FedViews
... economic recovery. The March jobs report posted a healthy payroll employment gain of 192,000. Clearly, the job market has shrugged off the adverse effects of the winter weather. Averaging over the past six months suggests continuing fairly solid gains in employment. Given the job gains over the past ...
... economic recovery. The March jobs report posted a healthy payroll employment gain of 192,000. Clearly, the job market has shrugged off the adverse effects of the winter weather. Averaging over the past six months suggests continuing fairly solid gains in employment. Given the job gains over the past ...
Unit 2 lesson 1 Macroeconomic Tools
... G= Government expenditures on goods and services X-M= Exports - Imports ...
... G= Government expenditures on goods and services X-M= Exports - Imports ...
Collapse and Recovery of the Global Economy: The 1970s and 80s
... Began in 1974 and most severe since Great Depression Strangely accompanied by inflation Rose as high as 27% in GB ’75 Economic growth slowed or stopped 32 million people were out of work in free market nations • 10.2% in US (1982) • Unemployment benefits cushioned the blow for Western nations • Stru ...
... Began in 1974 and most severe since Great Depression Strangely accompanied by inflation Rose as high as 27% in GB ’75 Economic growth slowed or stopped 32 million people were out of work in free market nations • 10.2% in US (1982) • Unemployment benefits cushioned the blow for Western nations • Stru ...
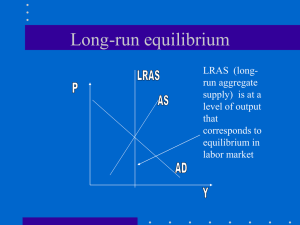
Long-run equilibrium
... market) • This means that AD and AS intersect LRAS and that the economy is operating at its potential level of RGDP (Real GDP). • Imagine now that the something happens to decrease AD. ...
... market) • This means that AD and AS intersect LRAS and that the economy is operating at its potential level of RGDP (Real GDP). • Imagine now that the something happens to decrease AD. ...
Explain what data might be employed in this assessment of
... nomy. Examining unemployment figures based on the Labor Force Survey method will be more useful than examining unemployment figures based on the claimant count when comparing the economic health of the nation with other countries. As well as considering trends in economic growth, inflation, unemploy ...
... nomy. Examining unemployment figures based on the Labor Force Survey method will be more useful than examining unemployment figures based on the claimant count when comparing the economic health of the nation with other countries. As well as considering trends in economic growth, inflation, unemploy ...
Price Level
... Movements in the LRAS curve 1. Increases in quantities of factors of production For example, an increase in the quantity of physical capital, or land (eg. discovery of oil reserves) - the economy is capable of producing more real GDP. 2. Reductions in the natural rate of unemployment 3. Improvement ...
... Movements in the LRAS curve 1. Increases in quantities of factors of production For example, an increase in the quantity of physical capital, or land (eg. discovery of oil reserves) - the economy is capable of producing more real GDP. 2. Reductions in the natural rate of unemployment 3. Improvement ...
Chapter 09_20e
... Source: National Bureau of Economic Research, www.nber.org, and Minneapolis Federal Reserve Bank, www.minneapolisfed.gov. Output data are in 2000 dollars LO1 ...
... Source: National Bureau of Economic Research, www.nber.org, and Minneapolis Federal Reserve Bank, www.minneapolisfed.gov. Output data are in 2000 dollars LO1 ...
FedViews
... surveys of household perceptions of job availability, and temporary help employment—are improving. These indicators tend to lead job growth and unemployment declines, so we expect that the labor market will continue its gradual return to normal. ...
... surveys of household perceptions of job availability, and temporary help employment—are improving. These indicators tend to lead job growth and unemployment declines, so we expect that the labor market will continue its gradual return to normal. ...
MACRO 1-page graph summary 2011
... Demand = Investment Demand (business who borrow $) Use Real Interest Rate on this graph! Crowding Out: Supply shifts left as Gov’t savings falls (less national savings) Private investor are “crowded out” by ↑ real interest rates. (less (I) capital investment!) Real world example: Spain, Greece, Port ...
... Demand = Investment Demand (business who borrow $) Use Real Interest Rate on this graph! Crowding Out: Supply shifts left as Gov’t savings falls (less national savings) Private investor are “crowded out” by ↑ real interest rates. (less (I) capital investment!) Real world example: Spain, Greece, Port ...
Past Paper - Exam 2012
... economy to show how economic sanctions, which have the effect of limiting a country’s exports, will ceteris paribus affect a country’s level of output. If the economy enjoys balanced trade at the time that the sanctions are introduced, show why the sanctions will result in a trade deficit. ...
... economy to show how economic sanctions, which have the effect of limiting a country’s exports, will ceteris paribus affect a country’s level of output. If the economy enjoys balanced trade at the time that the sanctions are introduced, show why the sanctions will result in a trade deficit. ...
Monetary Policy
... What type of unemployment accounts for layoffs in the banking industry when ATM machines increasingly became the norm? ...
... What type of unemployment accounts for layoffs in the banking industry when ATM machines increasingly became the norm? ...
review sheet
... Take a change in excess reserves at one bank and multiply it by the money multiplier to give you the potential change in the money supply (M1). If the change in excess reserves was caused by an increase in demand deposits, you must decide if the demand deposit was previously held as currency in the ...
