Volcano Study Guide Extinct – Unlikely to erupt ever again Active
... 3. Describe how volcanoes form along the mid-ocean ridge. Volcanoes form when lava oozes out of cracks in the ocean floor. 4. How does subduction at convergent plate boundaries lead to the formation of volcanoes? 1st Oceanic plate subducts (sinks) through a trench, 2nd It melts in the mantle, 3rd So ...
... 3. Describe how volcanoes form along the mid-ocean ridge. Volcanoes form when lava oozes out of cracks in the ocean floor. 4. How does subduction at convergent plate boundaries lead to the formation of volcanoes? 1st Oceanic plate subducts (sinks) through a trench, 2nd It melts in the mantle, 3rd So ...
Lecture_Ch06 - earthjay science
... precisely, down to individual lava flows and the calendar year they erupted. • Volume and thickness of individual deposits provides clues to the magnitude of past eruptions, which in turn puts some constraints on how large a future eruption could be. • Long-range forecasts—state the probability that ...
... precisely, down to individual lava flows and the calendar year they erupted. • Volume and thickness of individual deposits provides clues to the magnitude of past eruptions, which in turn puts some constraints on how large a future eruption could be. • Long-range forecasts—state the probability that ...
Reactive-Transport Modelling Of the Native
... assessment of long-term sustainability has typically been guided by reservoir (thermal-hydrological-TH) and rock mechanical modeling. However, at higher temperatures the effects of water-rock-gas(supercritical fluid) interaction and inelastic mechanical deformation control many aspects of permeabili ...
... assessment of long-term sustainability has typically been guided by reservoir (thermal-hydrological-TH) and rock mechanical modeling. However, at higher temperatures the effects of water-rock-gas(supercritical fluid) interaction and inelastic mechanical deformation control many aspects of permeabili ...
Volcanic Eruptions
... • Generally results from lava eruption • Layers of hot mafic lava flow out around the vent, harden, and slowly build up to form a cone. • The Hawaiian Island are a chain of shield volcanoes. ...
... • Generally results from lava eruption • Layers of hot mafic lava flow out around the vent, harden, and slowly build up to form a cone. • The Hawaiian Island are a chain of shield volcanoes. ...
What can low frequency seismicity tell us about eruption processes
... a range of different eruption mechanisms. They can pose a significant hazard to surrounding populations, and a considerable challenge to management agencies. Activity at these volcanoes can also generate particularly rich and complex seismic data sets. Notably, this seismicity is often dominated by ...
... a range of different eruption mechanisms. They can pose a significant hazard to surrounding populations, and a considerable challenge to management agencies. Activity at these volcanoes can also generate particularly rich and complex seismic data sets. Notably, this seismicity is often dominated by ...
Volcanoes
... However, it is often very difficult to tell whether a volcano will erupt again…El Chichon, Mexico erupted in 1982 after being dormant for approximately 1200 years! ...
... However, it is often very difficult to tell whether a volcano will erupt again…El Chichon, Mexico erupted in 1982 after being dormant for approximately 1200 years! ...
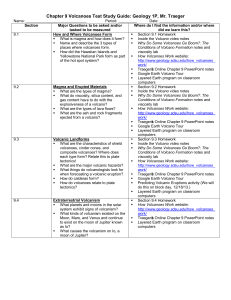
Chapter 9 Volcanoes Test Study Guide: Geology 1P, Mr. Traeger
... § What are the types of lava flows? § What are the ash and rock fragments http://www.geology.sdsu.edu/how_volcanoes_ ejected from a volcano? work/ § Traeger’s Online Chapter 9 PowerPoint notes § Google Earth Volcano Tour § Layered Earth program on classroom computers Volcanic Landforms ...
... § What are the types of lava flows? § What are the ash and rock fragments http://www.geology.sdsu.edu/how_volcanoes_ ejected from a volcano? work/ § Traeger’s Online Chapter 9 PowerPoint notes § Google Earth Volcano Tour § Layered Earth program on classroom computers Volcanic Landforms ...
File
... volcanoes covered by lush vegetation in the tropics pose no threat. Moreover, many without any past experience of a volcanic eruption or earthquake, are unlikely to comprehend the devastation such events might cause. Yet others may be in denial, or believe that a past event was a one-off event, not ...
... volcanoes covered by lush vegetation in the tropics pose no threat. Moreover, many without any past experience of a volcanic eruption or earthquake, are unlikely to comprehend the devastation such events might cause. Yet others may be in denial, or believe that a past event was a one-off event, not ...
Volcanoes and Igneous Activity Earth - Chapter 4
... Types of volcanoes • Composite cone (or stratovolcano) • Often produce nuée ardente • Fiery pyroclastic flow made of hot gases infused with ash • Flows down sides of a volcano at speeds up to 200 km (125 miles) per hour • May produce a lahar – volcanic mudflow ...
