldera type volcano. (3) In the 1960s, NASA had taken hi ...
5volcano notes chapter
... Island arc-volcanoes produced from magma seeping through ocean floor. Hot spot- material deep within mantle rises and melts-Hawaii formed on hot spot. Volcanic eruptions 1. When a volcano erupts, the force of the expanding gases pushes magma from the magma chamber through the pipe until it flows or ...
... Island arc-volcanoes produced from magma seeping through ocean floor. Hot spot- material deep within mantle rises and melts-Hawaii formed on hot spot. Volcanic eruptions 1. When a volcano erupts, the force of the expanding gases pushes magma from the magma chamber through the pipe until it flows or ...
Volcanoes
... When the pressure builds up, eruptions take place. As well as lava and rock, a volcano can trigger all these things: tsunamis, flash floods, earthquakes, mudflows and land slides. ...
... When the pressure builds up, eruptions take place. As well as lava and rock, a volcano can trigger all these things: tsunamis, flash floods, earthquakes, mudflows and land slides. ...
Debris Avalanches
... Mud flows have the consistency of wet cement Travel along valleys at 20-40 mph for up to 200 miles. Destroy or bury almost everything in their path. They are the second most destructive volcanic hazard (after pyroclastic flows and surges) and are responsible for 27,000 deaths since 1600 A.D. ...
... Mud flows have the consistency of wet cement Travel along valleys at 20-40 mph for up to 200 miles. Destroy or bury almost everything in their path. They are the second most destructive volcanic hazard (after pyroclastic flows and surges) and are responsible for 27,000 deaths since 1600 A.D. ...
about volcanoes Power point
... What a volcano is. Understand that there are 3 main types of volcanoes. ...
... What a volcano is. Understand that there are 3 main types of volcanoes. ...
Chapter 10.1
... • They have steep sides. The volcano is usually formed from one eruption that may last a few weeks to a few years. Usually once that eruption is over the volcanoes magma chamber solidifies and it never erupts again. These are usually smaller volcanoes. ...
... • They have steep sides. The volcano is usually formed from one eruption that may last a few weeks to a few years. Usually once that eruption is over the volcanoes magma chamber solidifies and it never erupts again. These are usually smaller volcanoes. ...
Volcanoes
... earth’s formation; more heat is generated by the decay of radioactive elements in the earth • Volcanoes are generated at: ...
... earth’s formation; more heat is generated by the decay of radioactive elements in the earth • Volcanoes are generated at: ...
Earthquakes and Volcanoes
... Alternating layers of rock particles and lava Beginning violent eruption with bombs, cinders, and ash from vent Followed by quiet eruption with lava flow that covers rock particles Large cone-shaped mountain result of many alternating eruptions Mount Vesuvius in Italy and Mount Etna in Sicily ...
... Alternating layers of rock particles and lava Beginning violent eruption with bombs, cinders, and ash from vent Followed by quiet eruption with lava flow that covers rock particles Large cone-shaped mountain result of many alternating eruptions Mount Vesuvius in Italy and Mount Etna in Sicily ...
Earthquakes
... Volcanoes cause fewer deaths than many other natural disasters. Generally some activity (earth trembles, smoke, ash) occurs before an eruption to warn people to leave. Sometimes the eruption is violent and sudden – these eruptions are the most dangerous. Most deaths in sudden eruptions are c ...
... Volcanoes cause fewer deaths than many other natural disasters. Generally some activity (earth trembles, smoke, ash) occurs before an eruption to warn people to leave. Sometimes the eruption is violent and sudden – these eruptions are the most dangerous. Most deaths in sudden eruptions are c ...
Volcano Glossary III
... Steep conical volcanoes built by eruptions of lava flows, tephra and pyroclastic flows. Stratovolcanoes erupt a variety of magma types, all of which are explosive except basaltic magma. Stratovolcanoes consist of many vents near the center and along the flanks of the volcano. These volcanoes also ar ...
... Steep conical volcanoes built by eruptions of lava flows, tephra and pyroclastic flows. Stratovolcanoes erupt a variety of magma types, all of which are explosive except basaltic magma. Stratovolcanoes consist of many vents near the center and along the flanks of the volcano. These volcanoes also ar ...
Ch 3 Sec 4: Volcanic Landforms
... cracks and travel a long distance before cooling and hardening forming high level areas. Over millions of years, these layers of lava build up over a large area to form a lava plateau. Ex. Columbia Plateau An enormous eruption may empty a volcano’s main vent and magma chamber. With nothing to suppor ...
... cracks and travel a long distance before cooling and hardening forming high level areas. Over millions of years, these layers of lava build up over a large area to form a lava plateau. Ex. Columbia Plateau An enormous eruption may empty a volcano’s main vent and magma chamber. With nothing to suppor ...
Take a `Chance` on the volcano erupting
... dioxide/carbon dioxide ratio is particularly significant; • Increases in the emission of steam and other gases at fumaroles (minor vents on the volcano’s surface); • Shallow seismic swarms (groups of small earthquake shocks), indicating very near surface movement of magma and gases; • Harmonic seism ...
... dioxide/carbon dioxide ratio is particularly significant; • Increases in the emission of steam and other gases at fumaroles (minor vents on the volcano’s surface); • Shallow seismic swarms (groups of small earthquake shocks), indicating very near surface movement of magma and gases; • Harmonic seism ...
6VolcanicT2 - Arizona State University
... Crater: depression at top formed by force of eruption ...
... Crater: depression at top formed by force of eruption ...
Notes -
... The volcanoes in southwestern British Columbia were formed by the subduction of the Juan de Fuca and the Explorer Plate which are remnants of the much larger Farallon Plate, under the North American Plate and has produced the Cascadia subduction zone. It is a 680-mile long fault, running 50 miles of ...
... The volcanoes in southwestern British Columbia were formed by the subduction of the Juan de Fuca and the Explorer Plate which are remnants of the much larger Farallon Plate, under the North American Plate and has produced the Cascadia subduction zone. It is a 680-mile long fault, running 50 miles of ...
Mount Etna

Mount Etna (Italian: Etna, Sicilian: Mungibeddu or â Muntagna, Latin: Aetna) is an active stratovolcano on the east coast of Sicily, Italy, in the Province of Catania, between Messina and Catania. It lies above the convergent plate margin between the African Plate and the Eurasian Plate. It is the tallest active volcano on the European continent, currently 3,329 m (10,922 ft) high, though this varies with summit eruptions. It is the highest mountain in Italy south of the Alps. Etna covers an area of 1,190 km2 (459 sq mi) with a basal circumference of 140 km. This makes it by far the largest of the three active volcanoes in Italy, being about two and a half times the height of the next largest, Mount Vesuvius. Only Mount Teide in Tenerife surpasses it in the whole of the European–North-African region. In Greek Mythology, the deadly monster Typhon was trapped under this mountain by Zeus, the god of the sky and thunder and king of gods, and the forges of Hephaestus were said to also be located underneath it.Mount Etna is one of the most active volcanoes in the world and is in an almost constant state of activity. The fertile volcanic soils support extensive agriculture, with vineyards and orchards spread across the lower slopes of the mountain and the broad Plain of Catania to the south. Due to its history of recent activity and nearby population, Mount Etna has been designated a Decade Volcano by the United Nations. In June 2013, it was added to the list of UNESCO World Heritage Sites.