... Take a change in excess reserves at one bank and multiply it by the money multiplier to give you the potential change in the money supply (M1). If the change in excess reserves was caused by an increase in demand deposits, you must decide if the demand deposit was previously held as currency in the ...
Test 4
... 18. In the early 1970s, President Nixon inherited an economy that was operating with an inflationary gap. The Nixon administration rationalized that through a combination of a government spending cuts and a decrease in the money growth rate, it could successfully A) reduce inflation, which would th ...
... 18. In the early 1970s, President Nixon inherited an economy that was operating with an inflationary gap. The Nixon administration rationalized that through a combination of a government spending cuts and a decrease in the money growth rate, it could successfully A) reduce inflation, which would th ...
Homework 2, Due in class Monday August 27 at 12:10 - uc
... this economy was growing steadily because of financial innovation. How would that affect the inflation rate? Explain. ...
... this economy was growing steadily because of financial innovation. How would that affect the inflation rate? Explain. ...
Eco 212_____Name
... A government wants to lower inflation by lowering the growth rate of the money supply. If it believes inflation expectations will adjust quickly to a dramatic change in policy, it will prefer the ____ approach to lowering inflation. a. b. c. d. e. ...
... A government wants to lower inflation by lowering the growth rate of the money supply. If it believes inflation expectations will adjust quickly to a dramatic change in policy, it will prefer the ____ approach to lowering inflation. a. b. c. d. e. ...
Midterm 3
... According to Keynesians, firms keep some workers on the payroll during recessions even if the firm doesn’t need them at that moment – to avoid losing hardto-replace workers. When demand increases, the firm can increase output without adding many new workers. This will make _____ appear to be pro-cyc ...
... According to Keynesians, firms keep some workers on the payroll during recessions even if the firm doesn’t need them at that moment – to avoid losing hardto-replace workers. When demand increases, the firm can increase output without adding many new workers. This will make _____ appear to be pro-cyc ...
Business Cycles, Unemployment, and Inflation
... real output is at or very close to the economy’s capacity. The price level is likely to rise at this level. Recession – period of decline in total output, income, and employment. The downturn, which lasts 6 months or more, is marked by widespread contraction of business activity in many industries. ...
... real output is at or very close to the economy’s capacity. The price level is likely to rise at this level. Recession – period of decline in total output, income, and employment. The downturn, which lasts 6 months or more, is marked by widespread contraction of business activity in many industries. ...
Goals
... The science of macroeconomics is positive economics: the study of economic facts and theories and how they work. Policy practice of macroeconomics is concerned with policies to achieve ...
... The science of macroeconomics is positive economics: the study of economic facts and theories and how they work. Policy practice of macroeconomics is concerned with policies to achieve ...
Dates - Houston ISD
... 2. Evaluate the official unemployment rate as an indicator of economic health, and describe alternative unemployment measures economists use. 3. Identify and describe the types of unemployment. 4. Explain why unemployment exists at full employment. 5. Describe the economic and noneconomic costs of u ...
... 2. Evaluate the official unemployment rate as an indicator of economic health, and describe alternative unemployment measures economists use. 3. Identify and describe the types of unemployment. 4. Explain why unemployment exists at full employment. 5. Describe the economic and noneconomic costs of u ...
Chapter 10: Inflation and Unemployment
... Official unemployment rate is not accurate; it may either understate or overstate the true level of unemployment in the Canadian economy. The factors affecting the official rates are _______________, _____________________ and ________________________. ...
... Official unemployment rate is not accurate; it may either understate or overstate the true level of unemployment in the Canadian economy. The factors affecting the official rates are _______________, _____________________ and ________________________. ...
Full employment
Full employment, in macroeconomics, is the level of employment rates where there is no cyclical or deficient-demand unemployment. It is defined by the majority of mainstream economists as being an acceptable level of unemployment somewhere above 0%. The discrepancy from 0% arises due to non-cyclical types of unemployment, such as frictional unemployment (there will always be people who have quit or have lost a seasonal job and are in the process of getting a new job) and structural unemployment (mismatch between worker skills and job requirements). Unemployment above 0% is seen as necessary to control inflation in capitalist economies, to keep inflation from accelerating, i.e., from rising from year to year. This view is based on a theory centering on the concept of the Non-Accelerating Inflation Rate of Unemployment (NAIRU); in the current era, the majority of mainstream economists mean NAIRU when speaking of ""full"" employment. The NAIRU has also been described by Milton Friedman, among others, as the ""natural"" rate of unemployment. Having many names, it has also been called the structural unemployment rate.The 20th century British economist William Beveridge stated that an unemployment rate of 3% was full employment. Other economists have provided estimates between 2% and 13%, depending on the country, time period, and their political biases. For the United States, economist William T. Dickens found that full-employment unemployment rate varied a lot over time but equaled about 5.5 percent of the civilian labor force during the 2000s. Recently, economists have emphasized the idea that full employment represents a ""range"" of possible unemployment rates. For example, in 1999, in the United States, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) gives an estimate of the ""full-employment unemployment rate"" of 4 to 6.4%. This is the estimated unemployment rate at full employment, plus & minus the standard error of the estimate.The concept of full employment of labor corresponds to the concept of potential output or potential real GDP and the long run aggregate supply (LRAS) curve. In neoclassical macroeconomics, the highest sustainable level of aggregate real GDP or ""potential"" is seen as corresponding to a vertical LRAS curve: any increase in the demand for real GDP can only lead to rising prices in the long run, while any increase in output is temporary.