... Types of volcanoes • Composite cone (or stratovolcano) • Often produce nuée ardente • Fiery pyroclastic flow made of hot gases infused with ash • Flows down sides of a volcano at speeds up to 200 km (125 miles) per hour • May produce a lahar – volcanic mudflow ...
Lecture Outlines PowerPoint Chapter 9 Earth Science, 12e Tarbuck
... Types of volcanoes • Composite cone (or stratovolcano) • Often produce nuée ardente • Fiery pyroclastic flow made of hot gases infused with ash • Flows down sides of a volcano at speeds up to 200 km (125 miles) per hour • May produce a lahar – volcanic mudflow ...
... Types of volcanoes • Composite cone (or stratovolcano) • Often produce nuée ardente • Fiery pyroclastic flow made of hot gases infused with ash • Flows down sides of a volcano at speeds up to 200 km (125 miles) per hour • May produce a lahar – volcanic mudflow ...
All About Volcanoes - Library Video Company
... as fine as sand and others the size of houses, fly into the sky. This type of volcano usually forms cone-shaped mountains from layers of ash and cinders. Composite volcanoes are formed as layers of cinder and hardened lava build up over time, creating a volcanic mountain with steep, even sides.All t ...
... as fine as sand and others the size of houses, fly into the sky. This type of volcano usually forms cone-shaped mountains from layers of ash and cinders. Composite volcanoes are formed as layers of cinder and hardened lava build up over time, creating a volcanic mountain with steep, even sides.All t ...
Fact sheet about the volcanic hazards of the Lassen Volcanic
... years. Lassen Peak and nearby volcanic domes are the most recently active parts of the Lassen “volcanic center,” which began to erupt about 600,000 years ago. From 600,000 to 400,000 years ago, eruptions built a large conical volcano, often referred to as “Brokeoff Volcano” or “Mount Tehama,” which ...
... years. Lassen Peak and nearby volcanic domes are the most recently active parts of the Lassen “volcanic center,” which began to erupt about 600,000 years ago. From 600,000 to 400,000 years ago, eruptions built a large conical volcano, often referred to as “Brokeoff Volcano” or “Mount Tehama,” which ...
Lecture 6: Volcanoes I. Introduction II. Magma A. Magma vs Lava 1
... C. Factors that determine characteristics of lava and volcanic eruptions 1. composition of magma 2. temperature 3. amount of dissolved gases, primarily water 4. amount of silica D. Silica content and viscosity 1. Definition of viscosity 2. Silica tetrahedra link to form polymers 3. Polymer formation ...
... C. Factors that determine characteristics of lava and volcanic eruptions 1. composition of magma 2. temperature 3. amount of dissolved gases, primarily water 4. amount of silica D. Silica content and viscosity 1. Definition of viscosity 2. Silica tetrahedra link to form polymers 3. Polymer formation ...
VOLCANOES - mmconcepcion
... came from Vulcan's furnace as he made thunderbolts for Jupiter, king of the gods, and weapons for Mars, the god of war. In Polynesia the people attributed eruptive activity to the beautiful but wrathful Pele, Goddess of Volcanoes, whenever she was angry or spiteful. Today we know that volcanic erupt ...
... came from Vulcan's furnace as he made thunderbolts for Jupiter, king of the gods, and weapons for Mars, the god of war. In Polynesia the people attributed eruptive activity to the beautiful but wrathful Pele, Goddess of Volcanoes, whenever she was angry or spiteful. Today we know that volcanic erupt ...
Section 2: Volcanic Activity - SS. Peter and Paul Salesian
... • Explain how the two types of volcanic eruptions differ depending on the characteristics of magma. • Identify some hazards of volcanoes • Identify types of volcanic activity other than eruptions. ...
... • Explain how the two types of volcanic eruptions differ depending on the characteristics of magma. • Identify some hazards of volcanoes • Identify types of volcanic activity other than eruptions. ...
Note - ees.nmt.edu
... Cascades • Subduction of Juan de Fuca plate beneath North America • Water released from slab aids melting above • Magma travels toward surface, some cools, other erupts • 6-7 of these volcanoes have erupted in last 200 years ...
... Cascades • Subduction of Juan de Fuca plate beneath North America • Water released from slab aids melting above • Magma travels toward surface, some cools, other erupts • 6-7 of these volcanoes have erupted in last 200 years ...
Igneous Rocks Magma • molten rock material consisting of liquid
... Explosive eruptions of silicic volcanoes can blow out large volumes of ash and magma. As a result, the summit area sometimes collapses, forming a large basinshaped depression known as a caldera. ...
... Explosive eruptions of silicic volcanoes can blow out large volumes of ash and magma. As a result, the summit area sometimes collapses, forming a large basinshaped depression known as a caldera. ...
Igneous Rocks - Crafton Hills College
... Explosive eruptions of silicic volcanoes can blow out large volumes of ash and magma. As a result, the summit area sometimes collapses, forming a large basinshaped depression known as a caldera. ...
... Explosive eruptions of silicic volcanoes can blow out large volumes of ash and magma. As a result, the summit area sometimes collapses, forming a large basinshaped depression known as a caldera. ...
Igneous Rocks - Occurrence and Classification
... Hawaiian – fluid basaltic lava is thrown into the air in jets from a vent or line of vents (a fissure) at the summit or on the flank of a volcano. Strombolian – distinct bursts of fluid lava (usually basalt or basaltic andesite) from the mouth of a magma-filled summit conduit. Vulcanian - short, vio ...
... Hawaiian – fluid basaltic lava is thrown into the air in jets from a vent or line of vents (a fissure) at the summit or on the flank of a volcano. Strombolian – distinct bursts of fluid lava (usually basalt or basaltic andesite) from the mouth of a magma-filled summit conduit. Vulcanian - short, vio ...
AP Physics SBHS Petyak
... Discuss the relationships between tsunamis and earthquakes. (9b) Describe two possible effects of a major earthquake on buildings.(9b) List three safety techniques to prevent injury caused by earthquake activity. (IE, 1m) Identify four methods scientists use to forecast earthquake risks. (9b ...
... Discuss the relationships between tsunamis and earthquakes. (9b) Describe two possible effects of a major earthquake on buildings.(9b) List three safety techniques to prevent injury caused by earthquake activity. (IE, 1m) Identify four methods scientists use to forecast earthquake risks. (9b ...
Shield Volcanoes
... Rhyolite caldera complexes are the most explosive of Earth's volcanoes but often don't even look like volcanoes. They are usually so explosive when they erupt that they end up collapsing in on themselves rather than building any tall structure (George Walker has termed such structures "inverse volca ...
... Rhyolite caldera complexes are the most explosive of Earth's volcanoes but often don't even look like volcanoes. They are usually so explosive when they erupt that they end up collapsing in on themselves rather than building any tall structure (George Walker has termed such structures "inverse volca ...
Courtney Kearney, Jon Dehn, Ken Dean
... related volcanoes is limited; however its 2330 km swath width allows the detection of large eruptive episodes. The algorithm MAP_SO2 provides a means to create SO2 concentration maps based on modelled radiance values. These maps provide a total SO2 tonnage emitted along with a further understanding ...
... related volcanoes is limited; however its 2330 km swath width allows the detection of large eruptive episodes. The algorithm MAP_SO2 provides a means to create SO2 concentration maps based on modelled radiance values. These maps provide a total SO2 tonnage emitted along with a further understanding ...
Volcano Vocab.
... Intro to Topographic Maps: 1. Complete Intro. to Topographic Maps activity in packet (page 1 front & back) When you finish: Work on mountains & volcanoes vocabulary organizer ...
... Intro to Topographic Maps: 1. Complete Intro. to Topographic Maps activity in packet (page 1 front & back) When you finish: Work on mountains & volcanoes vocabulary organizer ...
Mount Vesuvius
.png?width=300)
Mount Vesuvius (Italian: Monte Vesuvio, Latin: Mons Vesuvius) is a stratovolcano in the Gulf of Naples, Italy, about 9 km (5.6 mi) east of Naples and a short distance from the shore. It is one of several volcanoes which form the Campanian volcanic arc. Vesuvius consists of a large cone partially encircled by the steep rim of a summit caldera caused by the collapse of an earlier and originally much higher structure.Mount Vesuvius is best known for its eruption in AD 79 that led to the burying and destruction of the Roman cities of Pompeii, Herculaneum and several other settlements. That eruption ejected a cloud of stones, ash and fumes to a height of 33 km (20.5 mi), spewing molten rock and pulverized pumice at the rate of 1.5 million tons per second, ultimately releasing a hundred thousand times the thermal energy released by the Hiroshima bombing. An estimated 16,000 people died due to hydrothermal pyroclastic flows. The only surviving eyewitness account of the event consists of two letters by Pliny the Younger to the historian Tacitus.Vesuvius has erupted many times since and is the only volcano on the European mainland to have erupted within the last hundred years. Today, it is regarded as one of the most dangerous volcanoes in the world because of the population of 3,000,000 people living nearby and its tendency towards explosive (Plinian) eruptions. It is the most densely populated volcanic region in the world.